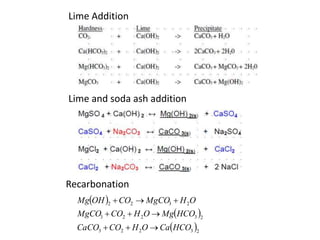
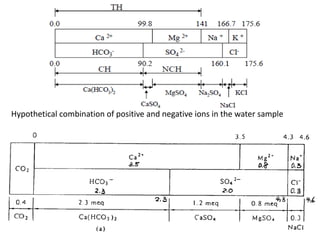
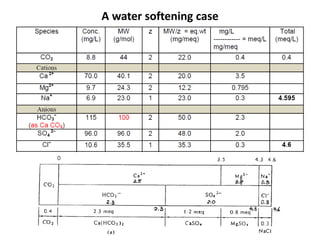
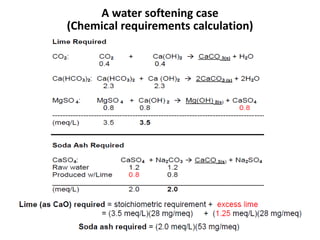
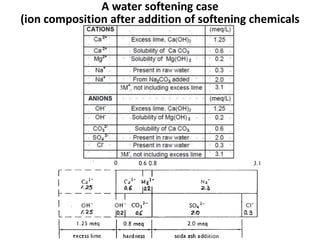
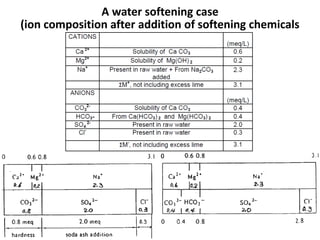
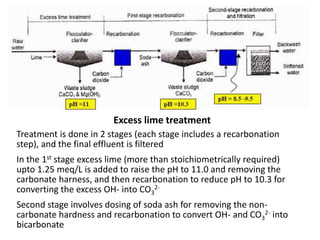
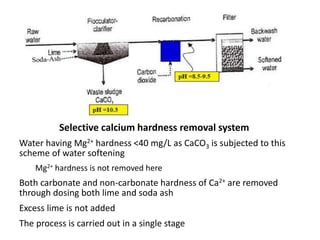
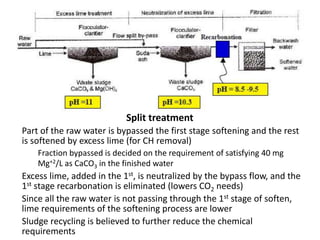
Hardness in water is caused by multivalent metal ions like calcium and magnesium. The document discusses the different types of hardness and methods for measuring and removing hardness, including lime-soda softening. Key points include that lime is used to remove carbonate hardness by precipitating calcium carbonate while soda ash removes non-carbonate hardness, and recarbonation converts precipitates back to bicarbonates to inhibit scaling. Bar diagrams and saturation indices are also discussed for analyzing water hardness levels and stability.



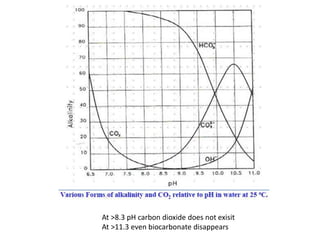


![Indices
(describing behavior of CaCO3 in water)
Langelier Saturation Index (LSI) and Ryznar Stability Index (RSI)
Langelier Saturation Index (LSI)
• A calculated number developed by Wilfred Langelier (1936)
• It predicts the CaCO3 stability of water (whether the carbonate will
precipitate, dissolve, or remain in equilibrium) and stated as
LSI = pH - pHs
• pHs (the pH at which water is saturated in CaCO3) is calculated by
pHs = (9.3 + A + B) - (C + D)
A = (Log10[TDS] - 1)/10
B = -13.12 x Log10(oC + 273) + 34.55 – (2.09 at 25°C)
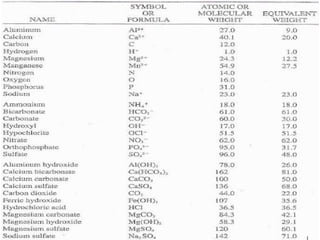
C = Log10[Ca2+ as CaCO3] - 0.4 - - (2.5(Ca2+)
D = Log10[alkalinity as CaCO3]
• LSI is temp. sensitive (increasing temp. increases the LSI value)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14-watersoftening-151214130537/85/12-water-softening-8-320.jpg)