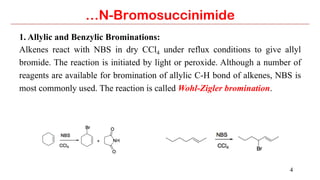
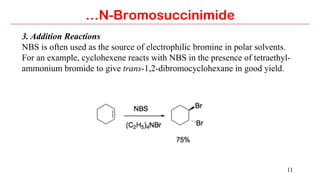
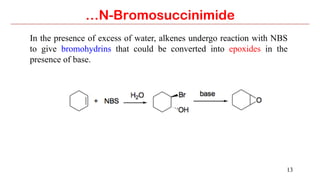
N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS) is a source of bromine for radical substitution and electrophilic addition reactions that is easier and safer to handle than bromine. NBS is used for allylic and benzylic brominations, alpha-bromination of carbonyl compounds, and addition reactions to alkenes to form bromohydrins or epoxides. The reactions involve a free radical mechanism initiated by a small amount of bromine radical from NBS.