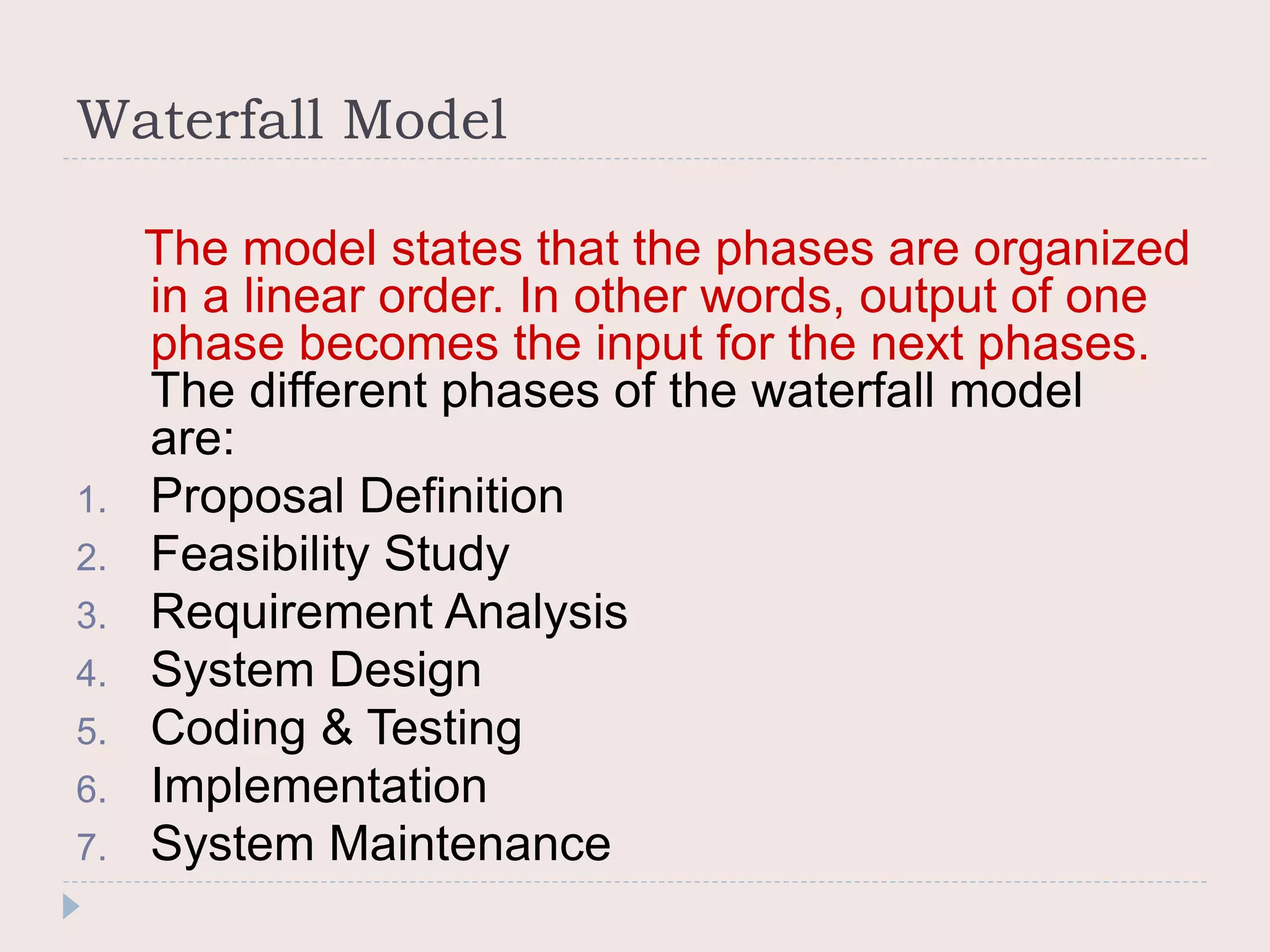
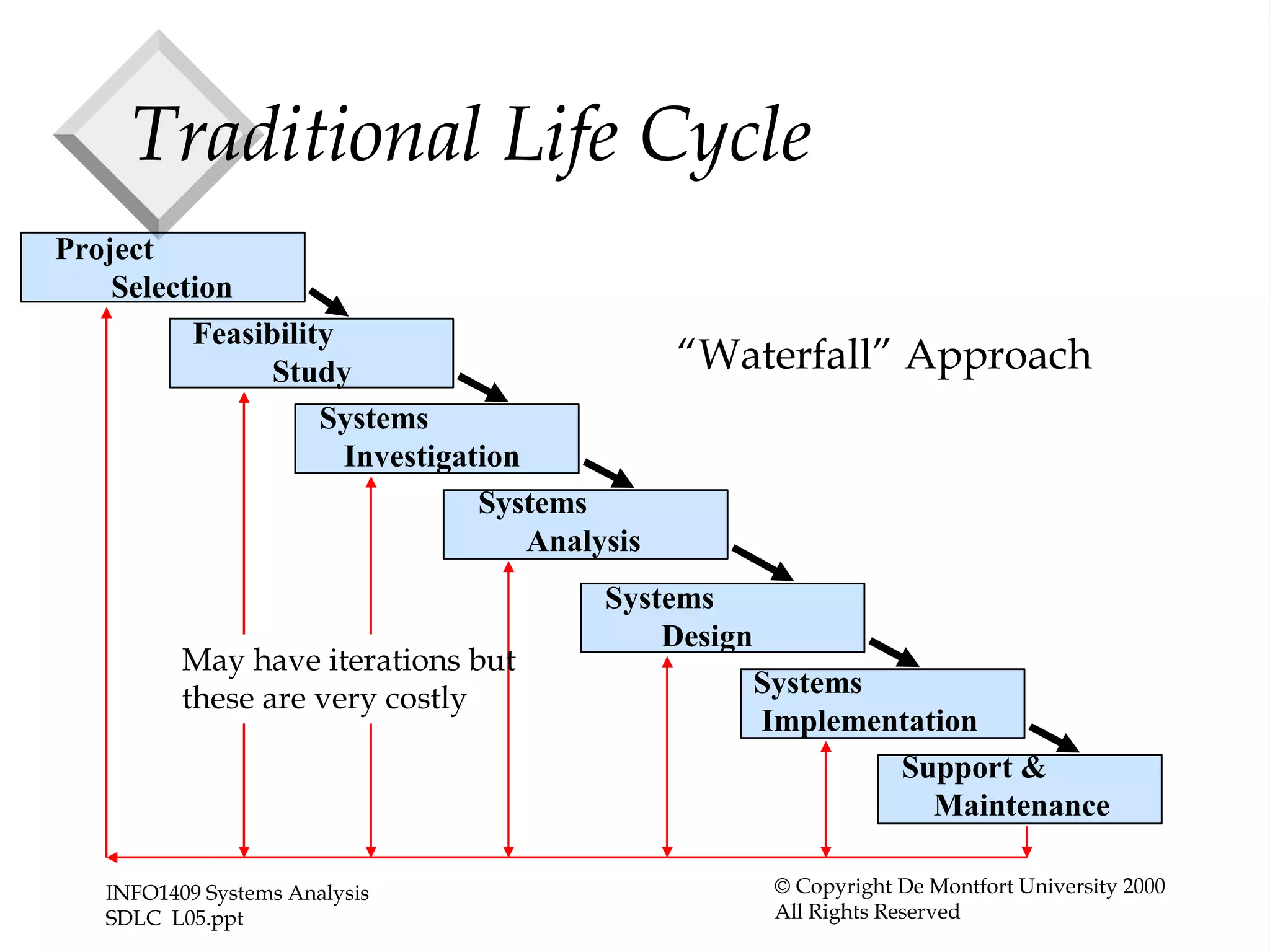
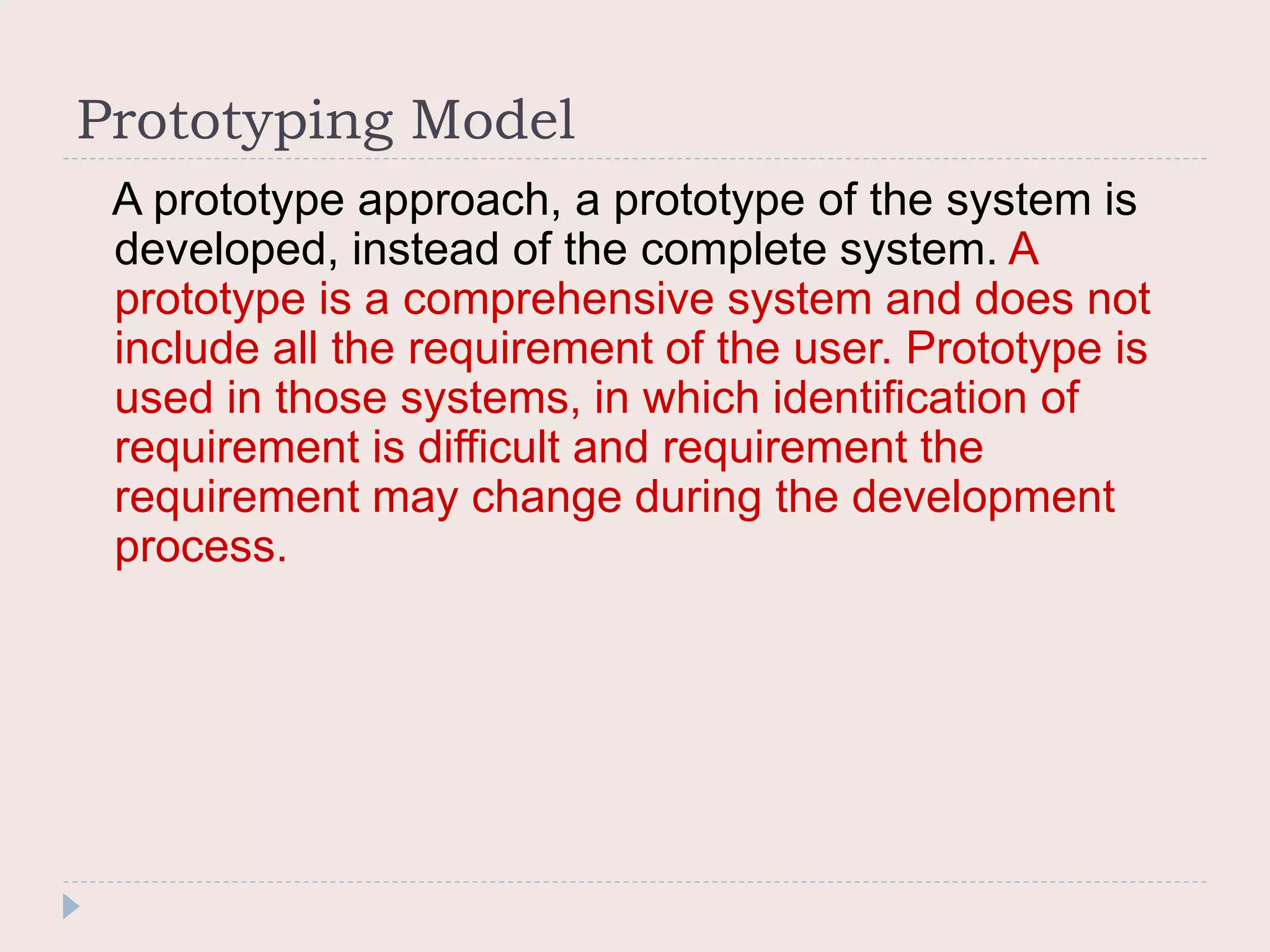
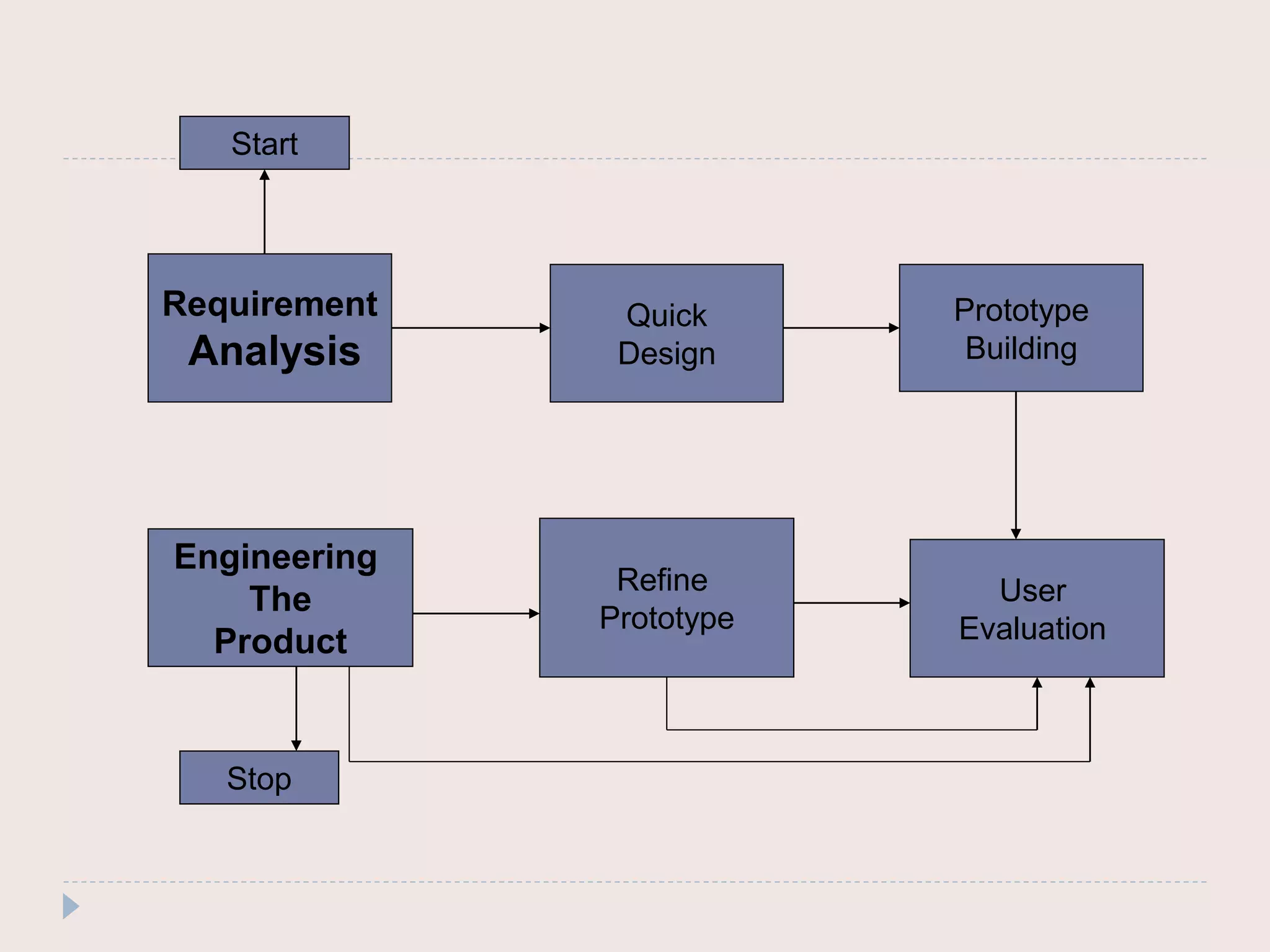
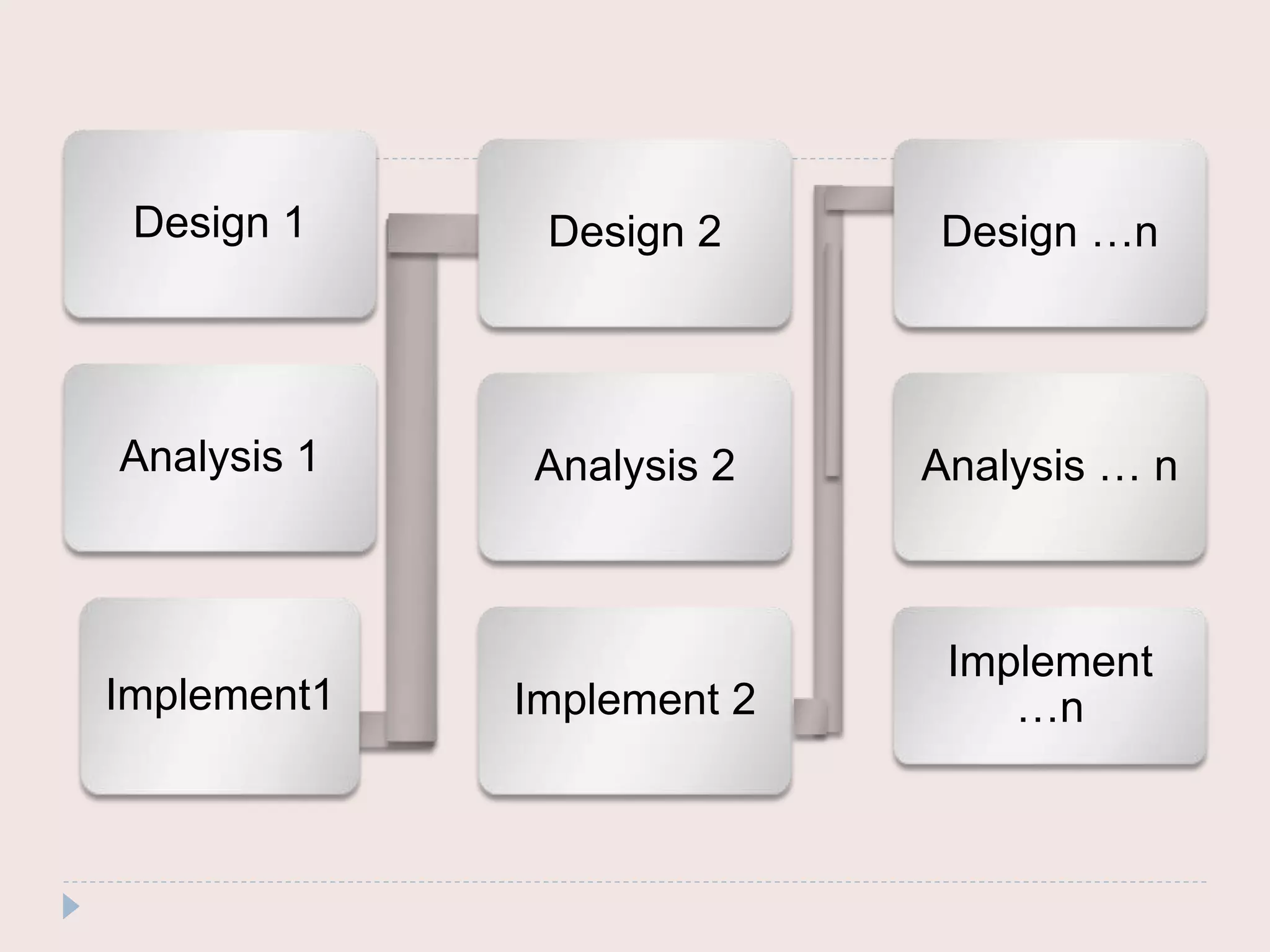
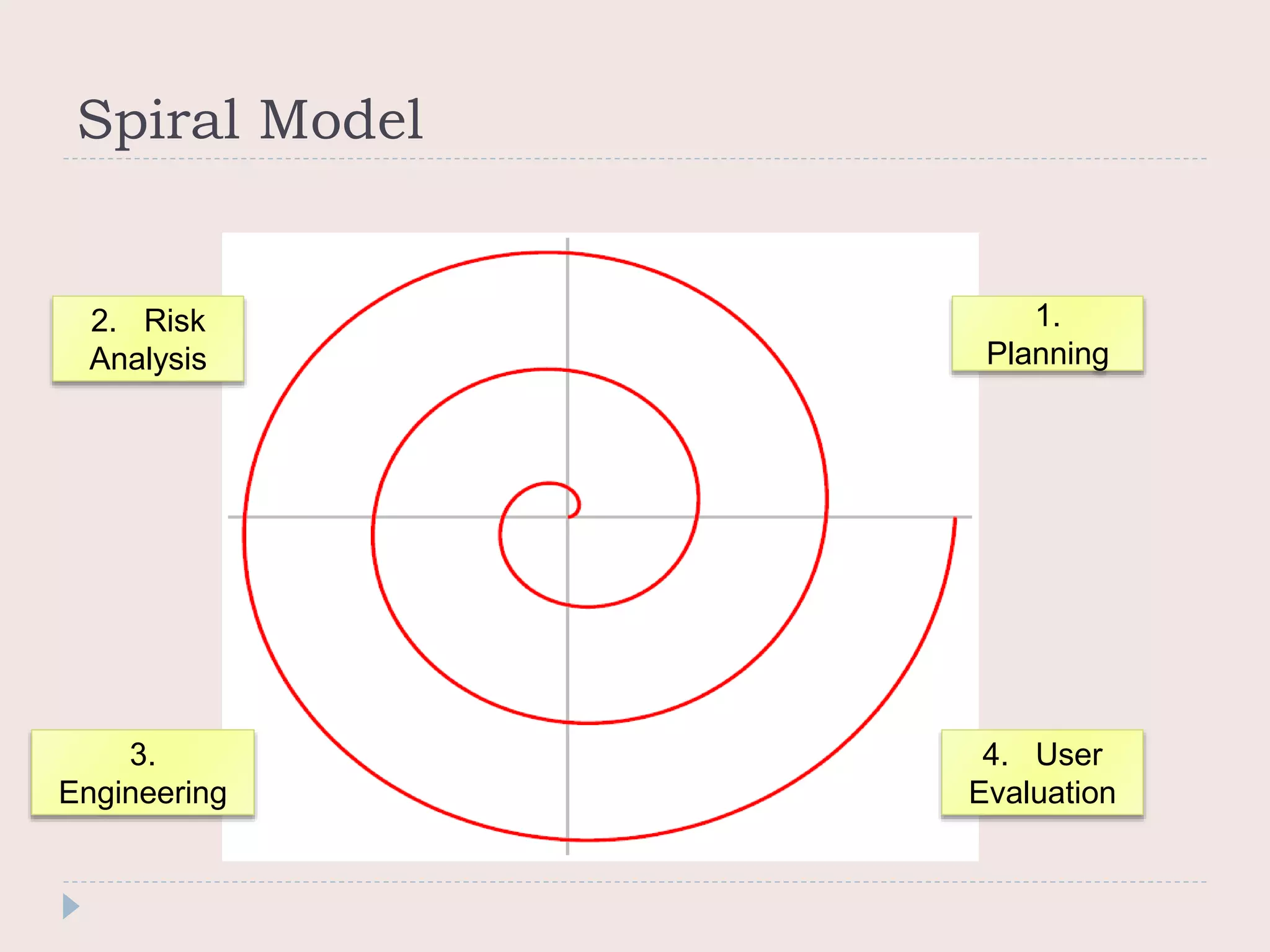
The document discusses four common system development models: the waterfall model, prototyping model, iterative enhancement model, and spiral model. The waterfall model is a linear model that progresses through phases from requirements to maintenance. Prototyping involves building prototypes to help define requirements. The iterative model develops the system incrementally in cycles. The spiral model progresses through risk analysis, engineering, and evaluation cycles in a cyclic fashion.