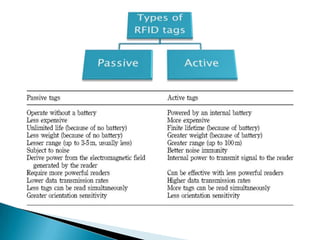
1) RFID is a wireless technology that uses radio waves to identify tagged products and objects. It consists of tags, antennas, and readers.
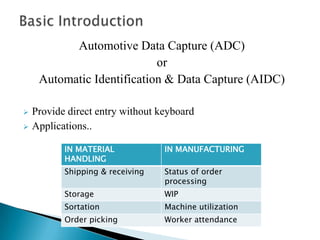
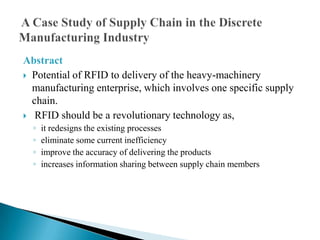
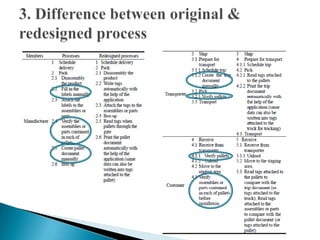
2) The document describes a case study of applying RFID in the supply chain of a heavy machinery manufacturing company. By implementing RFID, the company eliminated inefficiencies, improved delivery accuracy, and increased information sharing across the supply chain.
3) The case study found that RFID automation reduced human errors, tags represented product assemblies and parts for automated documentation, and the system provided real-time alerts and notifications.

![Drawbacks of manual data entry
Average error rate is 1 error/300
characters[1]
Time factor
ADC
Labor cost
Technology
Optical
Magnetic
Electromagnetic
Smart card
Why RFID??
Out of all the ADC technologies
available, RFID is one of the fastest
& accurate technology !
Touch
technique
Biometric
RFID](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationsofrfid-131012143740-phpapp02/85/Applications-of-rfid-3-320.jpg)

![o
o
o
o
o
Used in early 1900’s & was used in World War II[2]
In 1970’s, A noticeable development work started
By 1980’s, the full implementation of the technology
In 1990’s, the deployment of applications with RFID
21st century, the pace of development in RFID](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationsofrfid-131012143740-phpapp02/85/Applications-of-rfid-6-320.jpg)







![ise.tamu.edu/.../Applications%20of%20RFID%20in%20Supply%20Chain
/Applications of RFID in Supply Chains (Gary M. Gaukler & Ralf W.
Seifert)
Elsevier.com/RFID Application Strategy in Agri-Food Supply Chain
Based on Safety and Benefit Analysis (Min Zhang, Peichong Li)
Elsevier.com/Supply chain management with lean production and
RFID application: A case study(James C. Chen , Chen-Huan Cheng ,
PoTsang B. Huang )
Elsevier.com/RFID potential impacts and future evolution for green
projects (Yvan Duroc and Darine Kaddour)
Journal of Electronic Science and Technology of China /Vol.4 No.4
/RFID’s Impacts on Business Value: A Case Study of Supply Chain in
the Discrete Manufacturing Industry ( LIU Yun,SHAO Pei-ji, MO Zhiwu, WANG Tao, SUN Shu)
[1]- Automation, Production Systems and Computer-Integrated
Manufacturing by Mikell P. Groover
[2]ise.tamu.edu/.../Applications%20of%20RFID%20in%20Supply%20Chain
/Applications of RFID in Supply Chains (Gary M. Gaukler & Ralf W.
Seifert)/1.1.1/Paragraph no. 3
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationsofrfid-131012143740-phpapp02/85/Applications-of-rfid-16-320.jpg)
