This document provides an overview of radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology. It discusses the history and components of RFID, including tags, readers, software, and communication networks. It then outlines several applications of RFID such as supply chain management, retail, and security/access control. Both advantages, like automatic identification without line of sight, and disadvantages, including cost and need for regulations, are mentioned. The document concludes by summarizing observations on using RFID in healthcare, gaming, and human activity detection.









![RFID tags are divided into three frequency
regions:
Low frequency (LF, 30-50 kHz)
High frequency ( HF, 10-15 MHz)
Ultra high frequency ( UHF, 850-950 MHz)
Low frequency tags are cheaper than all high
frequency tags. These tags are less influenced by
the presence of fluids or metals and disadvantage
of their low transmission speed.
[M.Ward et al.,2006]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rfidtechnologypowerpoint-200410073158/85/RFID-Technology-in-Food-Systems-10-320.jpg)
![High frequency tags have higher
transmission speed but they are expensive
than LF tags.
Ultra high frequency tags have the
highest rank of all tags.Their transmission
speed is extremely high .But these are
expensive than other high frequency and
low frequency tags
[M.Ward et al., 2006]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rfidtechnologypowerpoint-200410073158/85/RFID-Technology-in-Food-Systems-11-320.jpg)
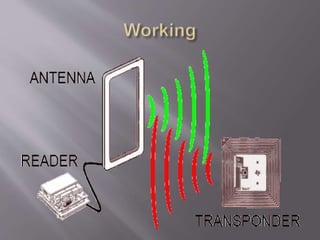
![RFID reader is a device that is used to
interrogate an RFID tag. The reader has an
antenna that emits radio waves ; the tag
responds by sending back its data.
[ Wisner et al.,]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rfidtechnologypowerpoint-200410073158/85/RFID-Technology-in-Food-Systems-12-320.jpg)




![ The tag does not need to be in line of sight with
the receiver to be read.
[Shepard ,2004 , p.58.]
RFID tags can store a lot of information.
Labour reduction . [Keith et al.,2002]
Asset tracking and Returnable items.
[Luke et al.,2005]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rfidtechnologypowerpoint-200410073158/85/RFID-Technology-in-Food-Systems-18-320.jpg)



