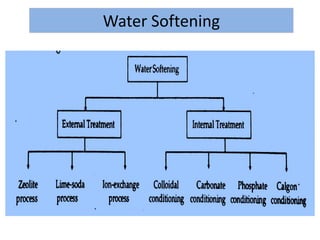
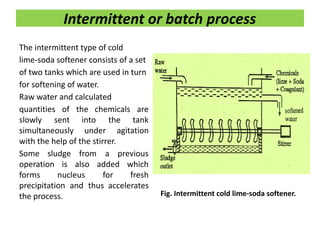
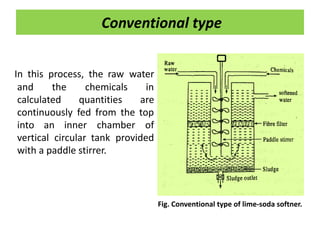
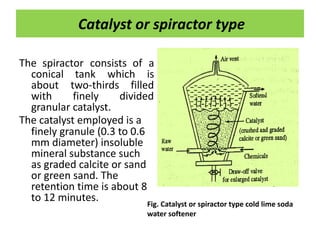
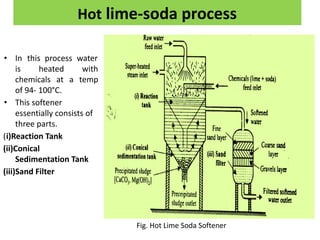
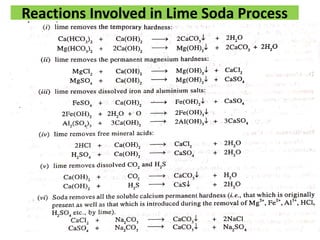
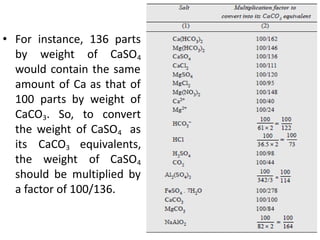
The document discusses different methods of water softening using lime soda processes. There are cold and hot lime soda processes, with the hot process being more efficient. The cold process can use intermittent, conventional, or catalyst types of softeners. The hot process treats water at 94-100 degrees C to accelerate reactions and precipitation, reducing hardness more effectively compared to the cold process. Proper addition of coagulants and calculation of chemical requirements are also discussed.