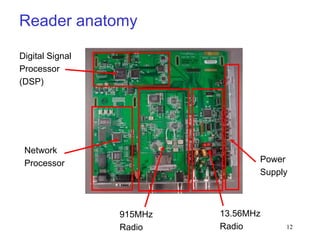
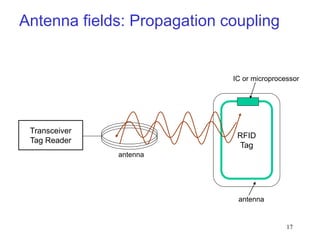
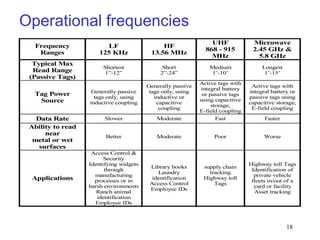
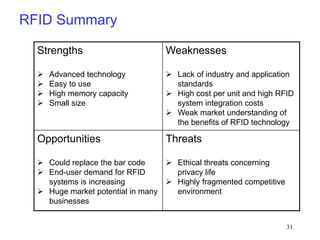
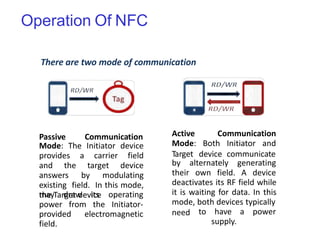
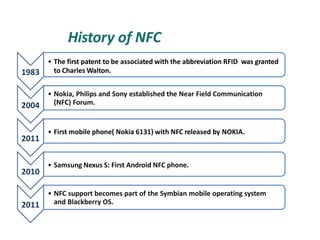
RFID is a technology that uses radio waves to identify objects. It consists of a small chip attached to an antenna that can be embedded in objects or cards. RFID readers send out electromagnetic waves to power a tag and read and write data to it wirelessly without contact or line-of-sight. Common applications of RFID include supply chain management, asset tracking, and access control. NFC is a short-range wireless technology that allows data exchange when devices are brought within 4 cm of each other. It builds on the RFID standard to enable two-way communication between electronic devices like phones and readers. Common uses of NFC include contactless payments, data sharing, and access control.