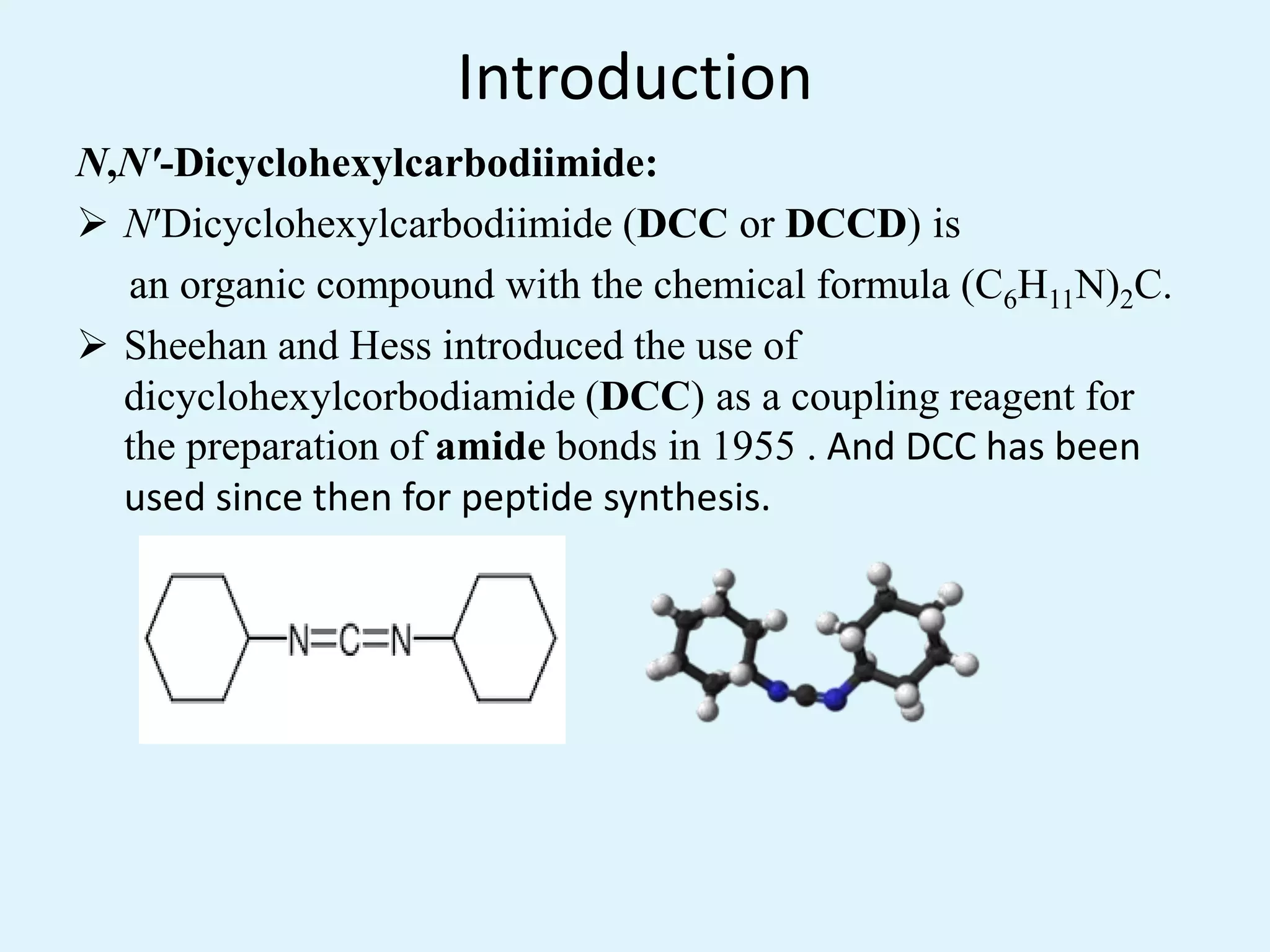
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) is an organic compound that is commonly used as a synthetic reagent to couple amino acids during peptide synthesis. It was first introduced for this purpose in 1955. DCC is a waxy white solid with a sweet odor that is highly soluble in organic solvents but insoluble in water. It has a low melting point, which allows it to be easily melted and handled. DCC is commonly used to catalyze esterification reactions and form amide bonds, as well as synthesize peptides, ethers, acid anhydrides, and lactones. One of its key applications is in the synthesis of beta-lactam rings in penicillin.







![5. Synthesis of Diacyl peroxide: Diacyl peroxide can be synthesized
by the treatment of carboxylic acids with hydrogen peroxide under
the mild condition with DCC
6. Synthesis of lactones: [ DCC in pyridine ] has been found to be a
better reagent for the synthesis of lactone by the lactonization of γ-
hydroxy acids. And also this method has been widely used in the
synthesis of Reserpine.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationdccss1-220314154322/75/Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-9-2048.jpg)
![7. Synthesis of Lactams: Lactams are cyclic amides. Β- Lactams are
highly strained ring, sensitive to acids while most reagents for amide
linkage involves strongly acid reagents. This caused a serious
problems in penicillin synthesis. However , the difficulty was
overcome by using DCC for the amide linkage.
Di isopropyl carbodiimide also has been found to be a better
reagent for amide ring formation but it is very mild reagent!
8. Synthesis of Peptides: The amino acids in the amino function has
been protected by Pthalyl [C6H4(CO)2] or Carbobenzoxy
[C6H5CH2–O–C=O] condense with amino acid esters in the
presence of DCC at room temperature to gives Peptides.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationdccss1-220314154322/75/Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-10-2048.jpg)
![ After hydrolysis of product the protecting group (Pthalyl group)
which is removed by hydrazine ( like Gabrial synthesis)
Pthalyl and Carbobenzoxy groups are used as a protecting groups ,
since they can be easily substitutesd and easily removed after
synthesis of particular products by Hydrogenolysis with [Pt + H2].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationdccss1-220314154322/75/Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-11-2048.jpg)

