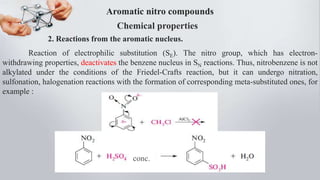
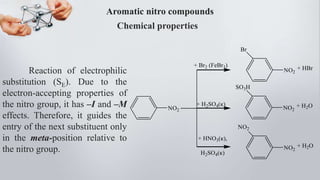
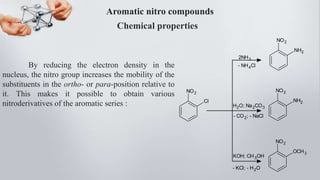
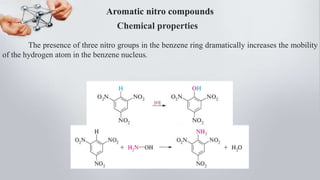
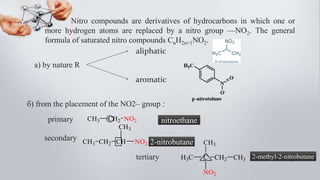
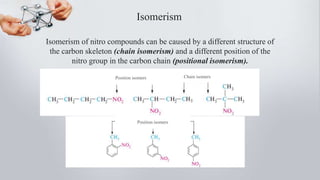
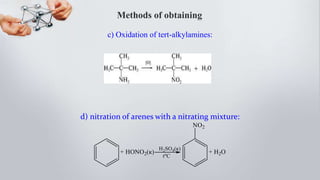
Nitro compounds contain a nitro (NO2) group bonded directly to carbon. They include nitroalkanes, nitroarenes, and others. Nitro compounds are polar due to the structure of the nitro group, which gives it electron-withdrawing properties. This allows nitroalkanes to exist as tautomers and undergo reactions like substitution. Nitroarenes are produced by nitrating aromatic compounds, with additional nitro groups requiring harsher conditions. They undergo reduction to amines, electrophilic substitution to meta derivatives, and nucleophilic substitution to ortho/para products. Important nitro compounds include nitrobenzene, nitromethane, picric acid, and trinitrotoluene.








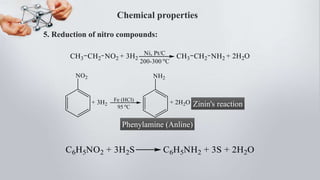


![Chemical properties
1. Reduction of nitroarenes (Zinin's reaction):
C6H5NO2 + 6[H] → C6H5NH2 + 2H2O
Depending on the pH of the reaction medium, the recovery process can follow two directions.
In a neutral and acidic medium :
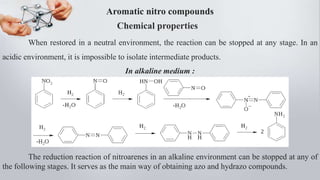
When restored in a neutral environment, the reaction can be stopped at any stage. In an
acidic environment, it is impossible to isolate intermediate products.
Aromatic nitro compounds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/org-230409173036-0f0a6da1/85/Org-chem_Lecture_6_Nitro_componds-pptx-15-320.jpg)