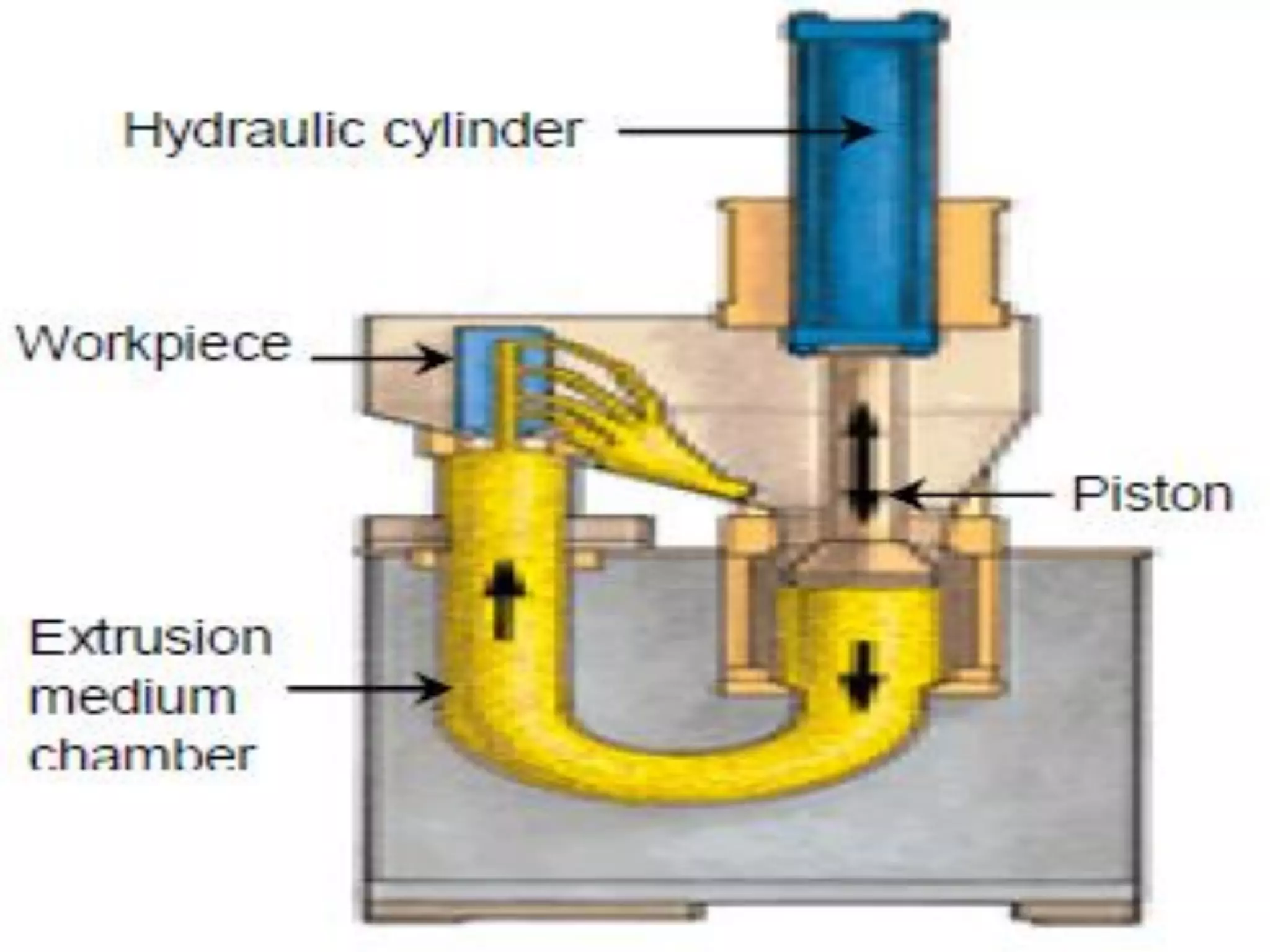
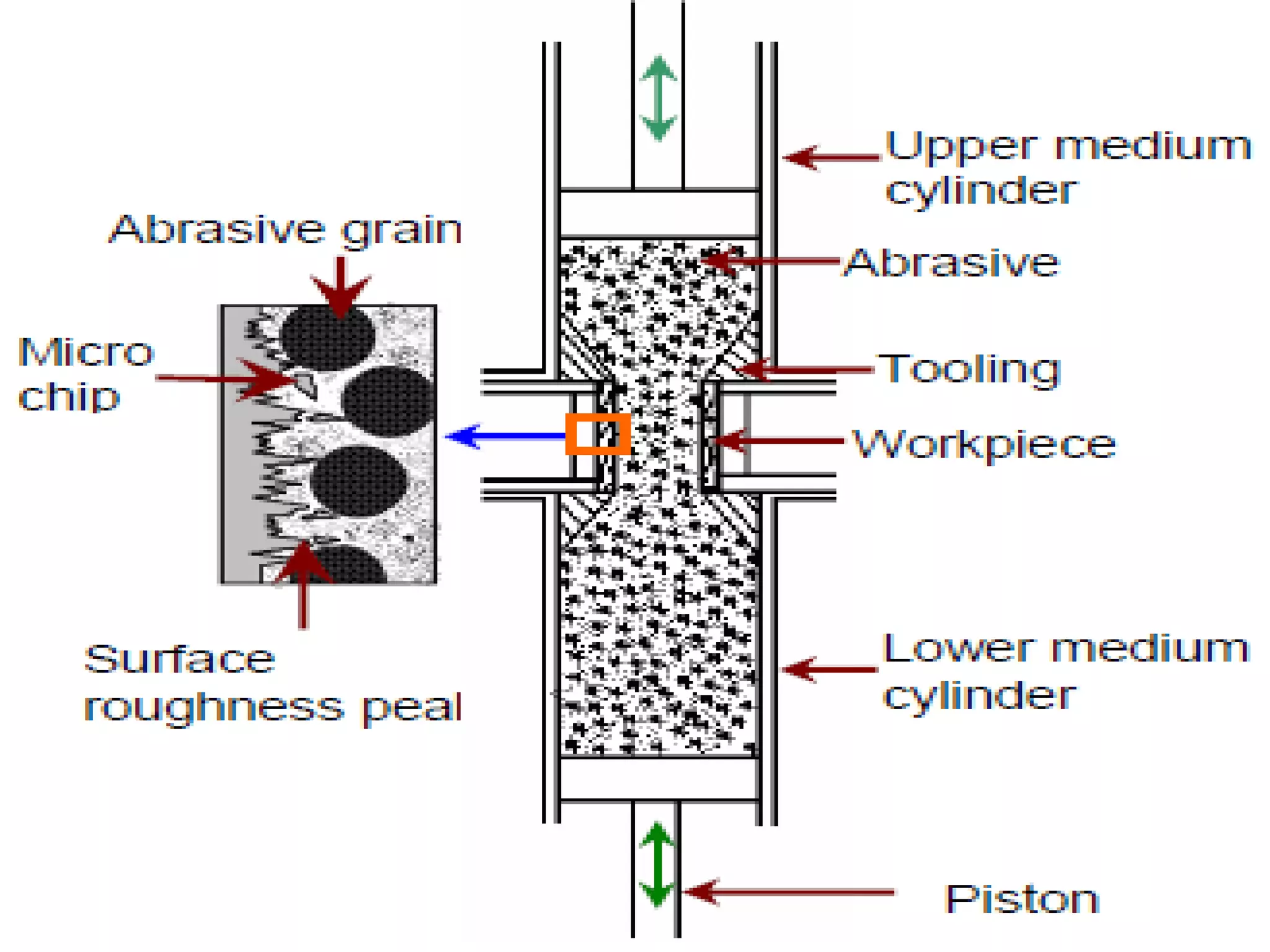
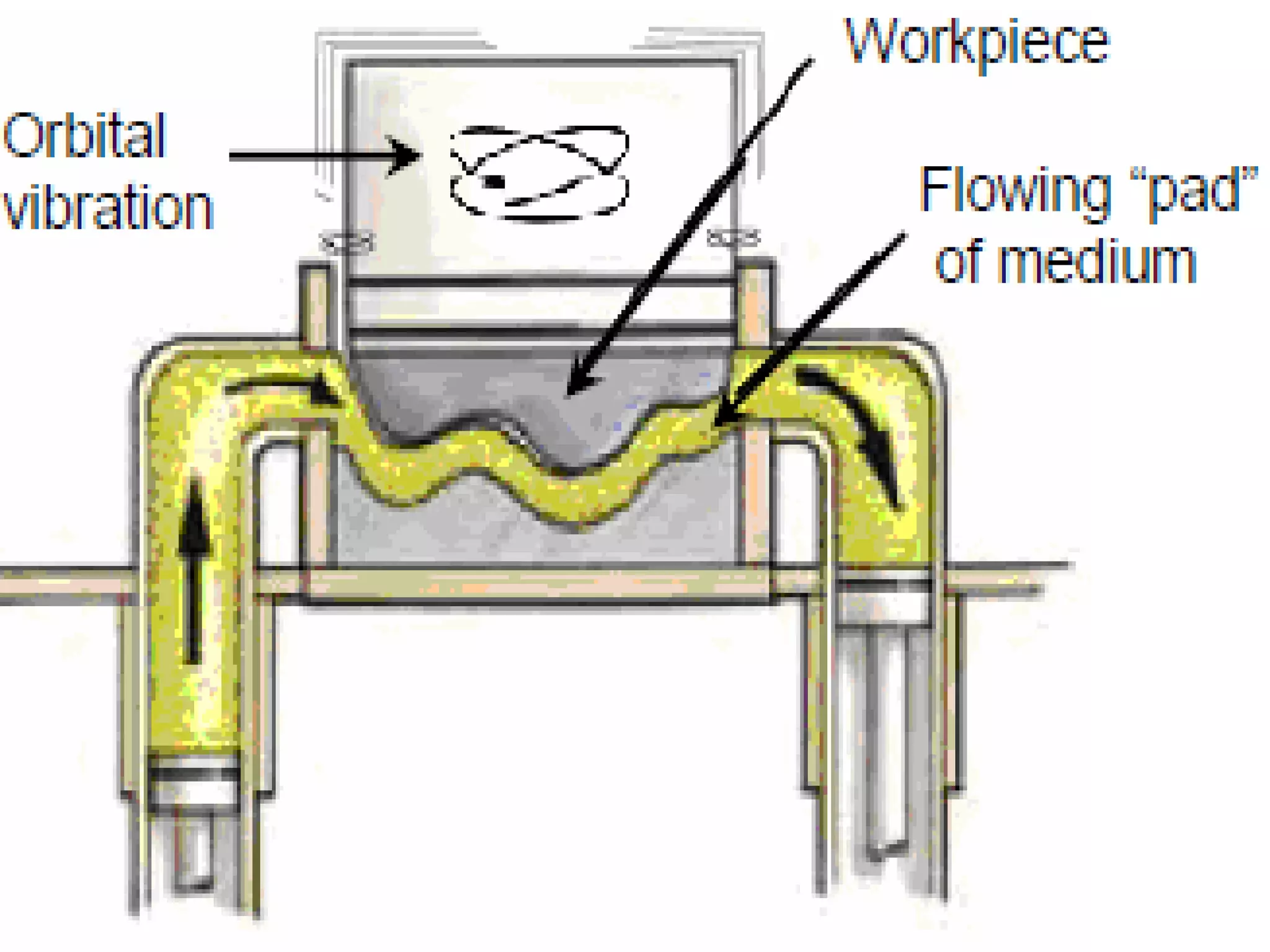
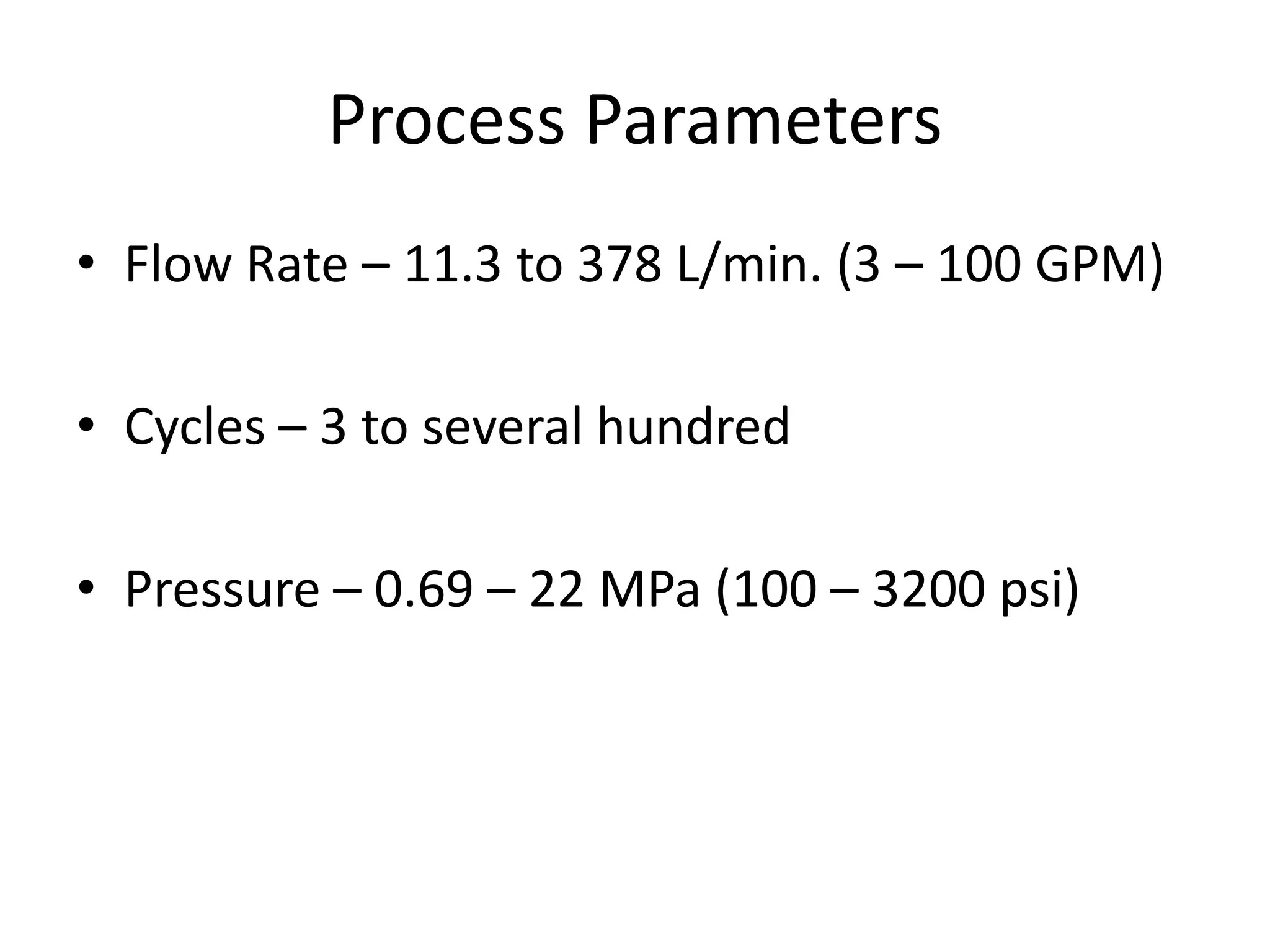
Abrasive flow machining is a finishing process that uses a semi-solid abrasive putty to remove small amounts of material from workpieces. The putty is forced through or across the workpiece using hydraulic pressure to deburr, radius, polish and perform other surface finishing operations. It is well suited for finishing metals, ceramics and plastics in a uniform and economical manner, though it is not used for heavy material removal due to its low material removal rate. The process involves selecting abrasive media based on the material and desired finish, and using tooling and pressure to direct the flow of media through restrictions in the workpiece.