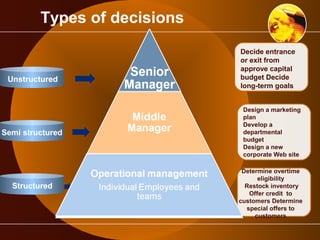
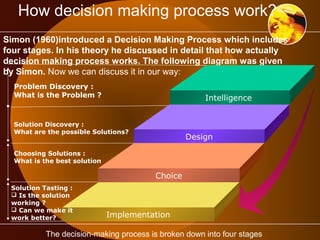
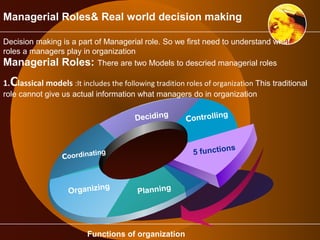
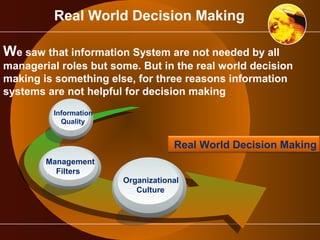
The document outlines the role of management information systems in decision-making processes at various organizational levels. It categorizes decisions into unstructured, semi-structured, and structured types, detailing the specific information systems utilized for each level and decision type. Additionally, it discusses the stages of the decision-making process, emphasizing the importance of intelligence, design, choice, and implementation.