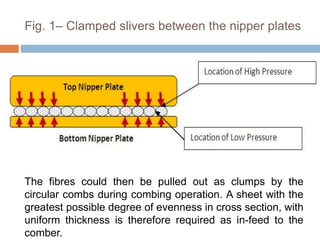
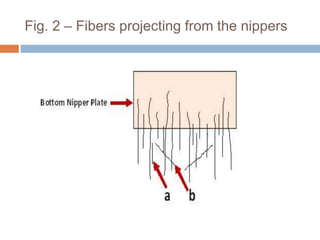
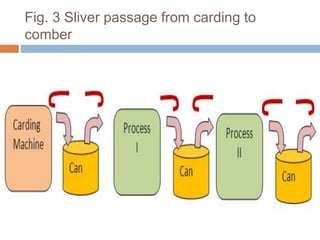
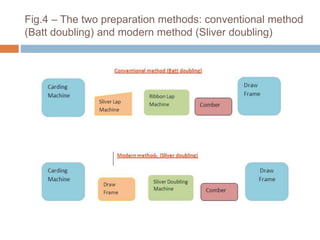
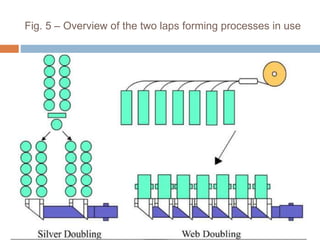
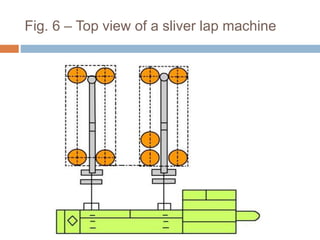
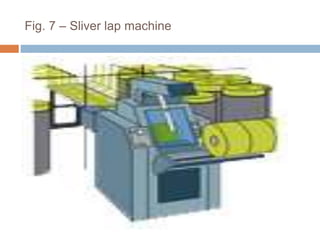
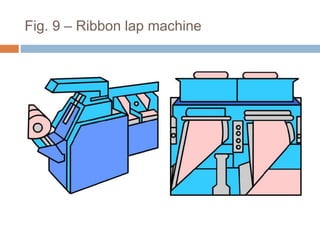
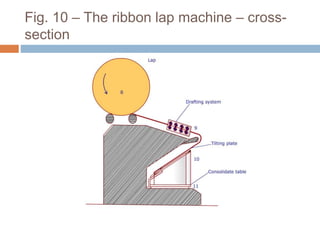
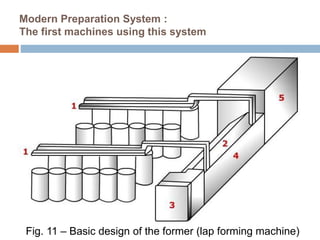
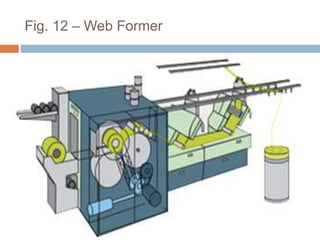
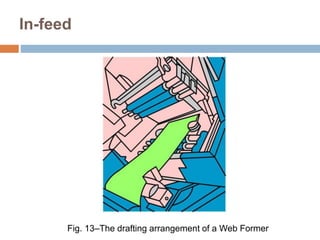
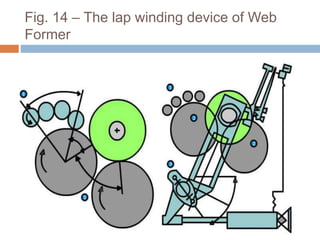
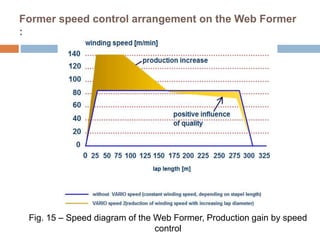
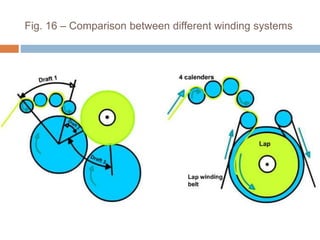
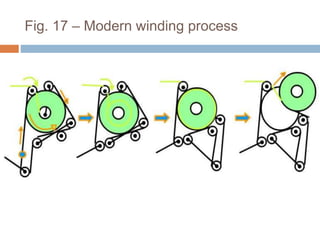
The document discusses the preparation of material for combing. It describes that card slivers alone are unsuitable for combing and must be further processed. It discusses two preparation methods - the conventional method using a sliver lap machine and ribbon lap machine, and the modern method using a draw frame and sliver doubling machine. Key points covered include the importance of an even batt thickness and fiber parallelization, as well as ensuring the majority of fibers have leading hooks for effective combing.