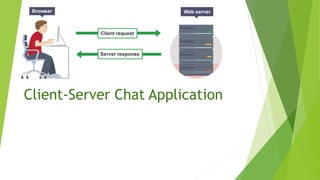
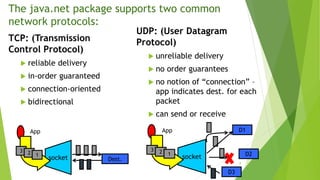
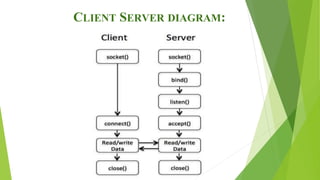
A socket represents a connection between two programs on a network and allows them to communicate. The document discusses sockets and how they enable client-server applications like a chat application. It provides code examples of how a chat client would connect to and send messages to a chat server, which would listen for incoming connections and send messages to connected clients. The key aspects are that the server binds to a port and listens for clients to connect, and then messages can be sent bidirectionally between the client and server over their socket connection.


![Socket Interface Types:
Socket interfaces can be divided into three
categories:
1. Stream Socket
2. Datagram Socket
3. Raw Socket
[We will talk about Raw Socket only]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/client-serverchatapplication-170415095228/85/Client-server-chat-application-4-320.jpg)





![CODE ILLUSTRATION FOR CLIENT:
public class ChatClient
{
// Declarations
ChatClient()
{
//codes
}
private void ConnectToServer()
{
// code
}
private void SendMessageToServer(String Message)
{
}
private void InitializeAppletComponents()
{
// Applet Initailization
}
private void LoginToChat()
{
ConnectToServer();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChatClient mainFrame = new ChatClient();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/client-serverchatapplication-170415095228/85/Client-server-chat-application-12-320.jpg)
![CODE ILLUSTRATION FOR SERVER:
public class ChatServer
{
//Declarations
public ChatServer()
{
//Codes
};
}
private void SendMessageToClient (Socket clientsocket, String message)
{
//Codes
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChatServer mainFrame = new ChatServer();
mainFrame.setVisible(true);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/client-serverchatapplication-170415095228/85/Client-server-chat-application-13-320.jpg)

