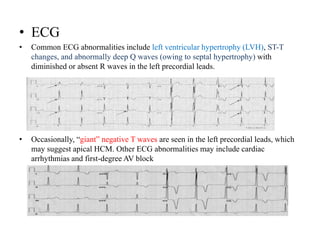
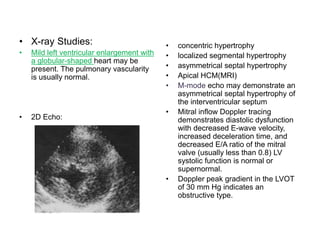
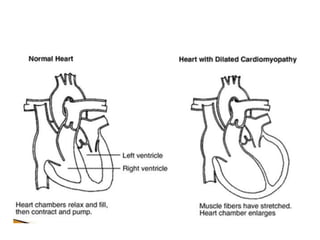
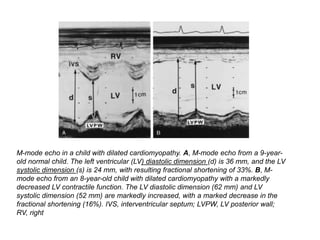
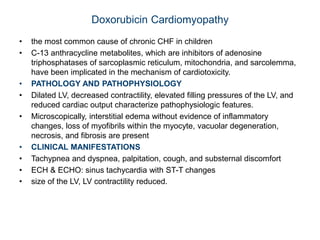
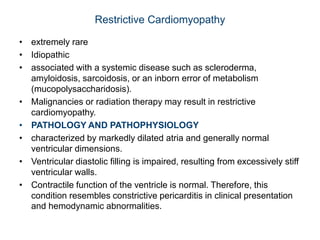
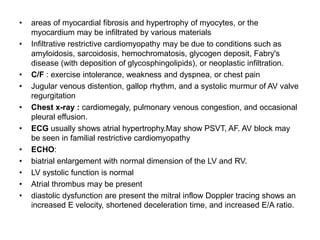
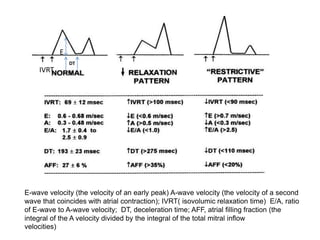
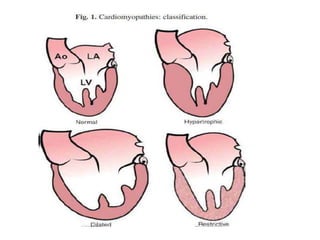
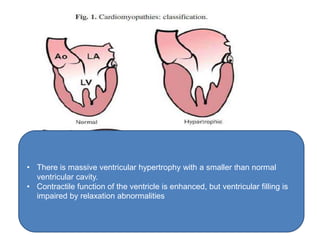
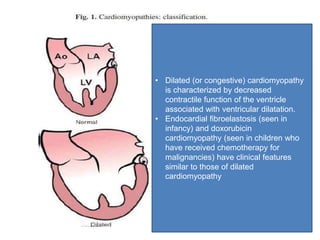
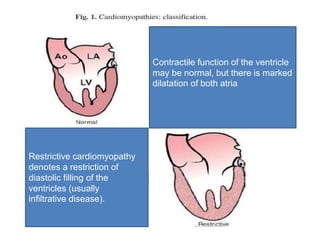
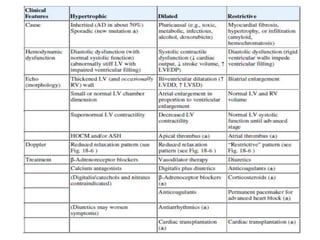
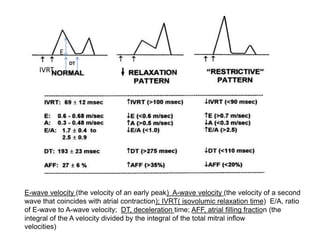
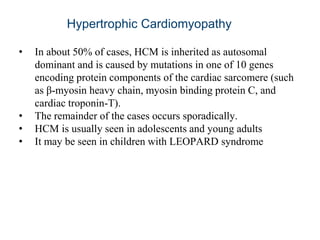
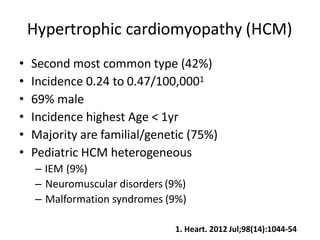
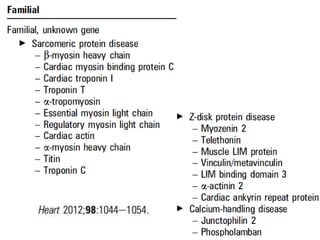
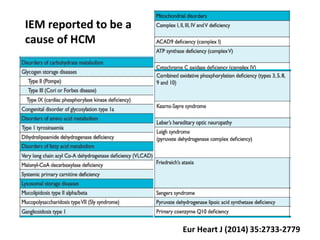
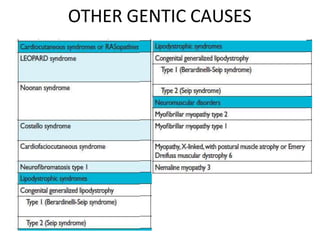
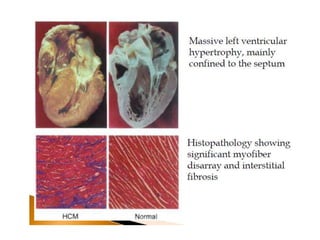
Cardiomyopathy refers to diseases of the heart muscle that are not caused by coronary artery disease, hypertension, or congenital heart defects. The main types are dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy, and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Dilated cardiomyopathy is characterized by decreased contractility and ventricular dilation, while hypertrophic cardiomyopathy involves ventricular hypertrophy with impaired diastolic function. Restrictive cardiomyopathy restricts diastolic filling. Management involves medications to reduce symptoms and progression such as ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, diuretics, and device therapy for refractory cases.





![Physical examination:
• A sharp upstroke of the arterial pulse is characteristic (in contrast to a slow
upstroke seen with fixed aortic stenosis [AS]).
• A grade 1 to 3/6 ejection systolic murmur of medium pitch is most audible
at the middle and lower left sternal borders or at the apex.
• A soft holosystolic murmur of mitral regurgitation (MR) is often present.
• The intensity and even the presence of the murmur vary from examination
to examination.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cardiomyopathy-190715182037/85/Cardiomyopathy-20-320.jpg)