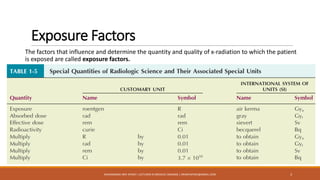
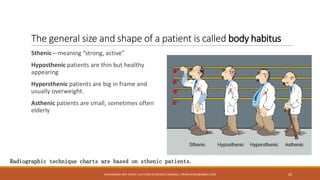
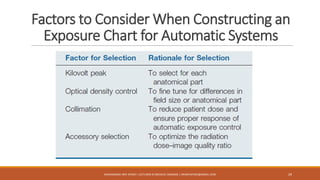
The document provides an overview of key exposure factors in screen film radiography, highlighting the four primary factors: kilovolt peak (kVp), milliamperes (mA), exposure time, and source-to-image receptor distance (SID). It also discusses secondary factors like focal-spot size and filtration, along with image quality factors such as optical density, contrast, detail, and distortion, all of which influence radiographic imaging outcomes. Additionally, the text emphasizes the importance of proper technique charts and automatic exposure control systems in achieving high-quality radiographs.