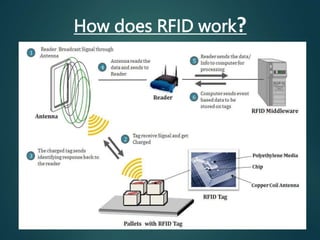
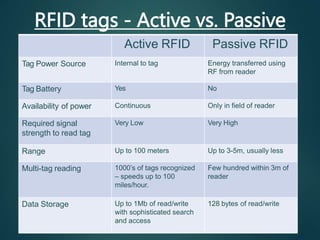
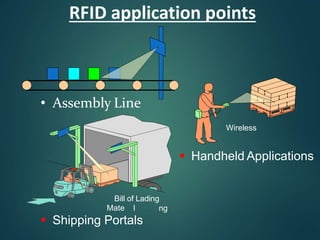
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) is an automatic identification method that uses radio waves to identify objects. It involves RFID tags attached to objects and RFID readers that can read the tags wirelessly. The key components of an RFID system are RFID tags, readers, and a data processing subsystem. RFID provides advantages over barcodes such as contactless identification and ability to read multiple tags simultaneously. While it has many applications in supply chain management, retail, security, and more, concerns over privacy and security of personal information are disadvantages that need to be addressed. The future of RFID involves increasing capabilities and expanding uses in areas like healthcare and smart home technologies.