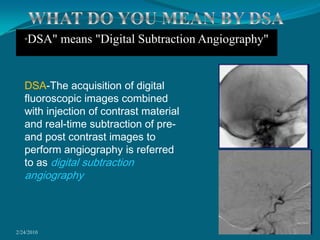
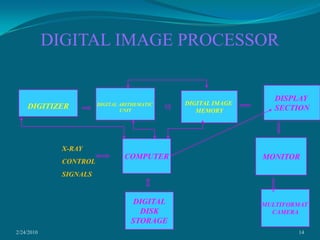
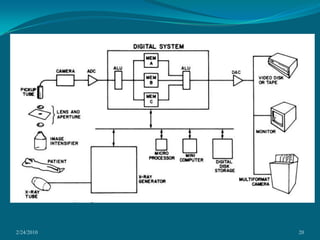
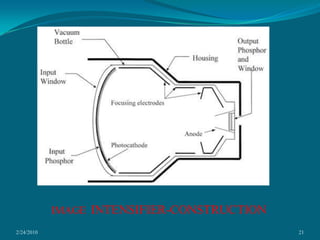
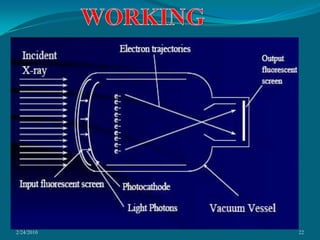
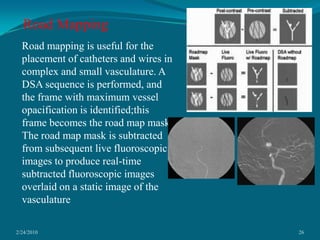
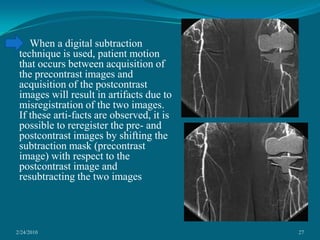
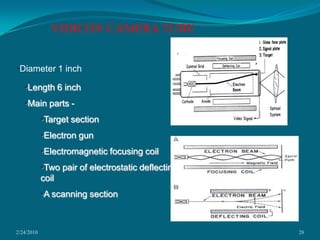
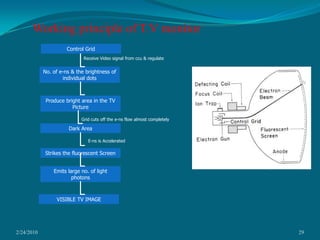
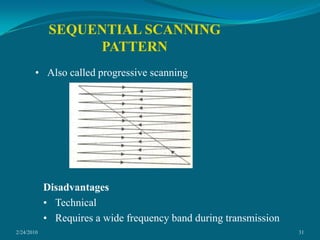
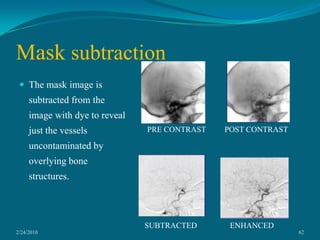
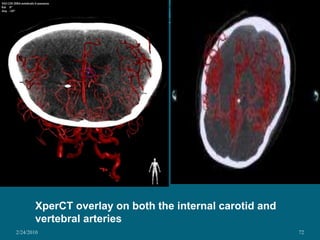
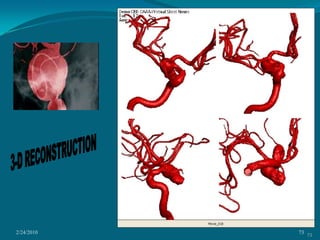
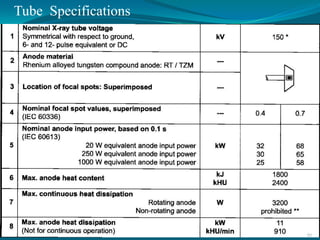
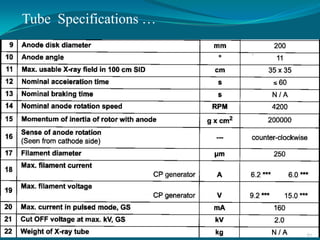
This document discusses digital subtraction angiography (DSA), including its history, equipment, and applications. DSA involves acquiring digital fluoroscopic images before and after injecting contrast material, and using computer subtraction to remove bone structures and leave an image of blood vessels. It originated in the 1970s and allows for real-time angiography with improved vessel contrast compared to conventional techniques. Key components of DSA systems include an x-ray unit, image intensifier, computer, and software for image processing functions like subtraction, enhancement, and roadmapping.