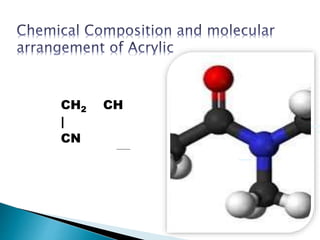
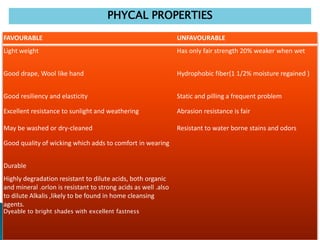
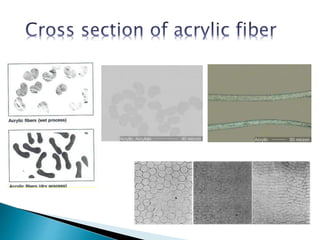
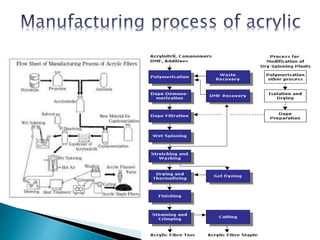
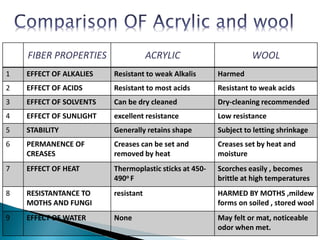
Amit Biswas is a student in the Department of Textile Engineering at Green University of Bangladesh with ID number 143003014. The document discusses acrylic fibers, which are synthetic polymers composed of at least 85% acrylonitrile monomer units. Acrylic fibers are resistant to water damage, sunlight, mold, mildew, and insects but are flammable. The document also discusses the properties, manufacturing process, uses, and comparisons of acrylic and wool fibers.