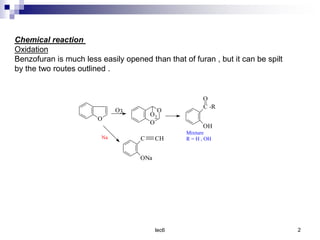
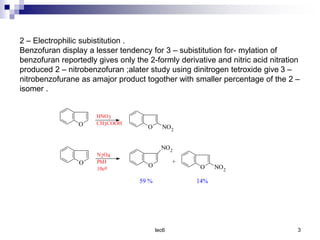
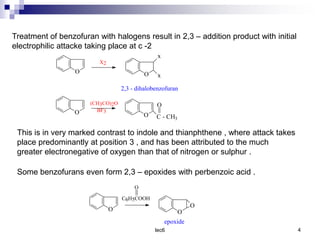
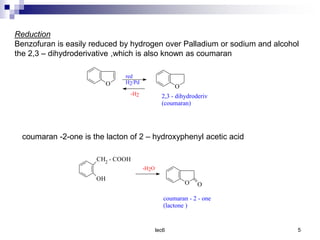
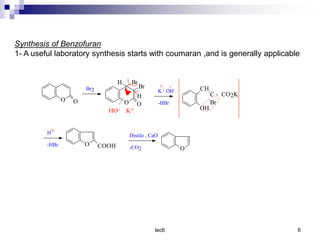
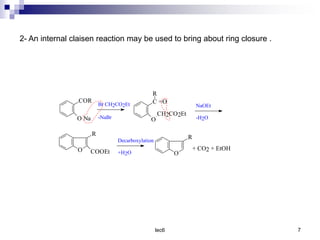
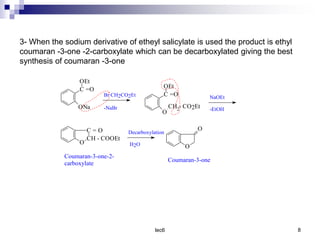
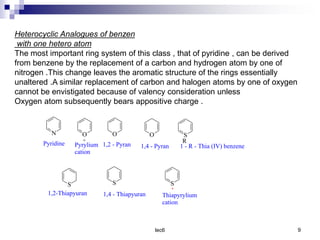
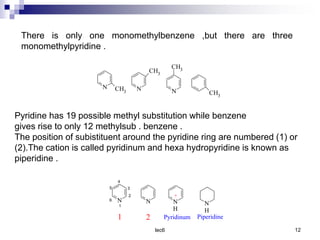
Benzofuran is a colorless liquid with an aromatic structure that can be treated as a resonance hybrid with major contribution from structure 1. It is more stable to chemical attack than furan due to its aromatic properties. Benzofuran undergoes electrophilic substitution at the 2-position and addition reactions at the 2,3-positions. It can be reduced to the 2,3-dihydroderivative coumaran. Several syntheses of benzofuran and coumaran are described starting from bromo derivatives.