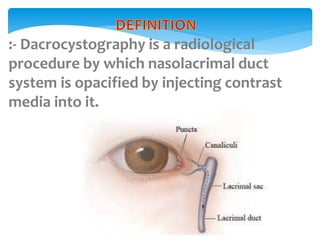
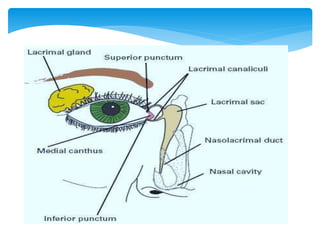
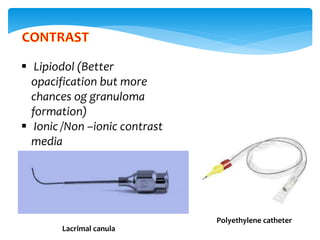
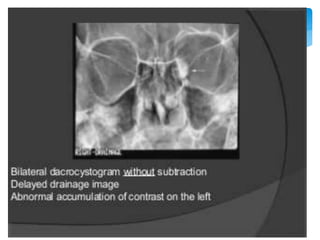
Dacrocystography is an imaging procedure used to evaluate the lacrimal drainage system. Contrast media is injected through the puncta into the lacrimal drainage structures and X-rays are taken to identify any obstructions or abnormalities. The lacrimal drainage system includes the lacrimal gland, conjunctival sac, puncta, canaliculi, lacrimal sac, and nasolacrimal duct. Dacrocystography can be used to investigate various conditions affecting tear production and drainage such as epiphora, fistulas, tumors, diverticula, obstructions, and infections.