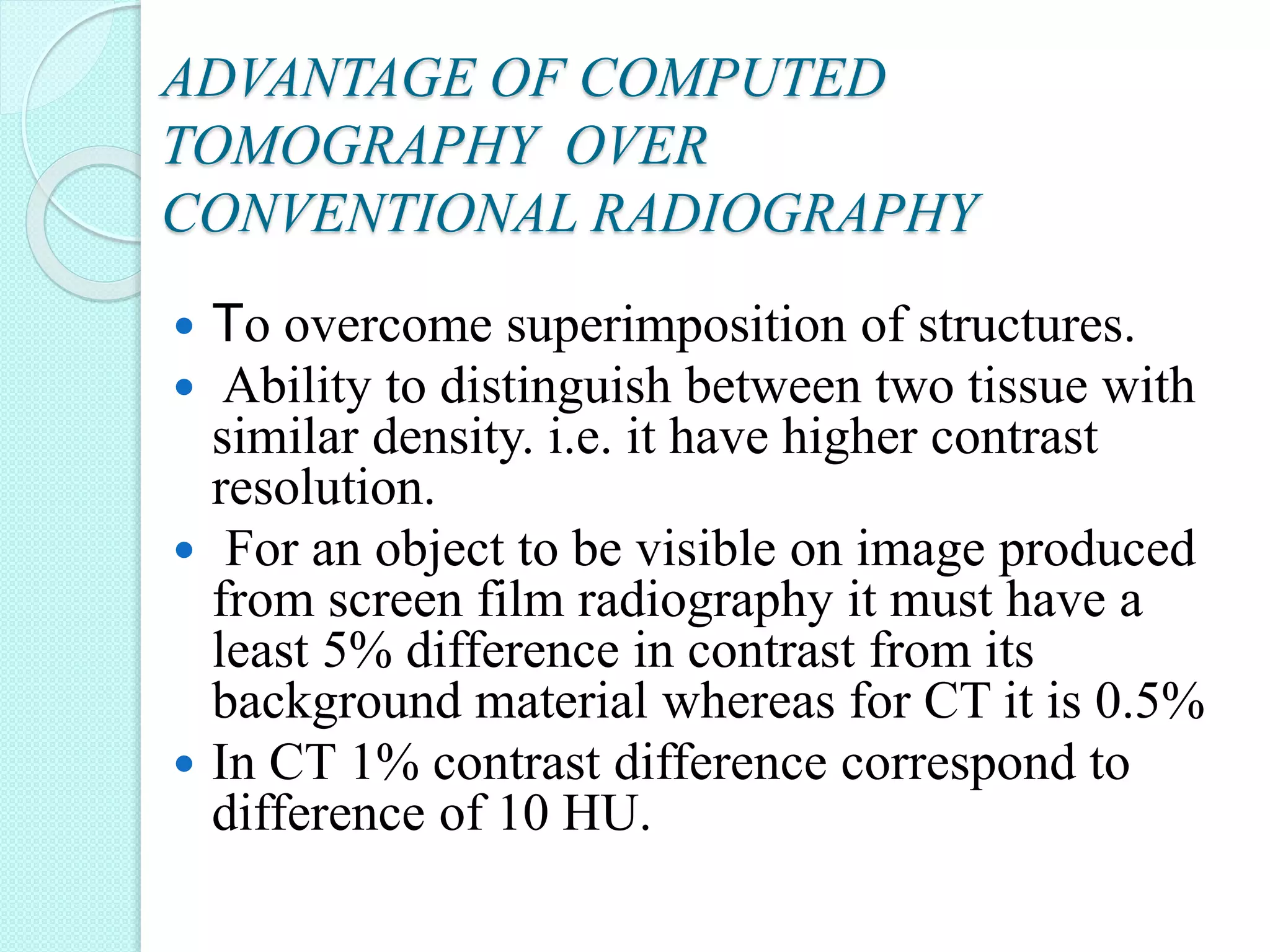
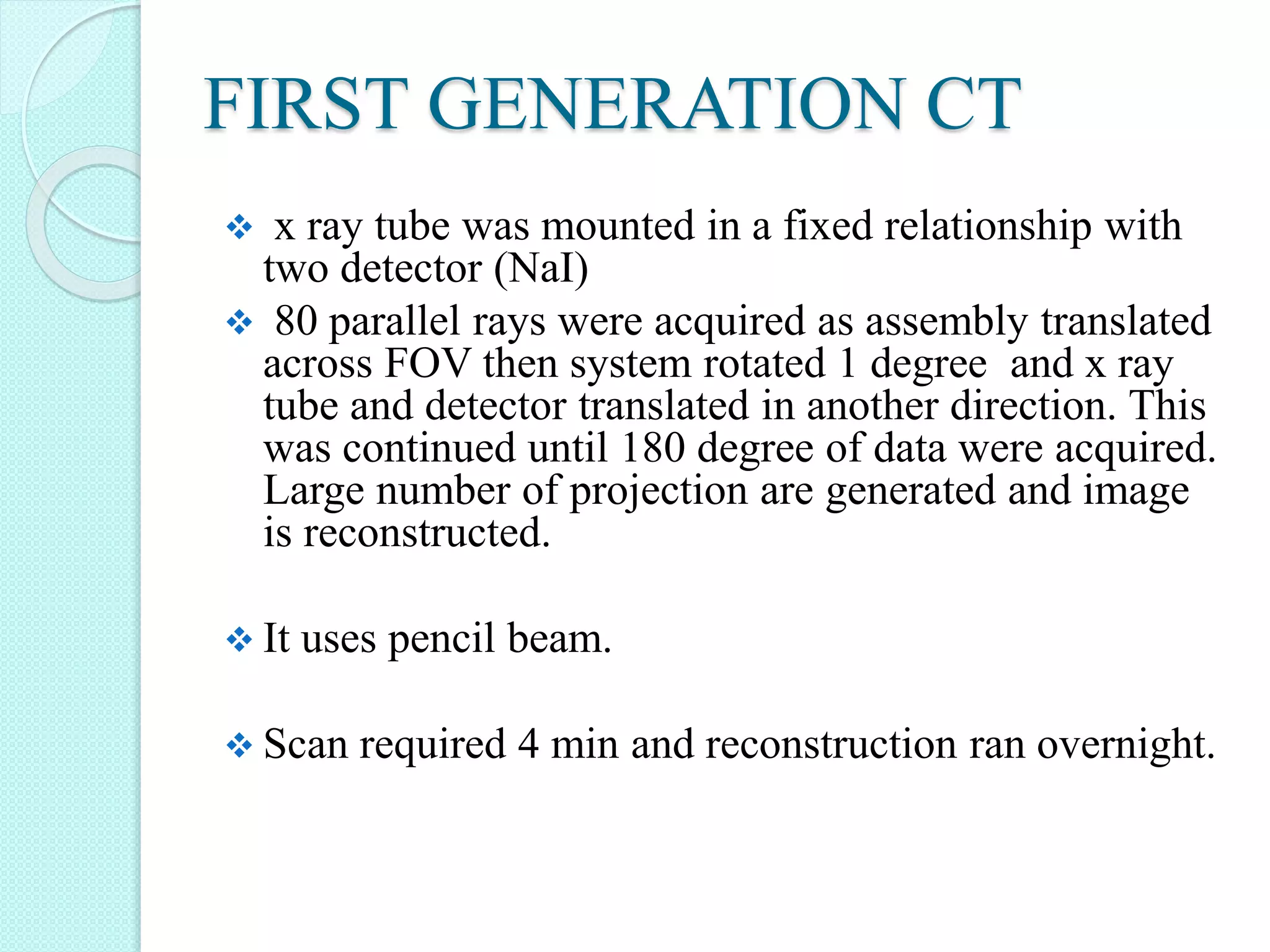
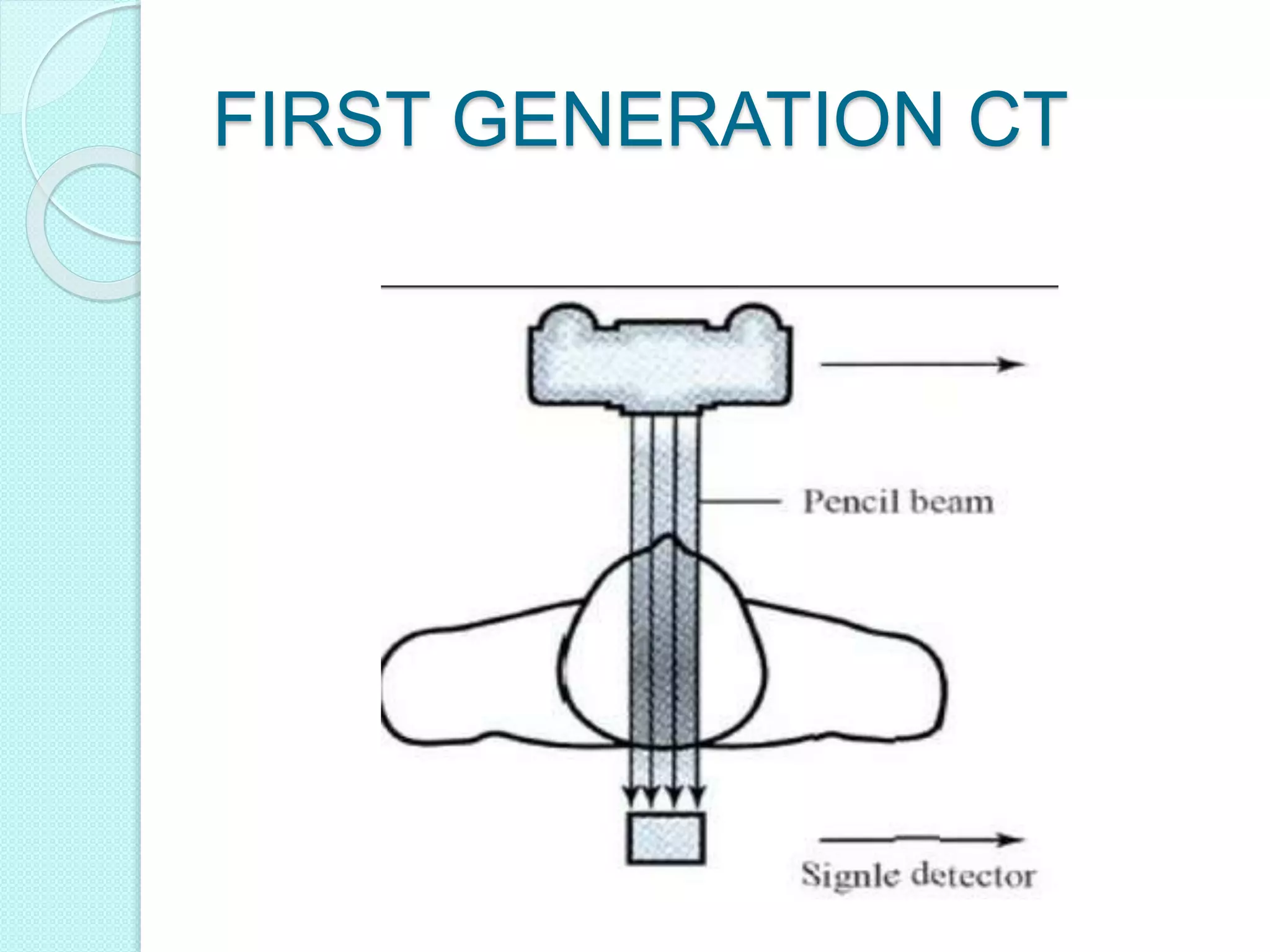
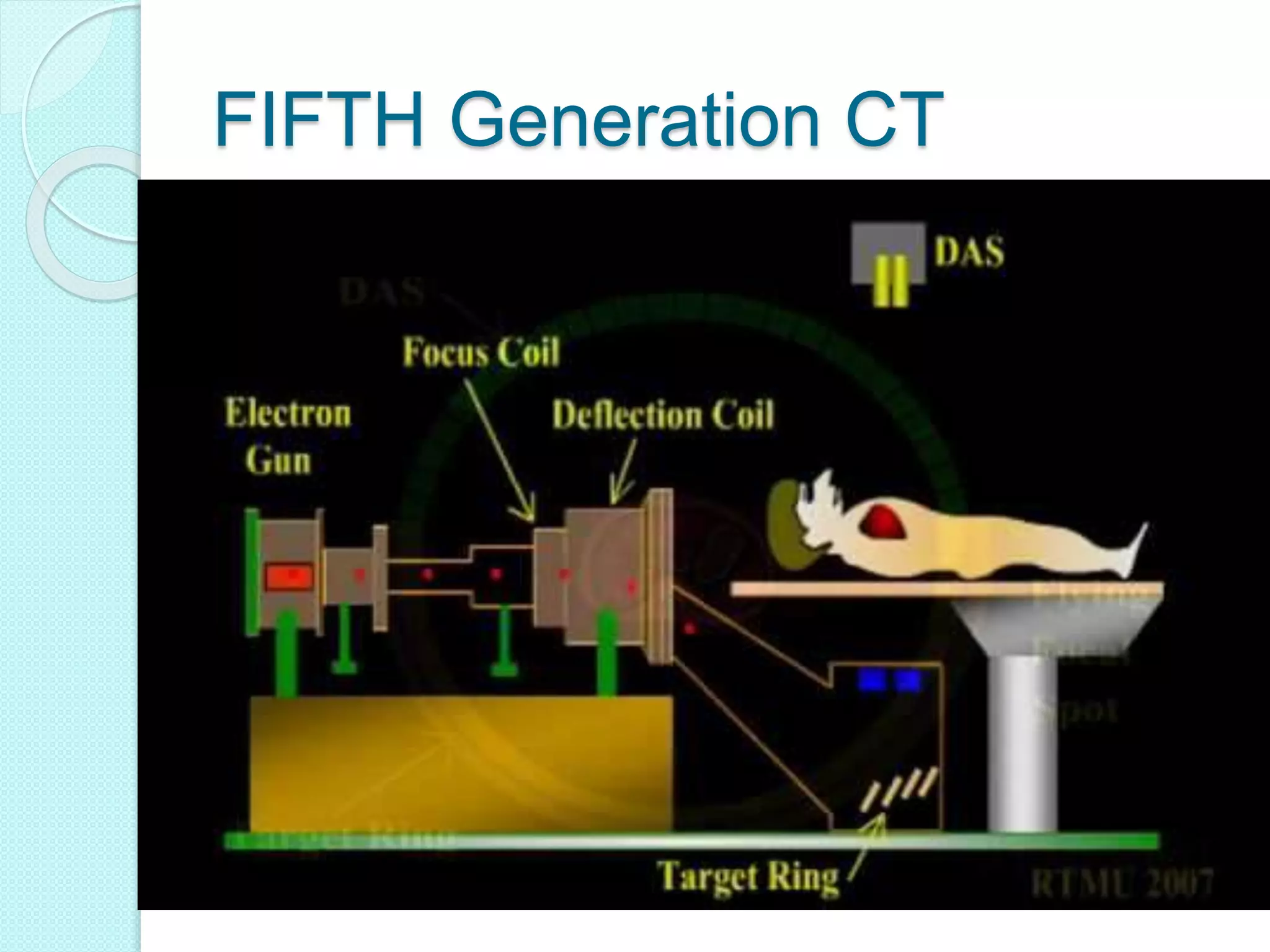
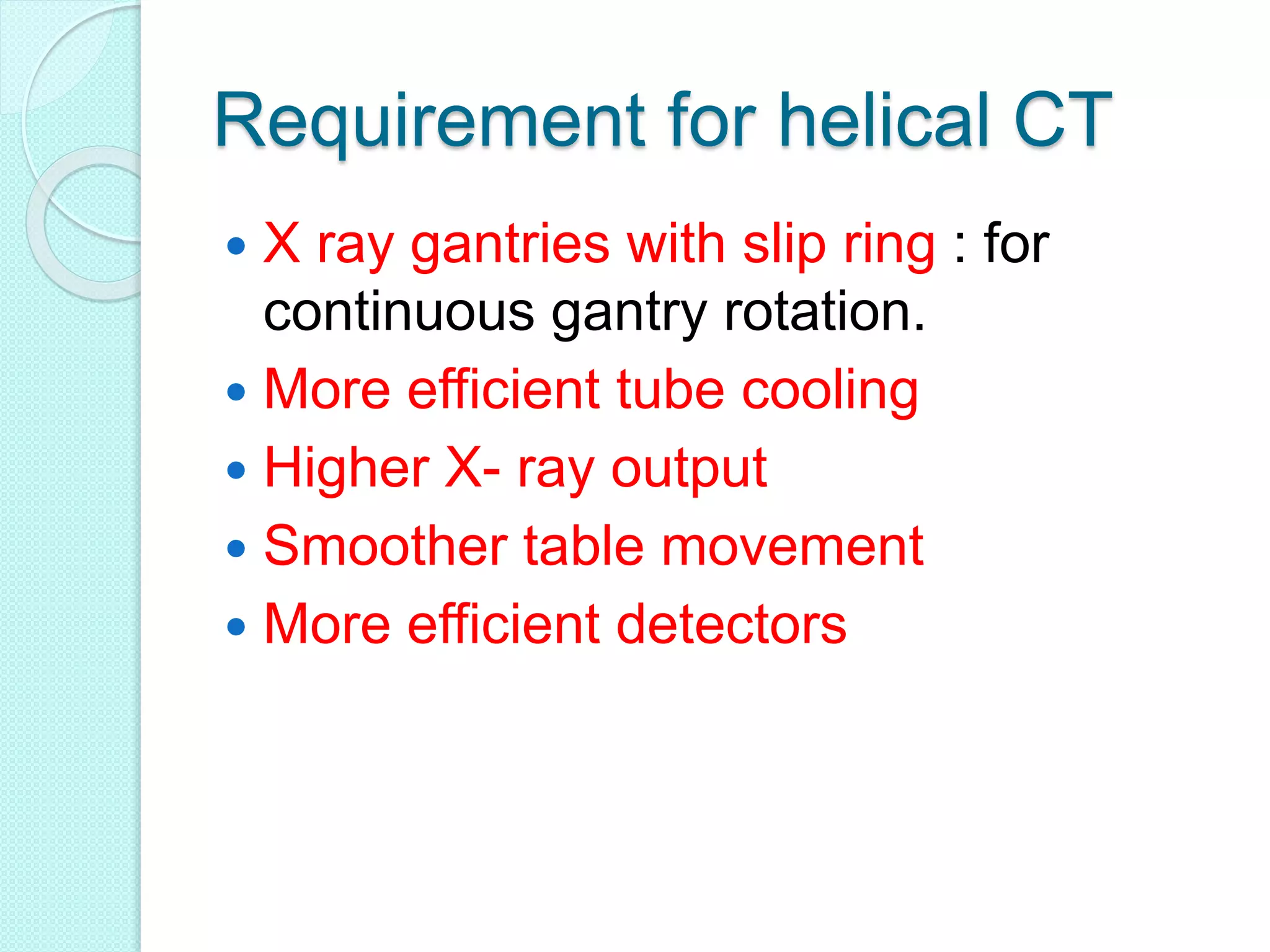
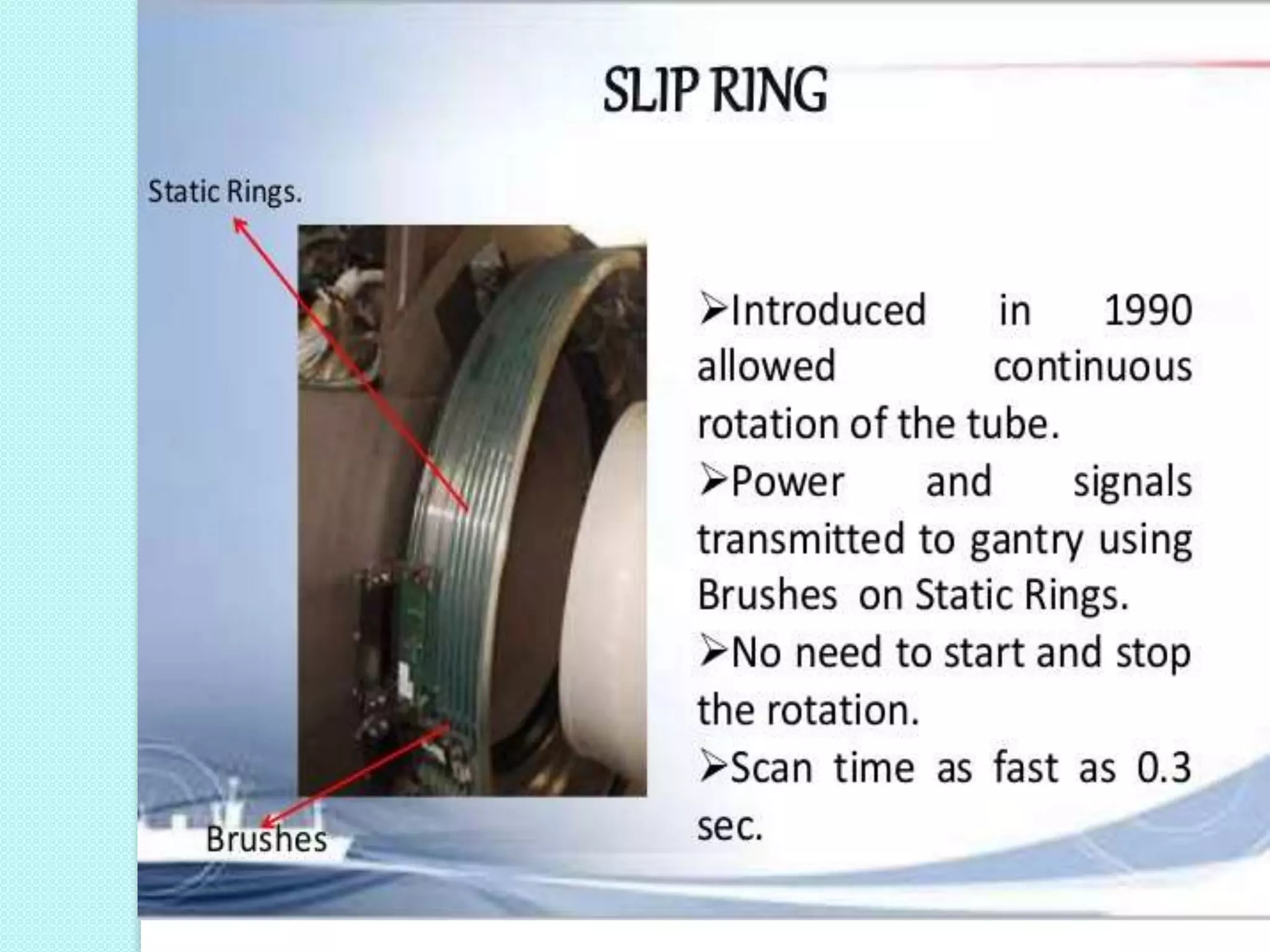
Computed tomography (CT) provides cross-sectional images of the body using X-rays. CT has evolved through several generations with advances in technology. Modern multi-detector CT allows acquisition of multiple slices simultaneously, reducing scan time. Helical or spiral CT involves continuous table movement and X-ray rotation, allowing whole organ or body coverage with minimal artifacts. Pitch relates the table speed to beam width and affects radiation dose and anatomic coverage. CT has advantages over conventional radiography including better contrast resolution and ability to distinguish between tissues.