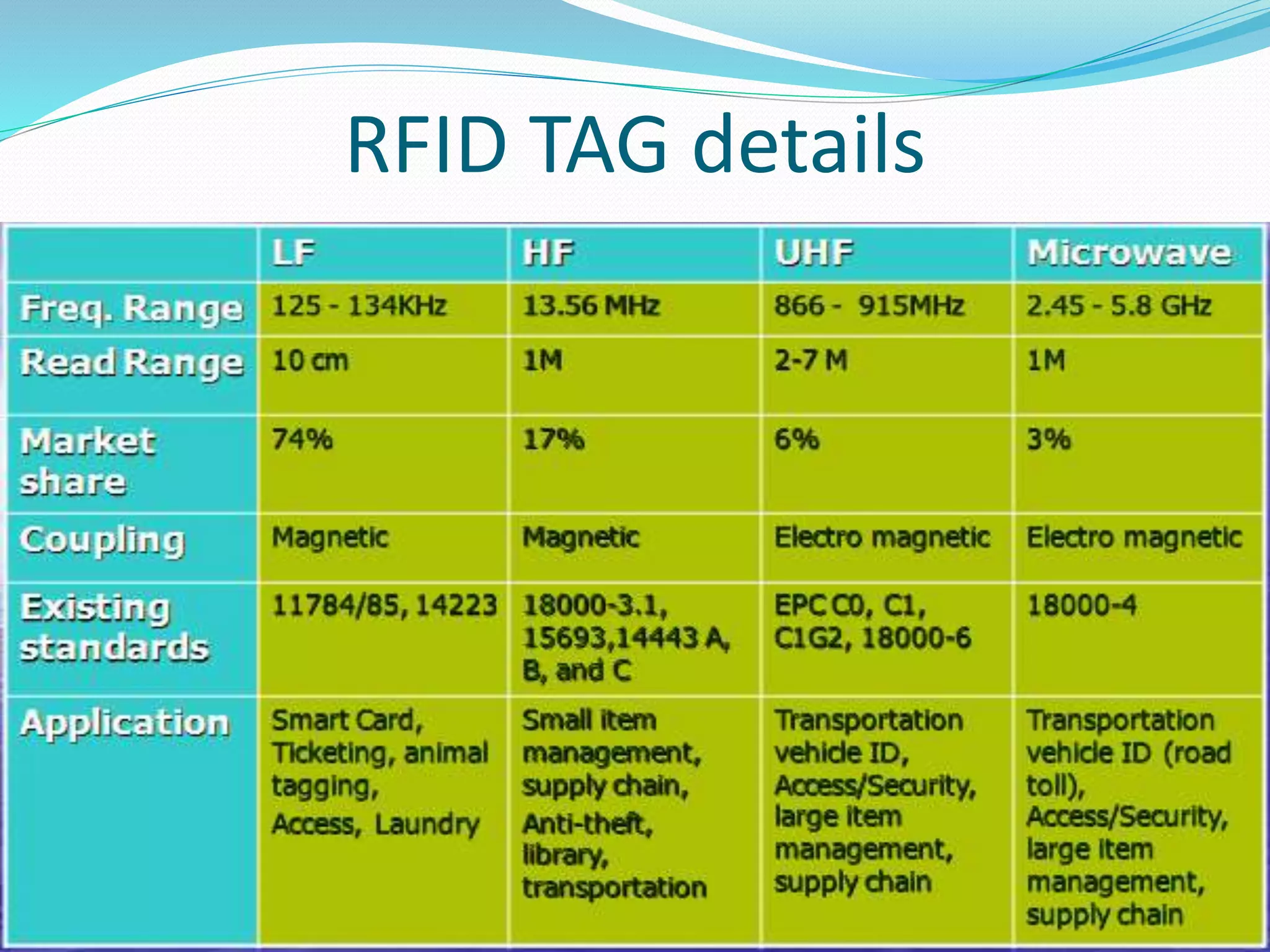
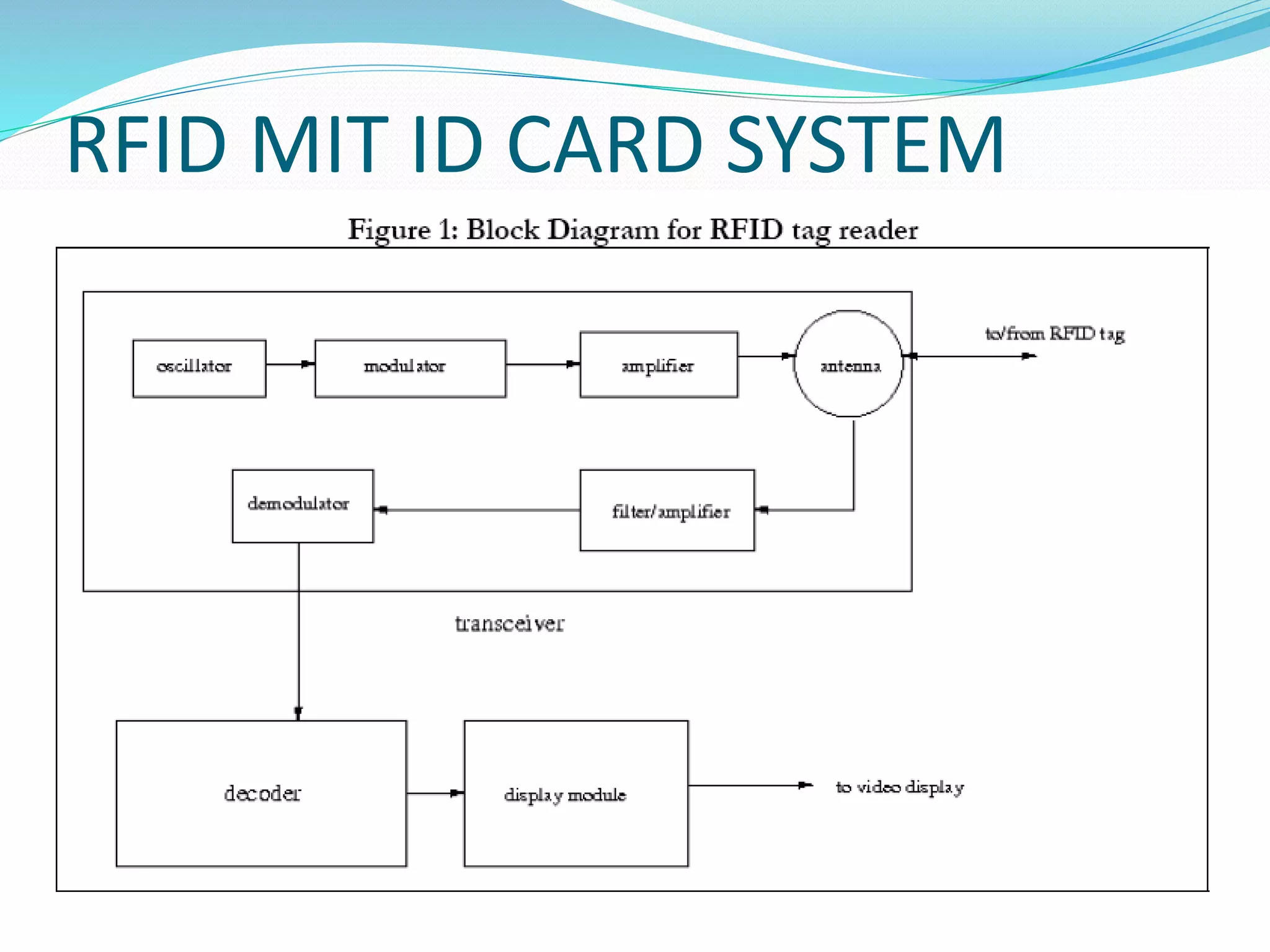
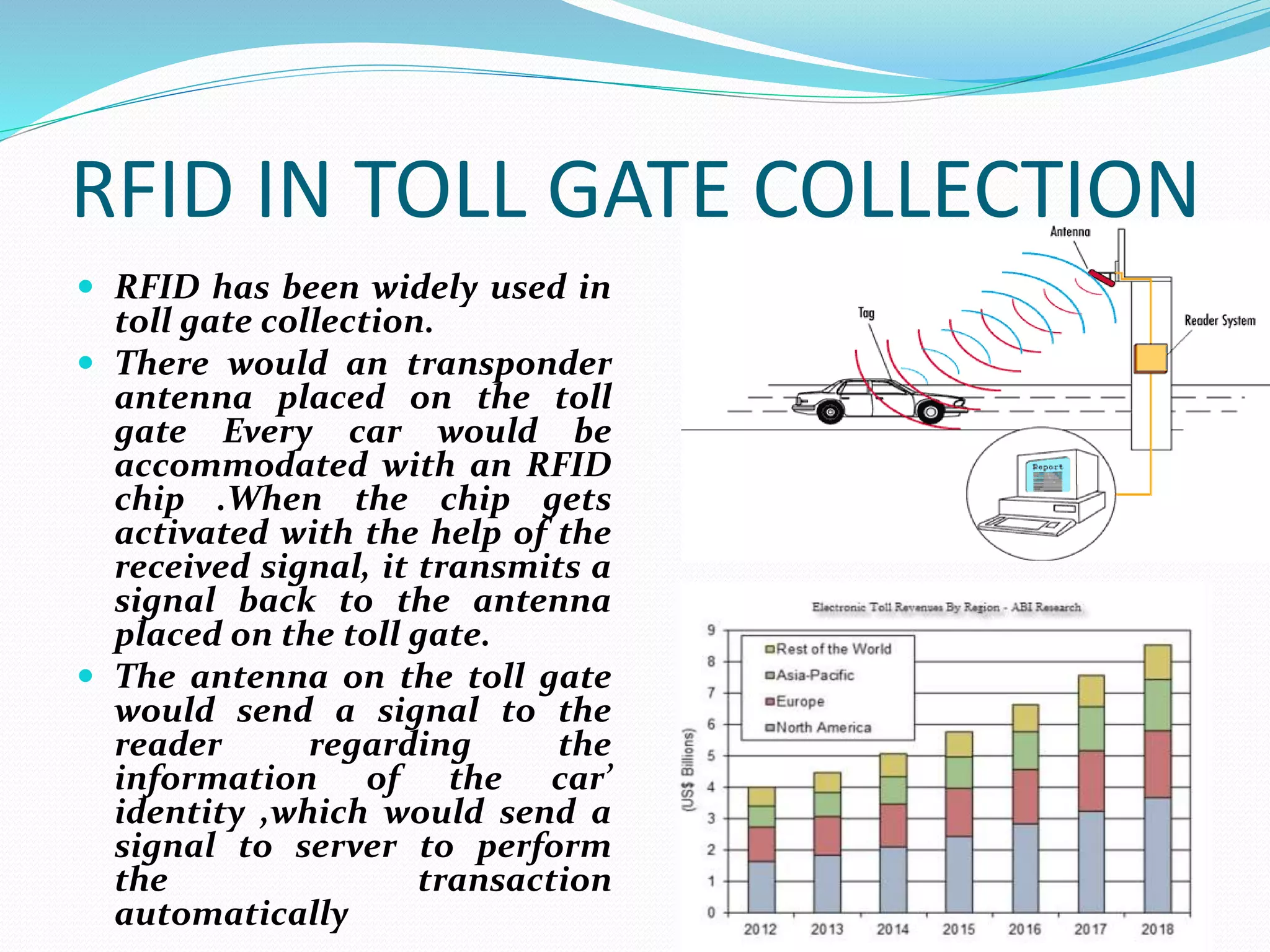
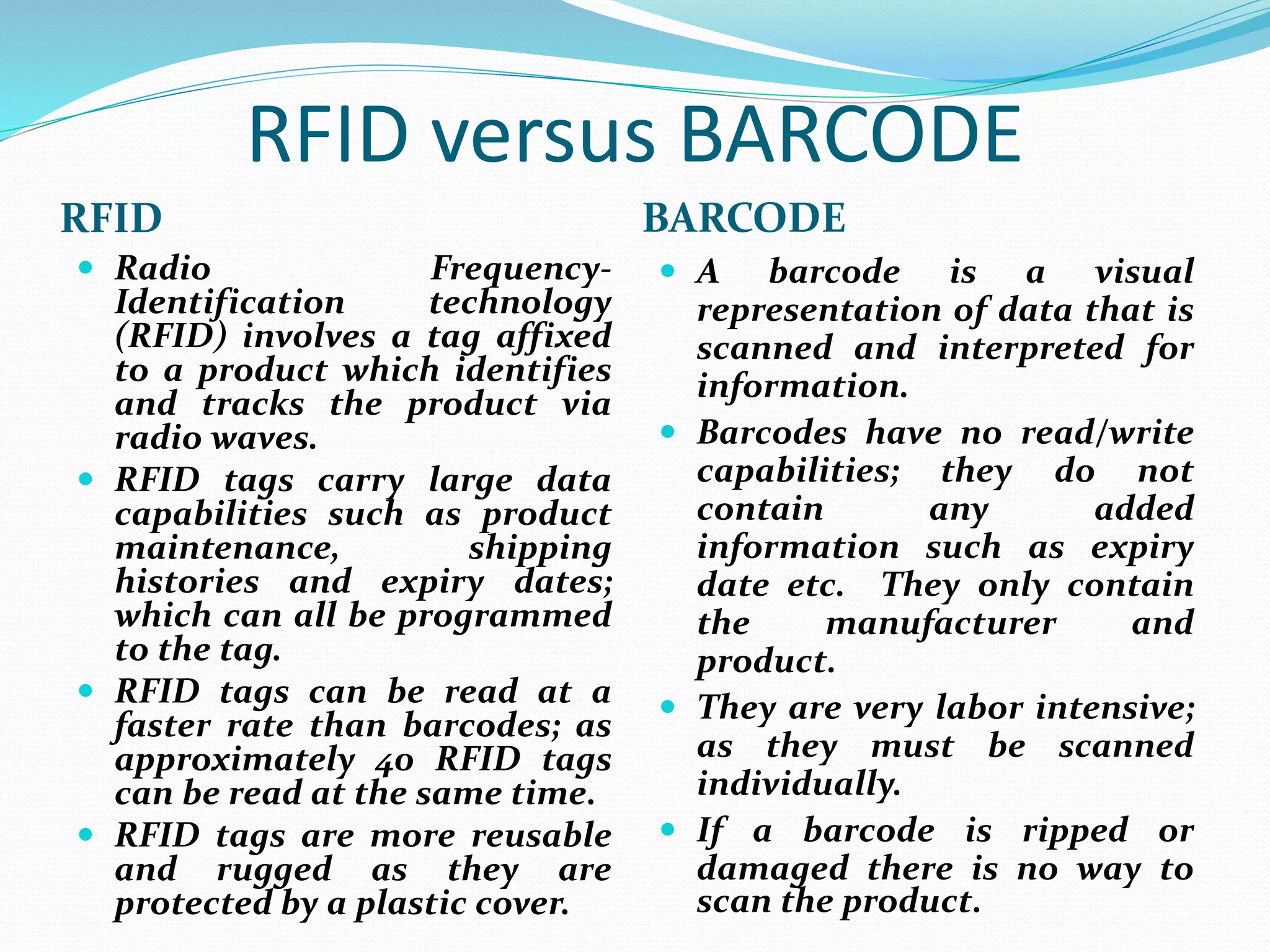
RFID technology, with roots tracing back to World War II, is utilized for asset tracking and communication via radio waves. Its applications span various fields including transportation, healthcare, and banking, providing automation and convenience. While offering benefits like location pinpointing and data storage, RFID also faces challenges regarding privacy concerns and potential interception of information.