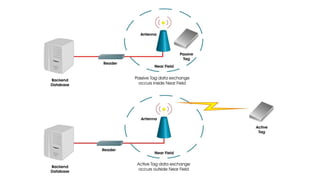
RFID is a technology that uses radio waves to automatically identify objects. It has been used since WWII but is now becoming more mainstream. An RFID system consists of tags attached to objects and readers that can identify tags within range. There are two main types of tags: active tags with internal power sources and passive tags that are powered by readers. RFID provides benefits across various industries like manufacturing, warehouses, distribution and supply chain management by improving visibility, accuracy, efficiency and reducing costs.