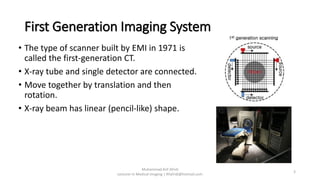
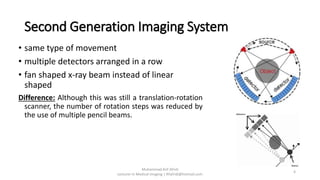
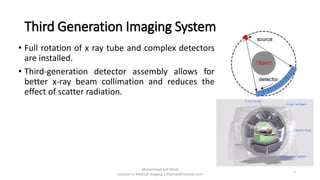
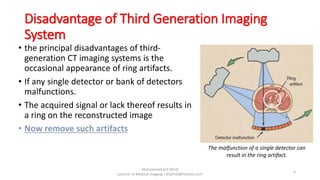
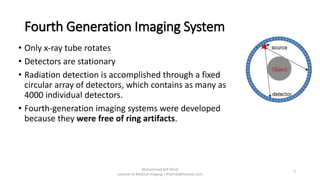
There are four generations of computed tomography (CT) imaging systems. The first generation used a single detector and pencil beam, taking 5 minutes per scan. The second generation used an array of detectors and fan beam, reducing scan time to 30 seconds. The third generation rotated the x-ray tube and array of detectors, achieving subsecond scan times but risked ring artifacts from detector failures. The fourth generation kept detectors stationary and only rotated the x-ray tube, eliminating ring artifacts. Today, third generation CT systems with helical and multi-slice capabilities are most common.