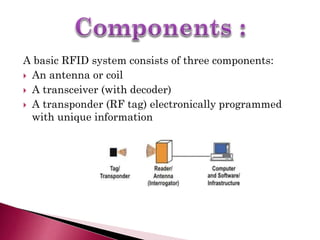
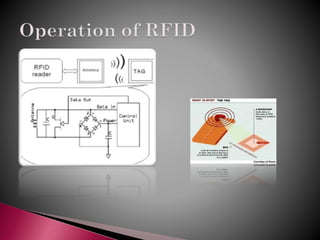
An RFID system consists of an antenna, transceiver, and transponder tag with unique information. There are two types of RFID tags: active tags with their own power source and longer read ranges but limited lifespan, and passive tags without a power source that are smaller and have unlimited lifespan. RFID tags contain protocol, organization, product class, and unique serial number data. Compared to barcodes, RFID tags don't require line of sight, can be read from greater distances, and allow reading and writing information.