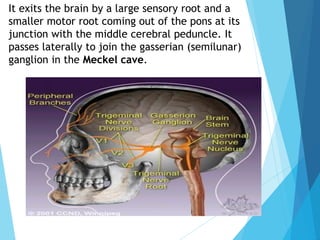
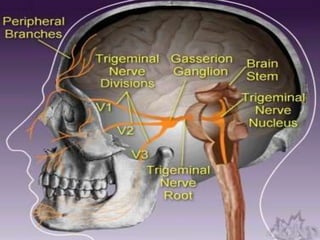
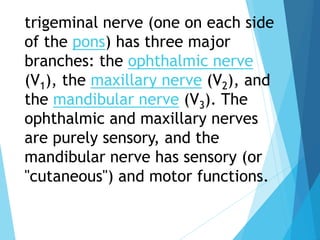
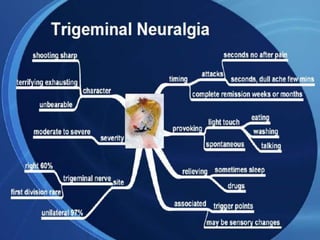
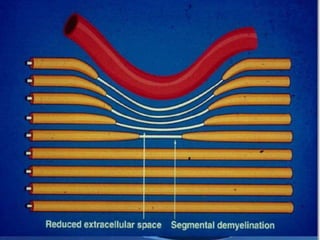
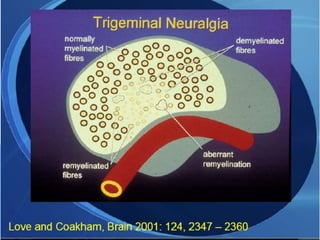
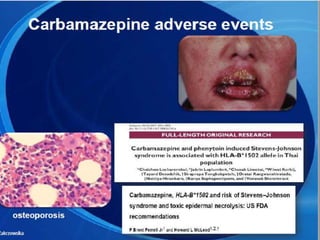
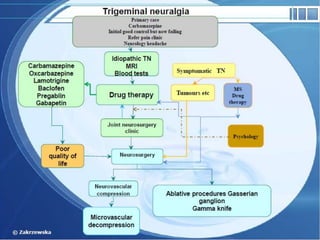
The trigeminal nerve is the largest cranial nerve, supplying sensation to the face and motor function to the muscles of mastication. It exits the brainstem and divides into three major branches - the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular nerves. Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition of severe, sporadic facial pain caused by compression of trigeminal nerve roots. It is characterized by episodes of electric shock-like pain in areas supplied by branches of the trigeminal nerve, often triggered by mundane activities like eating or talking. Treatment involves pharmacological options like carbamazepine or oxcarbazepine as first-line or surgical procedures if medications provide inadequate relief.