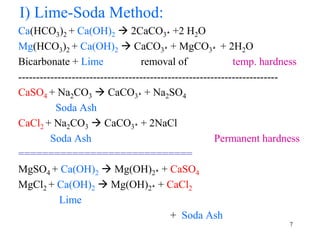
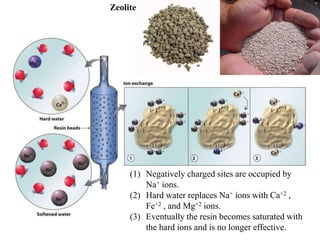
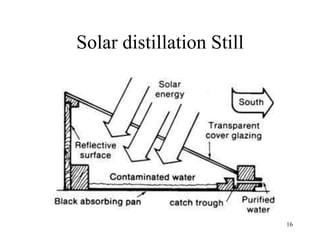
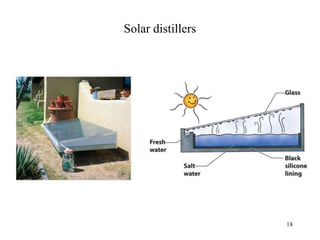
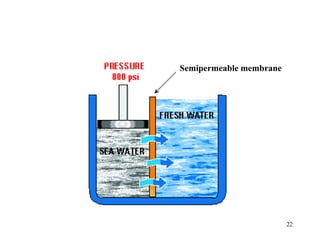
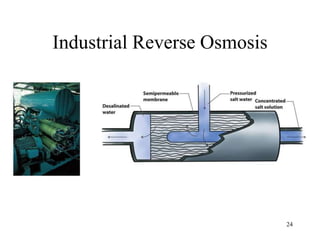
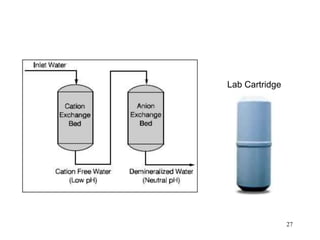
Water can be hard or soft depending on the amount of dissolved minerals like calcium and magnesium. Hard water causes scale buildup and reduces cleaning product efficiency. There are several methods to remove hardness from water including lime-soda softening, cation exchange, distillation, reverse osmosis, and ion exchange. Lime-soda softening uses lime and soda ash to precipitate minerals out of solution. Cation exchange uses zeolites to replace calcium and magnesium ions with sodium ions.


![Hardness Removal / Water Softening
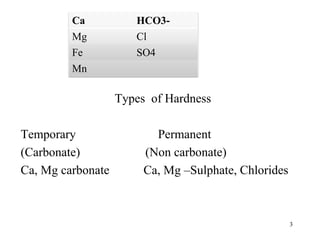
I) Temporary hardness
A) By Boiling
Ca.(HCO3)2 Heat CaCO3ꜜ + H2O +CO2ꜛ
Mg.(HCO3)2 Heat CaCO3ꜜ + H2O +CO2ꜛ
B) By Addition of Lime [Ca(OH)2 ]
Ca(HCO3)2 + Ca(OH)2 2CaCO3ꜜ +2 H2O
Mg(HCO3)2 + Ca(OH)2 CaCO3ꜜ + MgCO3ꜜ + 2H2O 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softeningdemineralization-160831114059/85/Softening-demineralization-4-320.jpg)