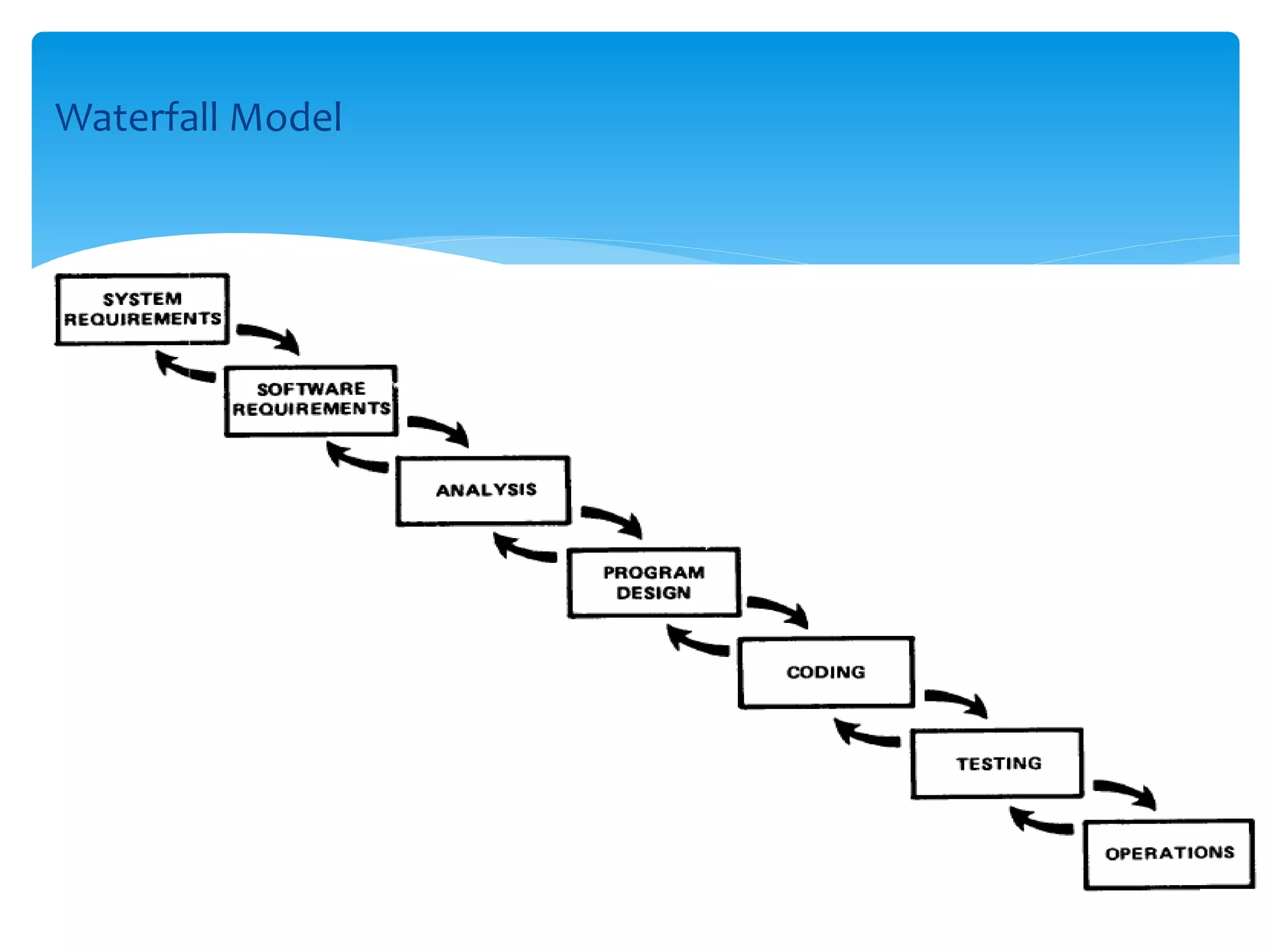
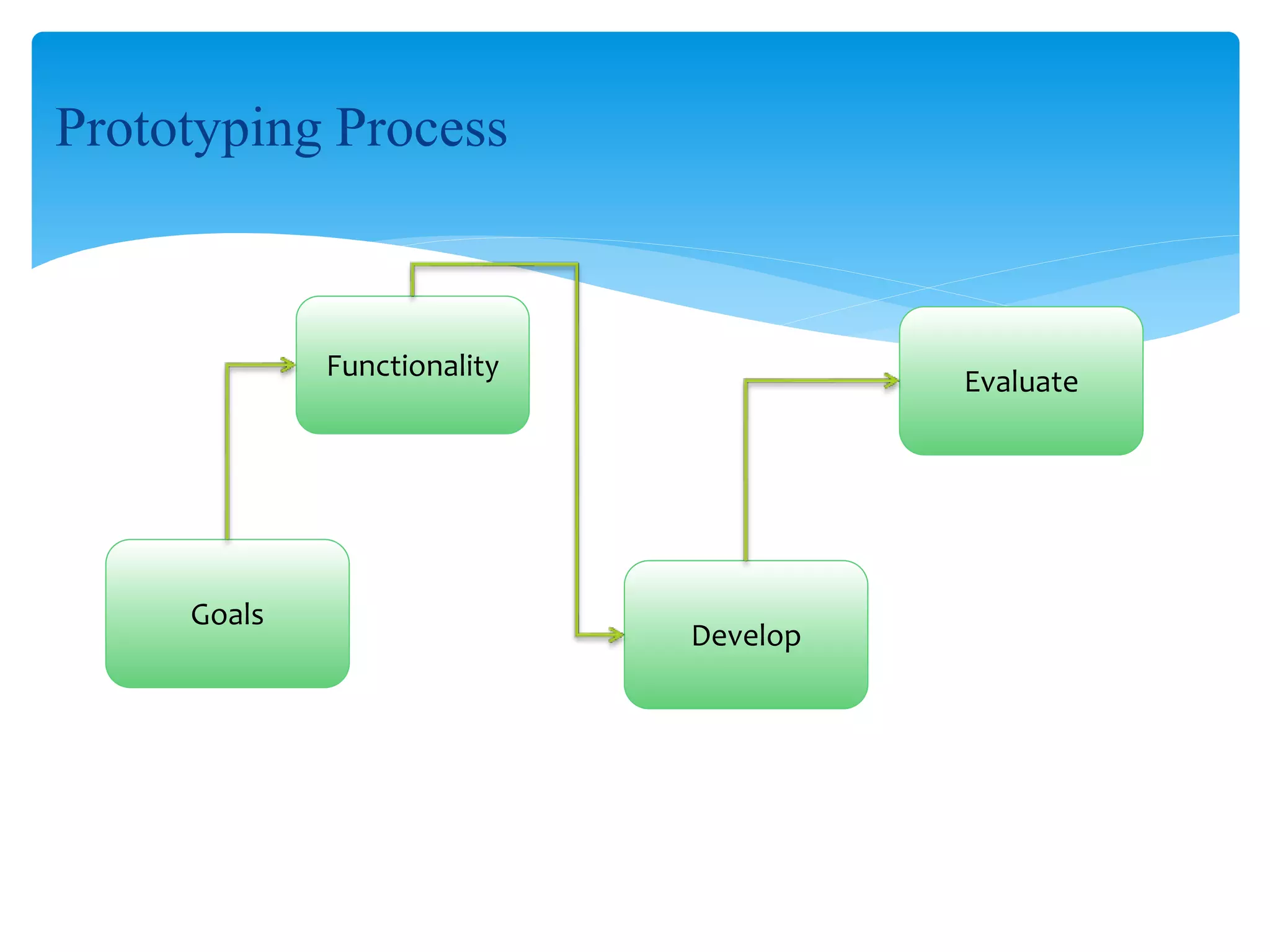
The document discusses several software process models including the waterfall model, evolutionary development, formal transformation, and reuse-based development. It then provides more details on the waterfall model and prototyping model. The waterfall model separates development into distinct phases like requirements, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. The prototyping model emphasizes early prototypes for feedback. The document also discusses the spiral model which combines prototyping and waterfall elements and is used for large, complex projects.