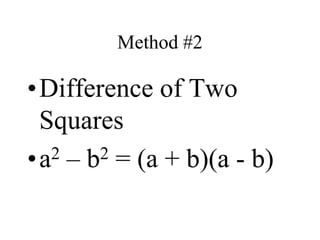
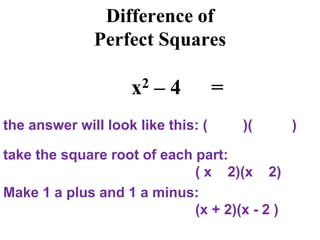
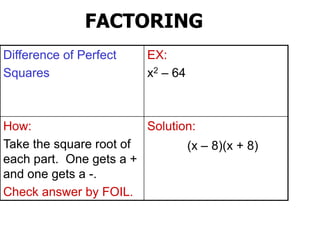
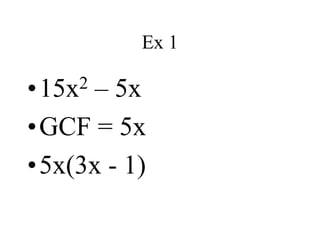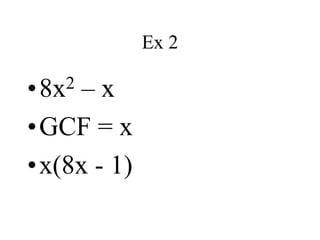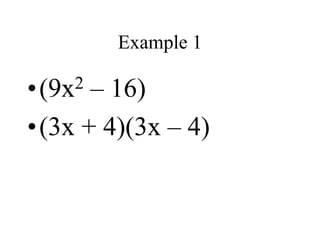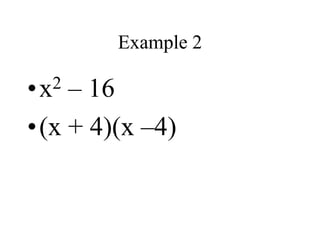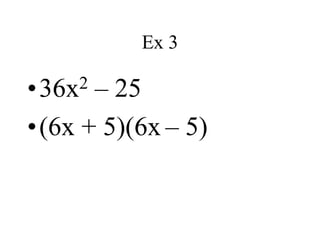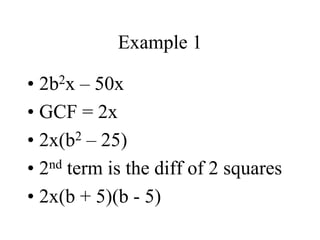This document discusses different factoring methods including the greatest common factor method and difference of two squares method. It provides examples of factoring polynomials using each method and emphasizes that the greatest common factor method should always be tried first before other factoring techniques. Students are given practice problems to factor polynomials using these methods and are reminded that sometimes a combination of factoring approaches is needed.