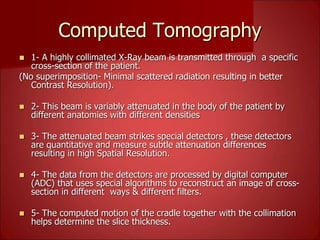
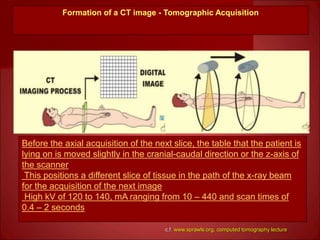
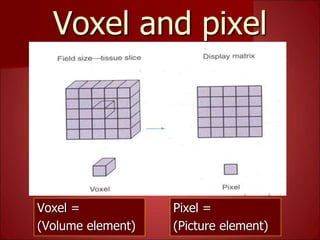
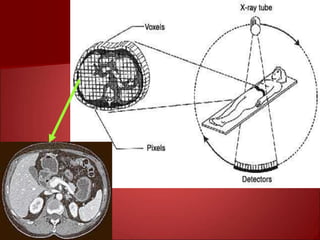
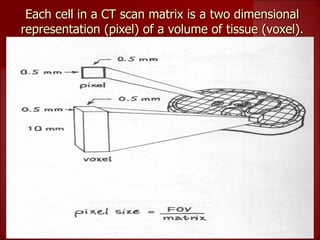
This document summarizes the evolution of computed tomography (CT) technology over several generations:
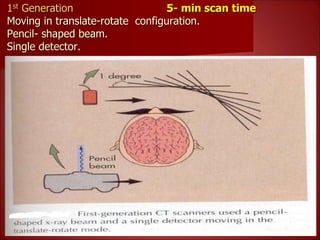
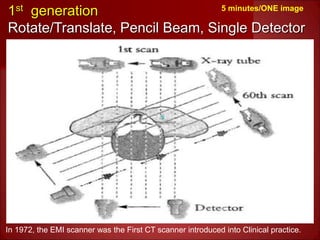
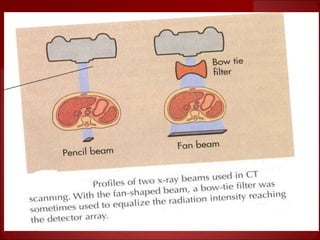
- 1st generation CT scanners from the 1970s took 5 minutes to generate a single image using a pencil-shaped beam and single detector.
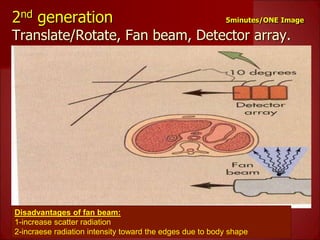
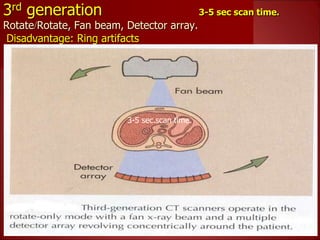
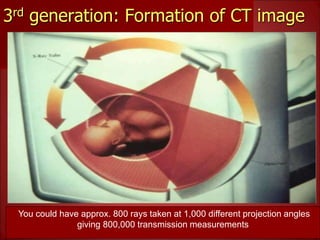
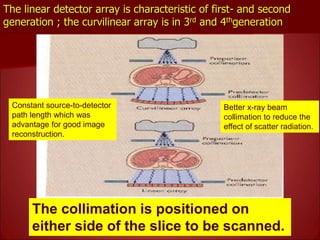
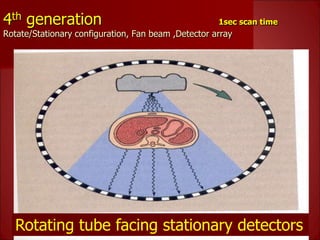
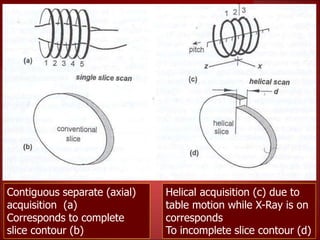
- 3rd generation scanners from the 1980s reduced scan time to 3-5 seconds using a fan beam and detector array while rotating continuously.
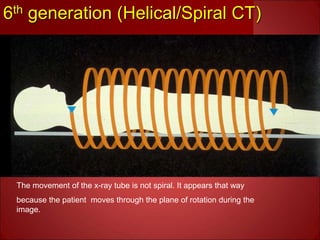
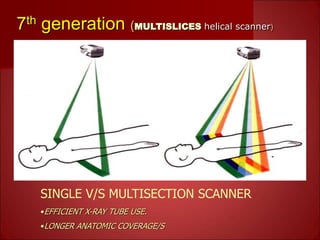
- Current multislice CT scanners can scan multiple slices simultaneously in under 1 second using multiple detector arrays.
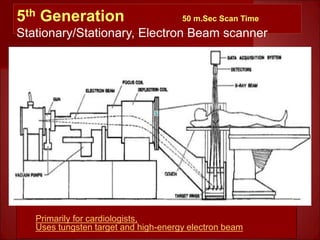
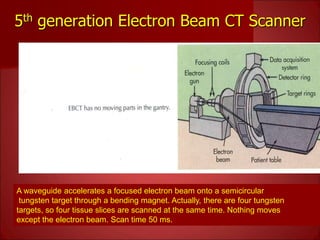
- The latest technology uses a stationary beam and detector configuration to achieve scan times under 50 milliseconds.