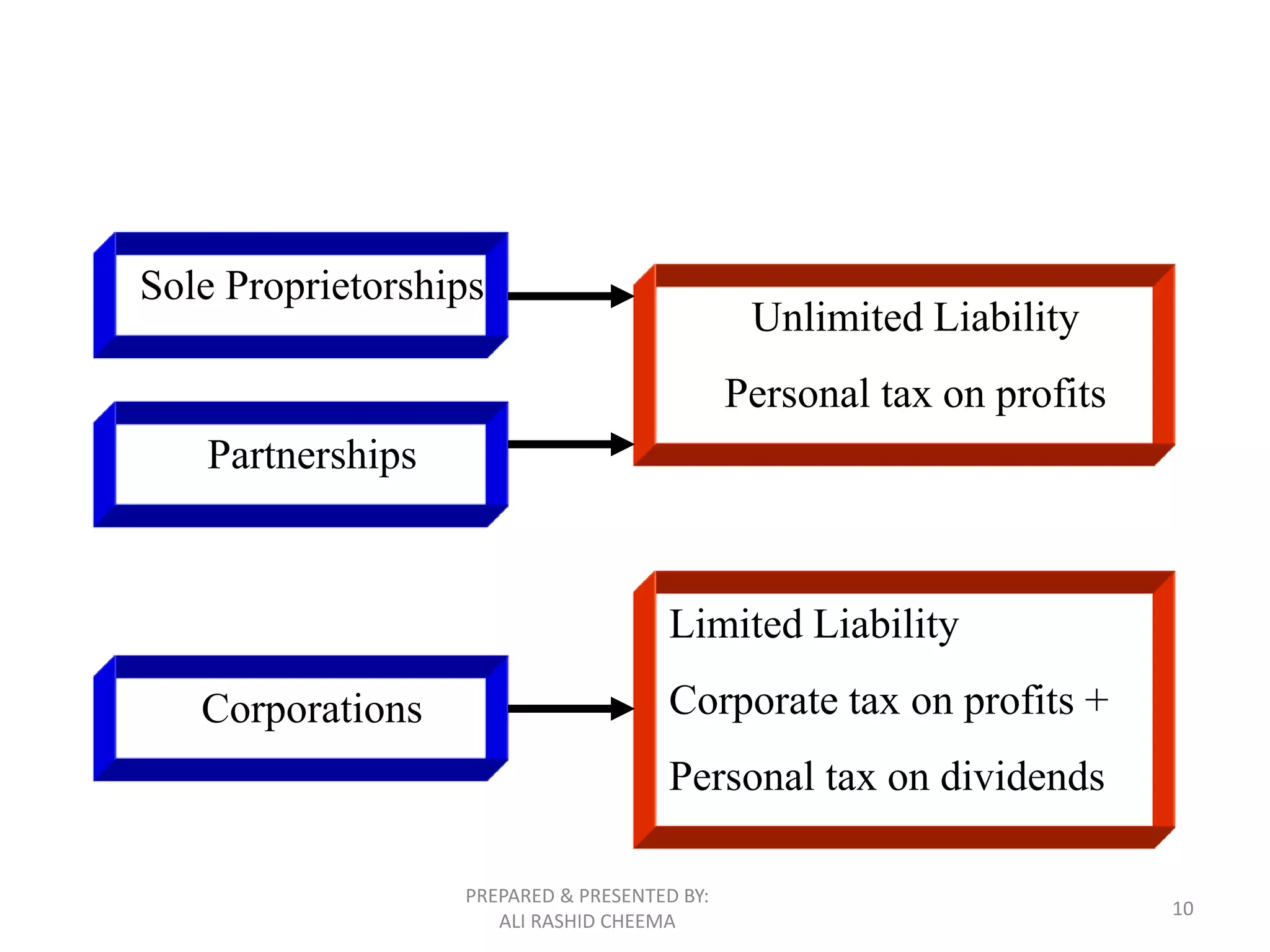
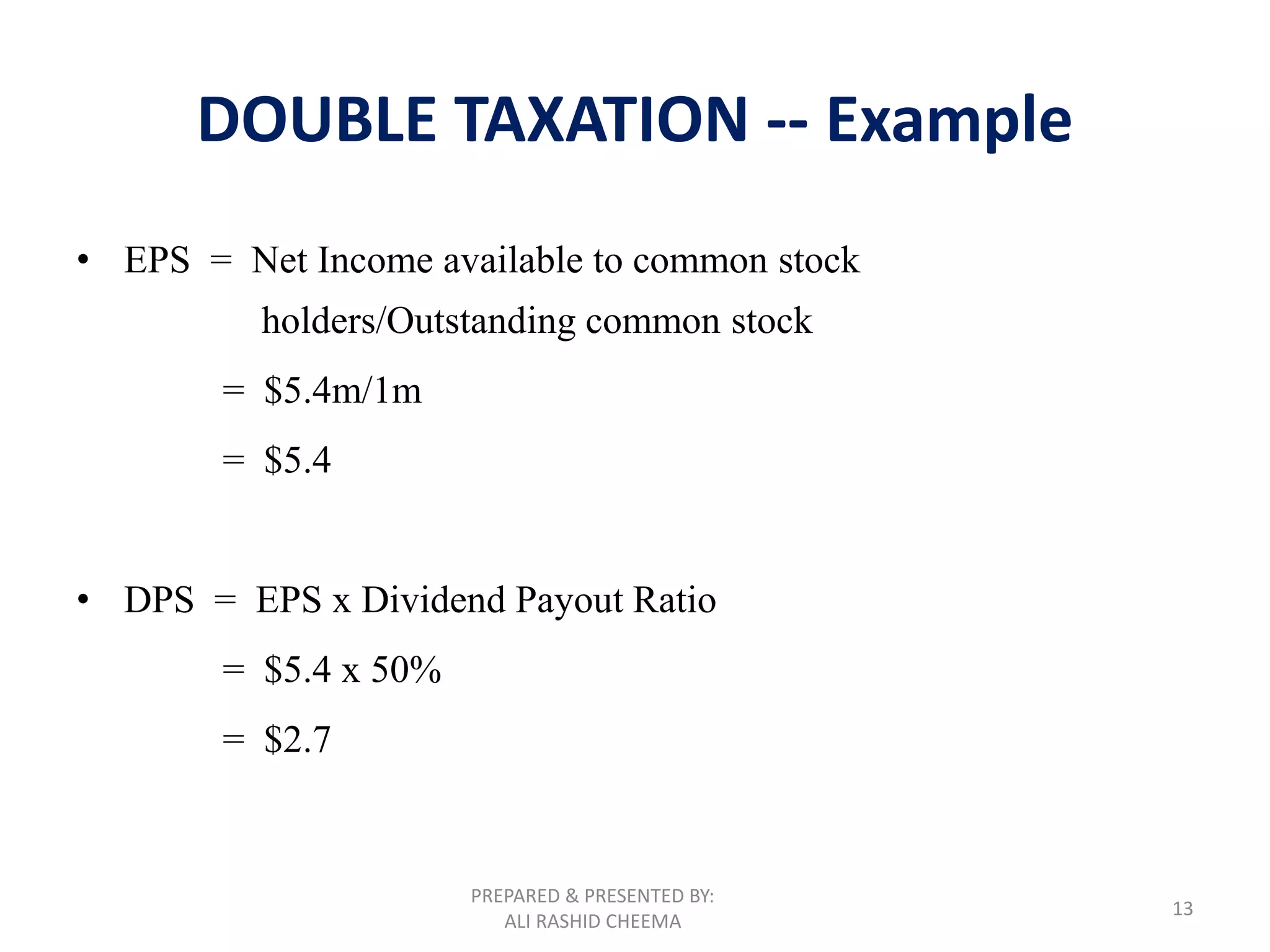
This document discusses different forms of business organizations including sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. Sole proprietorships are owned by one person, partnerships are owned by two or more people, and corporations are separate legal entities with transferable shares of stock. The document outlines advantages and disadvantages of each structure and provides an example of double taxation that can occur with corporations.