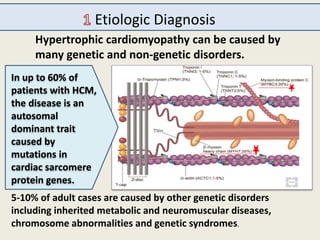
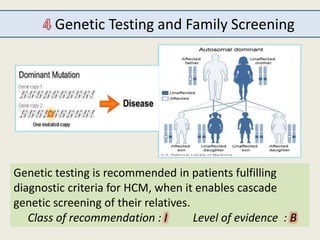
The document outlines the 2015 guidelines for the diagnosis and management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), detailing recommendations based on clinical trials, expert consensus, and various management strategies for associated conditions. Key points include the genetic and non-genetic causes of HCM, diagnostic criteria, and management of symptoms, left ventricular outflow tract obstruction, and prevention of sudden cardiac death. Special considerations for specific populations, such as pregnant women with HCM, are also addressed.



















![Prevention of sudden cardiac death
Model for estimating sudden cardiac death risk
The HCM Risk-SCD formula is as follows:
Probability = 1 – 0.998
where = [0.15939858 x maximal wall thickness
(mm)] - [0.00294271 x maximal wall thickness² (mm²)] +
[0.0259082 x left atrial diameter (mm)] + [0.00446131 x maximal
(rest/Valsalva) left ventricular outflow tract gradient (mm Hg)] +
[0.4583082 x family history SCD] + [0.82639195 x NSVT] +
[0.71650361 x unexplained syncope] - [0.01799934 x age at clinical
evaluation (years)].
SCD at 5 years
exp (Prognostic index)
The formula is available online
European Society of Cardiology. HCM Risk-SCD Calculator. 2014.
Available at:www.doc2do.com/hcm/webHCM.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2014esc-hcm-150226002403-conversion-gate02/85/2014-esc-hcm-22-320.jpg)











