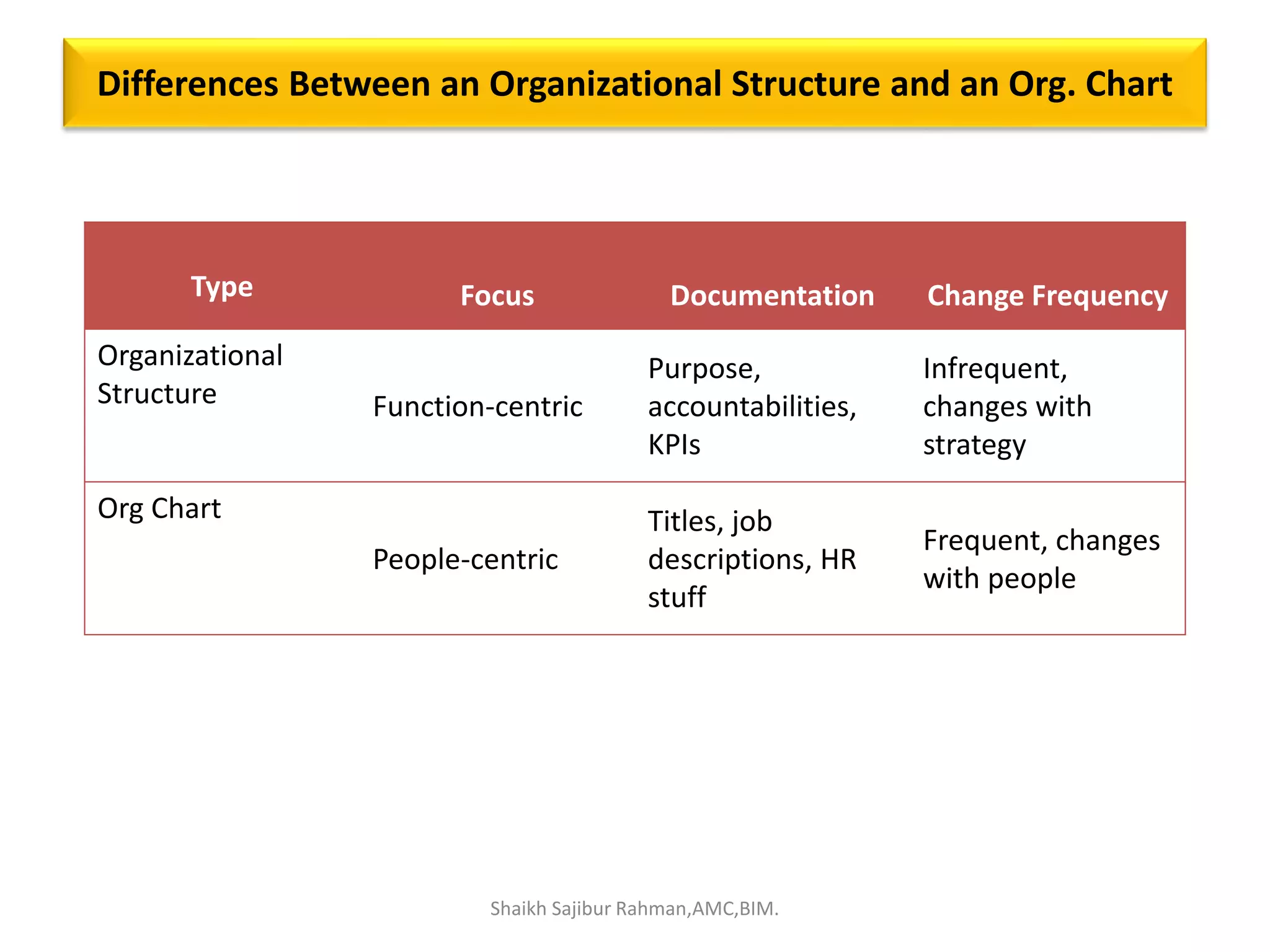
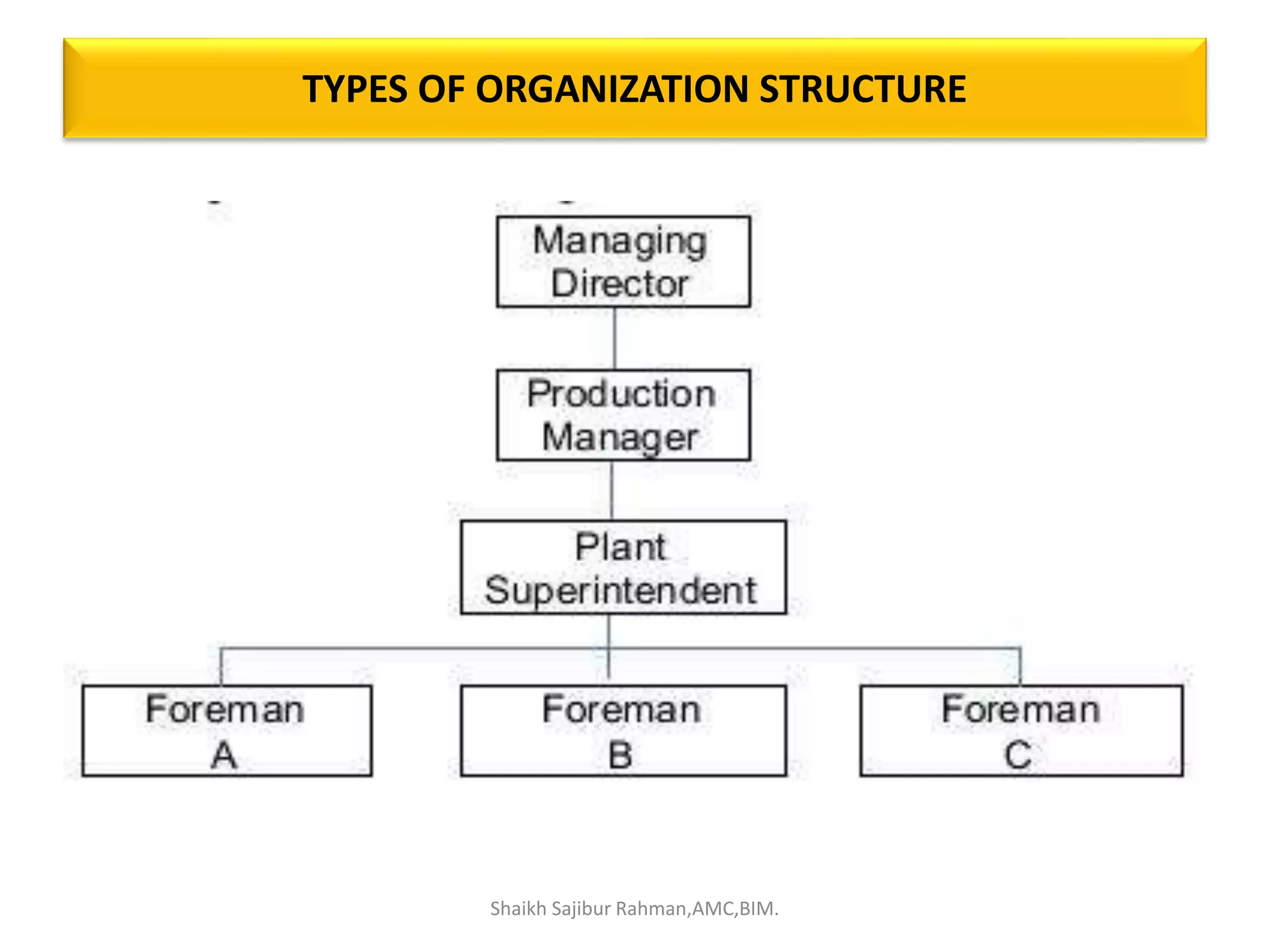
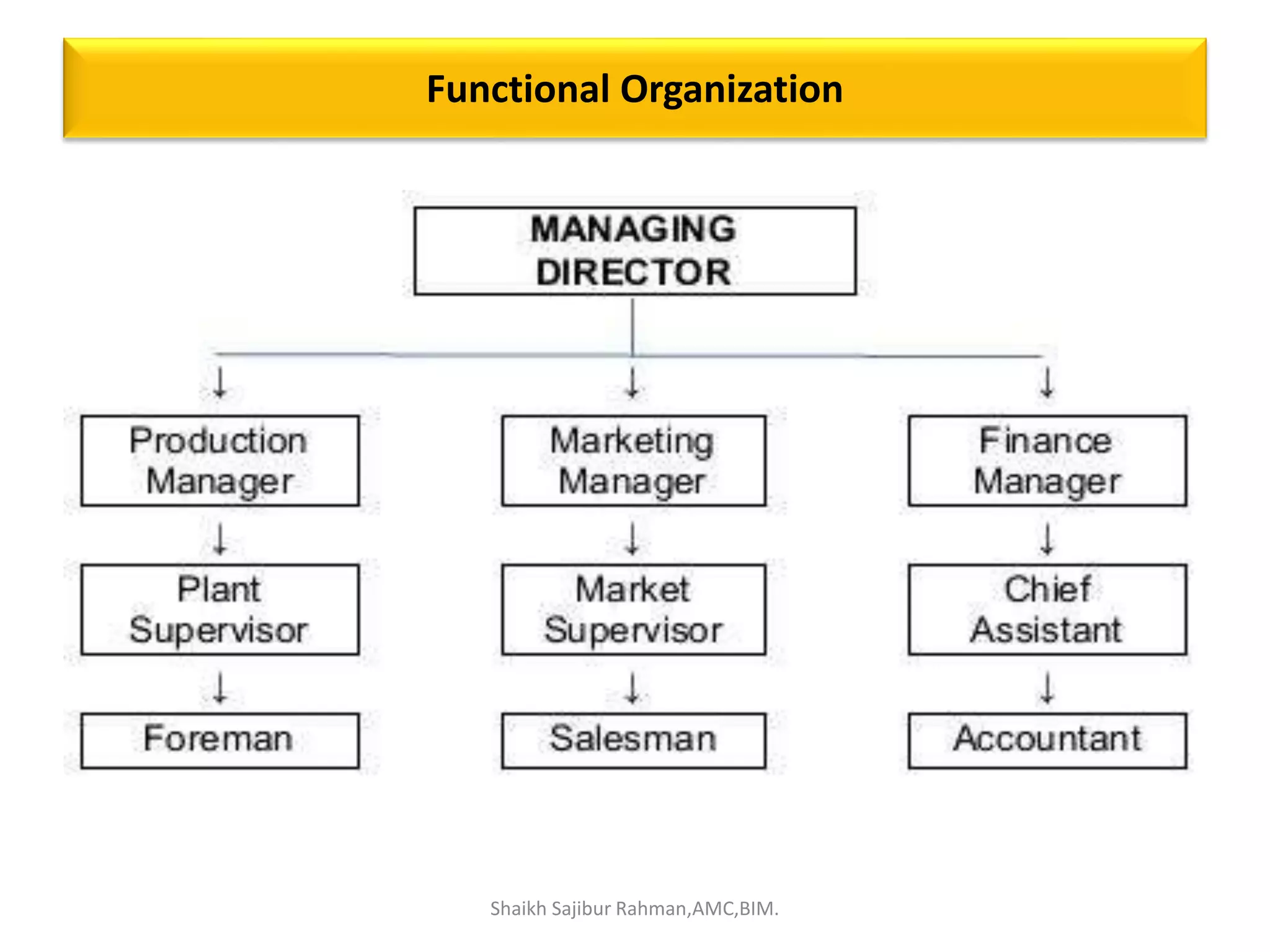
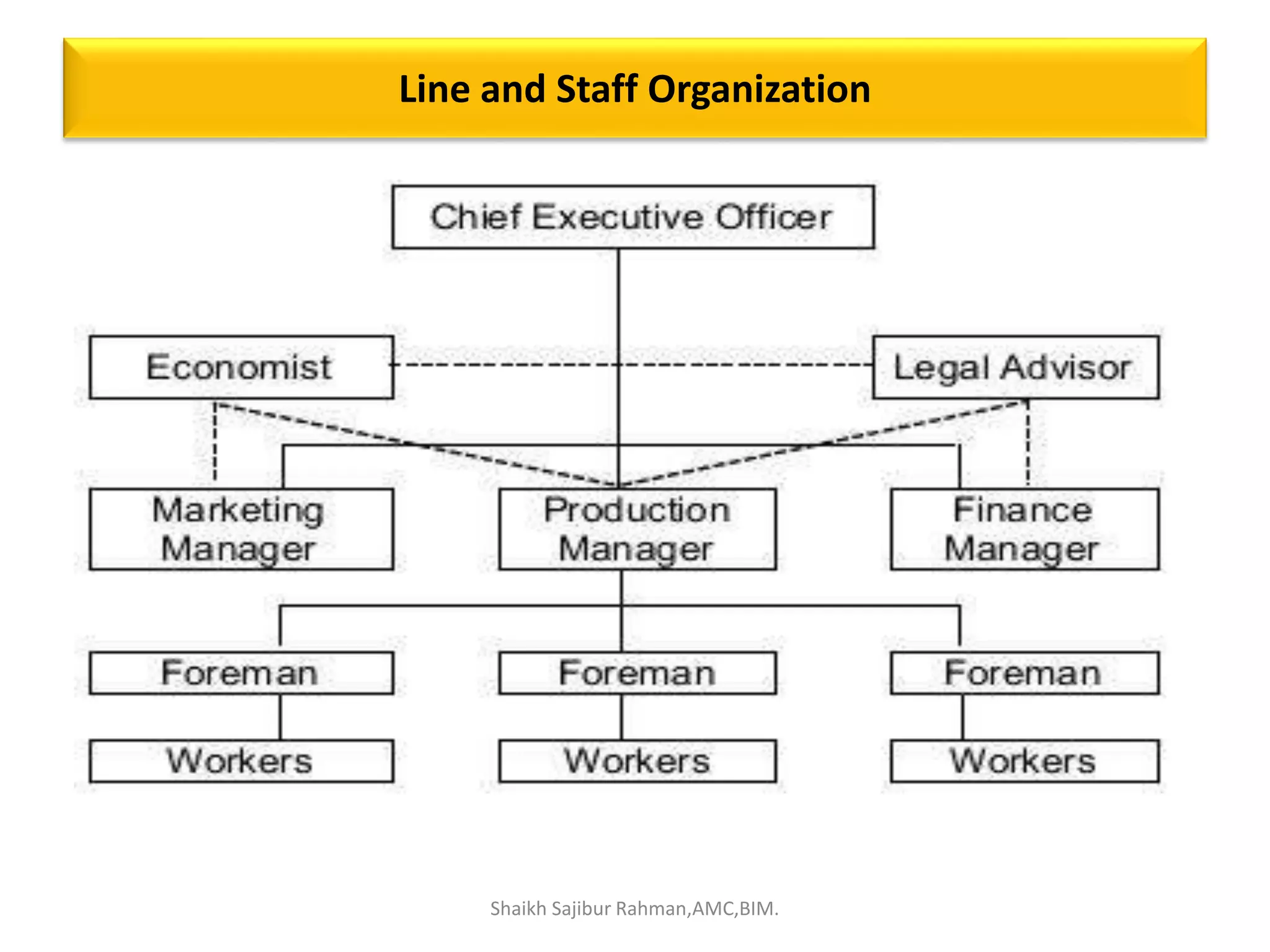
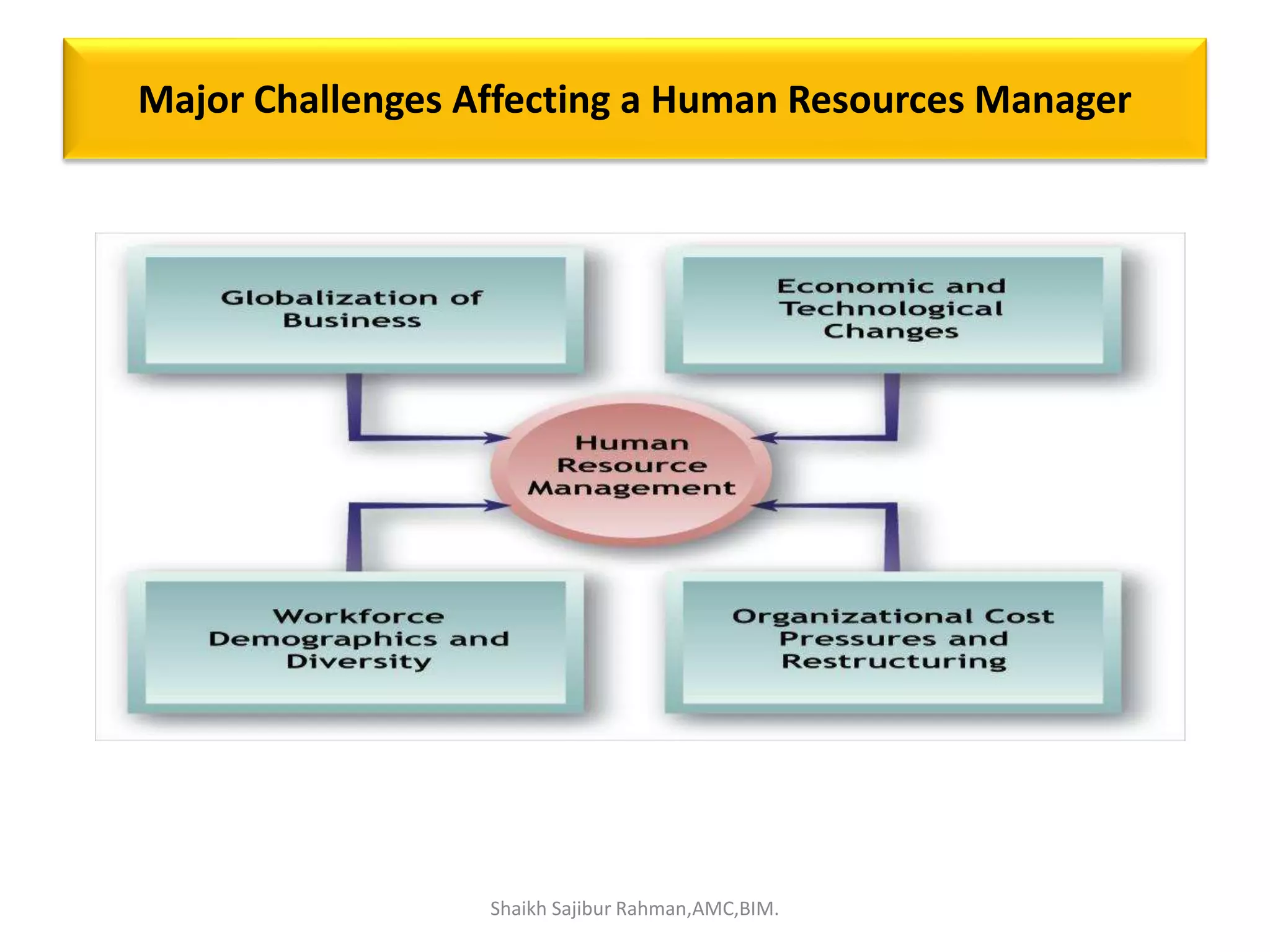
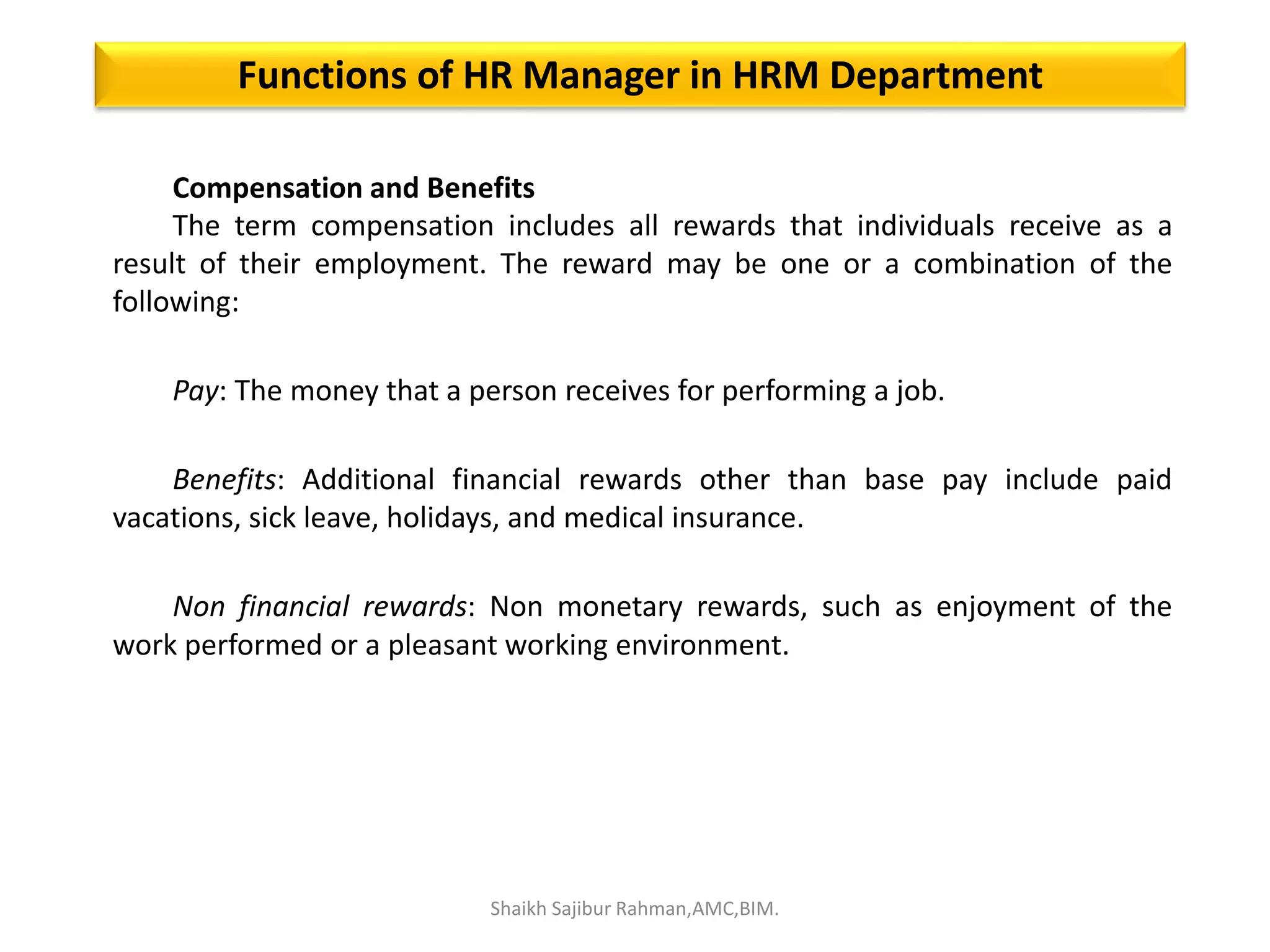
The document outlines the roles and responsibilities associated with authority in human resource management, emphasizing the distinction between line and staff authority, as well as the importance of organizational structure. It discusses various functions of HR managers, including recruitment, training, employee relations, and addressing safety, health, and compensation. Additionally, it highlights the collaborative nature of HR functions and the need for HR professionals to adapt to changing organizational demands.