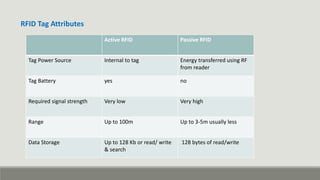
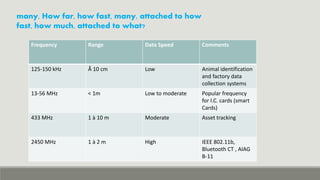
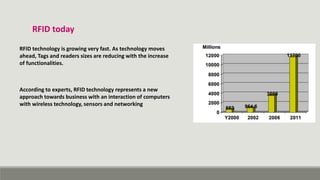
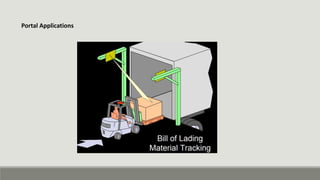
RFID technology uses radio waves to identify objects. It consists of tags attached to objects, readers that can detect tags, and software to process tag data. RFID has many applications including supply chain management, asset tracking, access control, and libraries. It provides benefits over barcodes like not requiring line of sight and being able to read multiple tags simultaneously. While initially used during World War II, RFID technology has advanced and miniaturized, finding growing use in various industries to enable real-time tracking of objects and inventory.