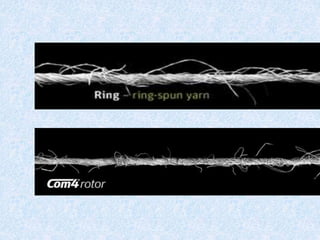
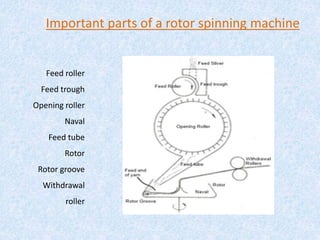
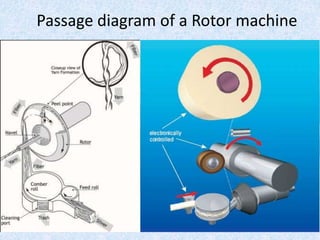
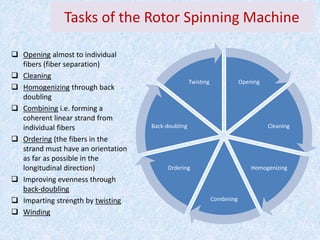
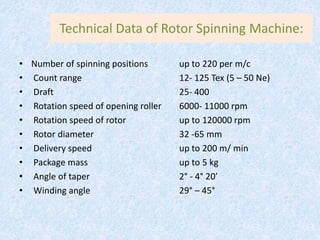
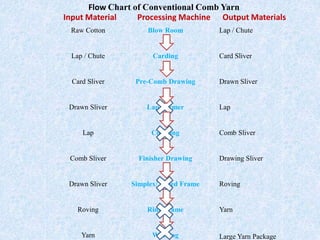
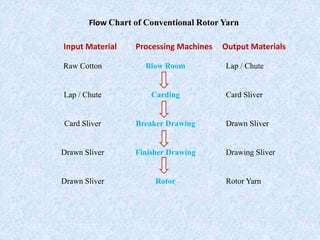
This document compares ring spinning and rotor spinning methods of yarn formation. It discusses that rotor spinning is a more recent method that omits the step of forming a roving. In rotor spinning, fibers are fed into a rotary beater and deposited onto the sides of a rotating disc called a rotor, where they are twisted without requiring package rotation. Rotor spinning allows for higher twisting speeds with lower power usage compared to ring spinning. It provides characteristics like higher productivity, larger sliver/package sizes, less power consumption, and more automation/flexibility. The document provides details on the parts of a rotor spinning machine and compares various parameters of ring-spun and rotor-spun yarns.






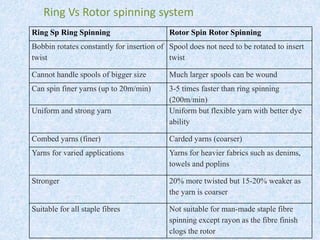

![Comparison between Ring and Rotor yarn [20 Ne]
Parameters Ring yarn (Card) Rotor yarn
Tenacity (cN/Tex) 17.5 15.1
CSP 2550 1830
Elongation % 3.75 4.35
TPI 14.23 18.31
Uster U% 9.774 9.41
CVm% [1cm] 12.412 11.872
CVm% [3m] 2.882 2.91
Thin [-40%]/Km 20.687 36.56
Thick [+35%] 446.25 178.75
Thick [+50%] 48.125 5
Neps [+200%] 60.3125 26.25
Hairiness Index [H] 7.21 4.65
Note: This experimental data is an average test result out of 8-10 tests. The tests were
done at The Delta Spinning mills Ltd.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rotorspinning-161123181701/85/Rotor-spinning-15-320.jpg)