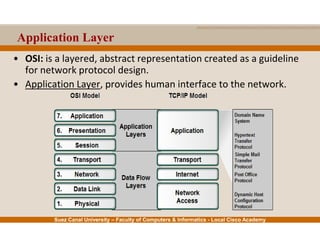
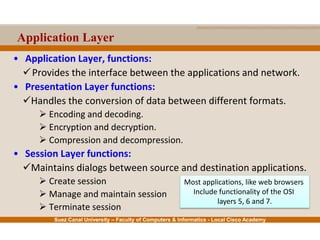
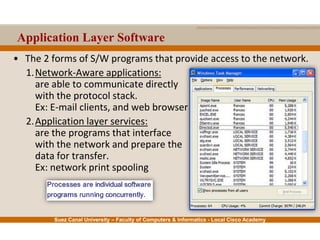
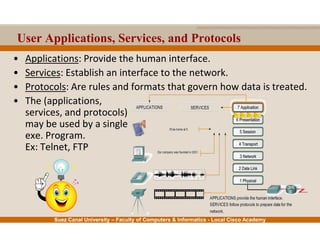
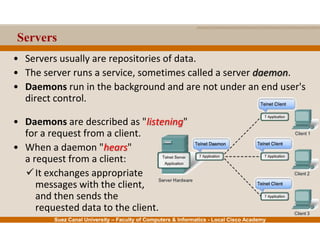
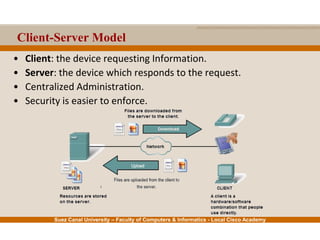
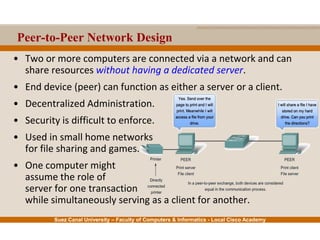
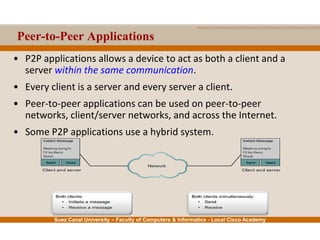
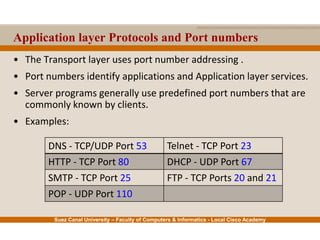
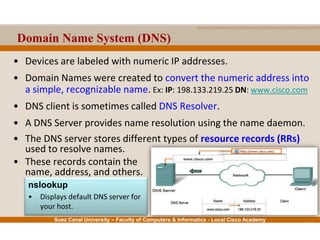
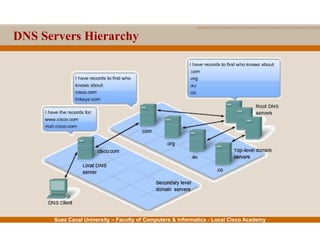
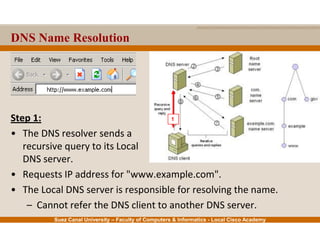
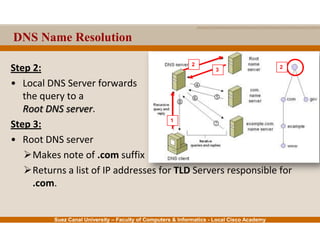
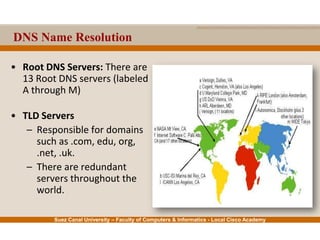
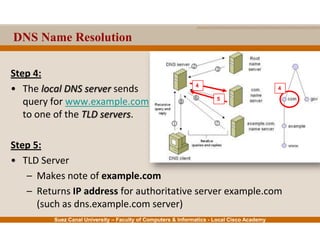
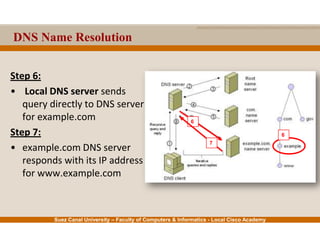
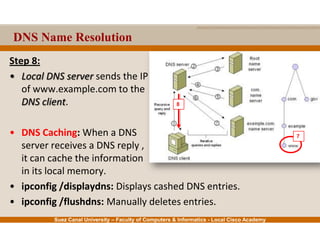
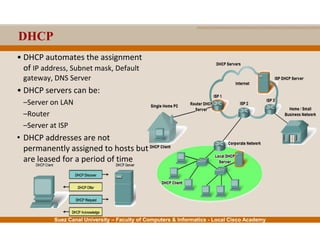
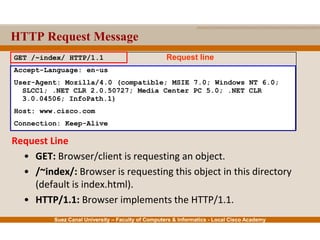
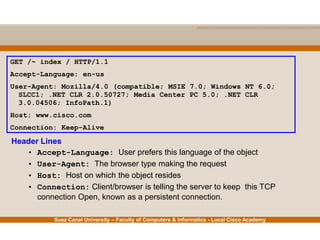
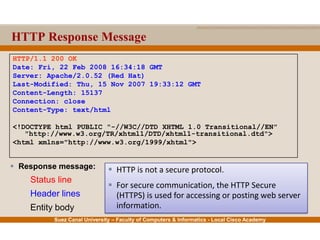
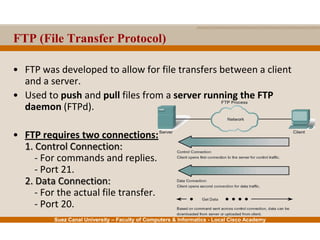
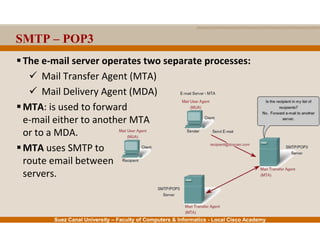
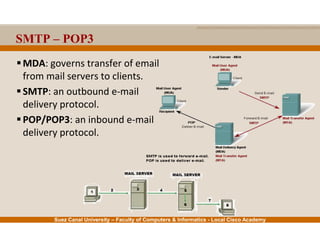
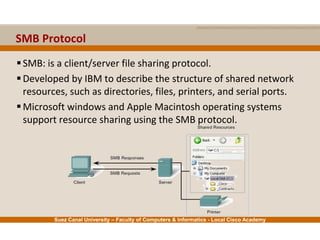
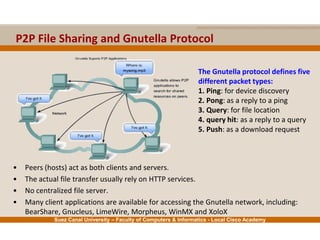
This document provides an overview of the application layer of the OSI model. It discusses application layer functions like providing an interface for applications to access the network. It describes application layer protocols like HTTP, FTP, SMTP, and DNS. It also covers topics like client-server and peer-to-peer networking, application layer software, and application layer protocols and port numbers.