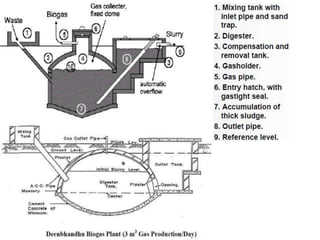
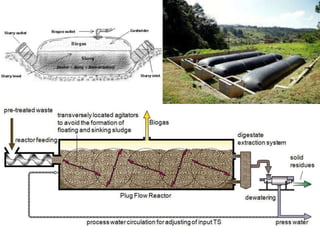
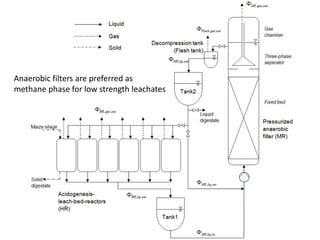
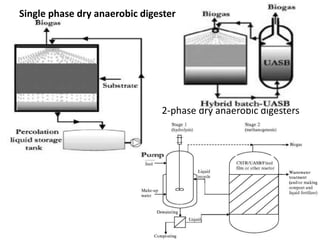
Solid waste bio-methanation plants use anaerobic digestion to stabilize the biodegradable waste fraction and produce biogas. There are two types of digesters: wet digesters which use a liquid slurry system, and dry digesters which process higher consistency waste without water addition. The digestion process involves four stages - hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis - with acid-forming and methane-forming bacteria and archaea working together to break down organic matter into biogas and digestate. Nutrients and optimal temperature and pH levels must be maintained for the microbes to function effectively in the anaerobic treatment process.