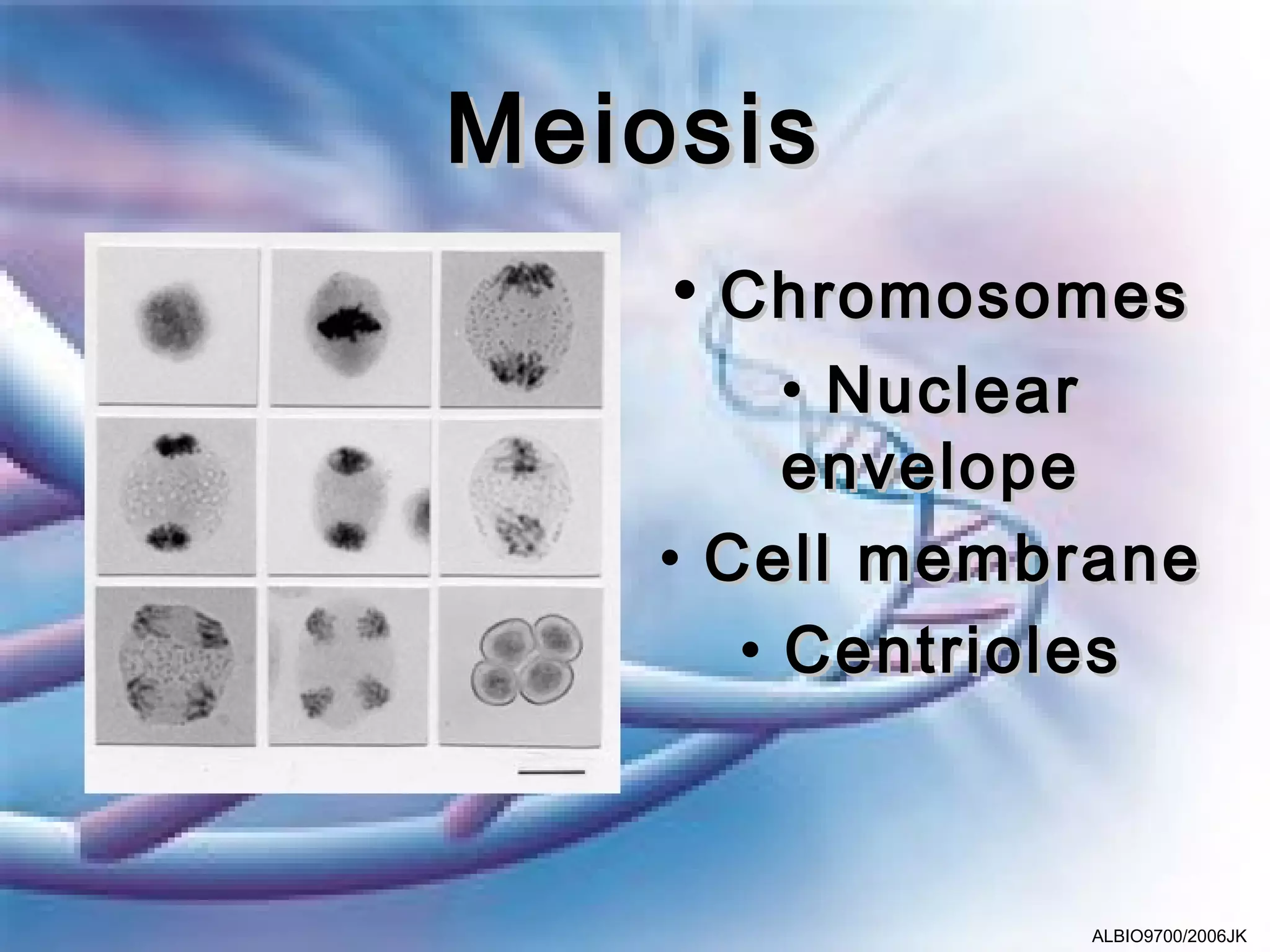
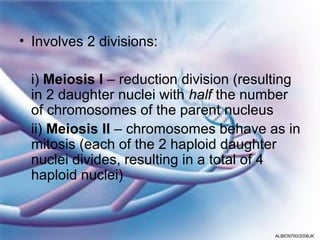
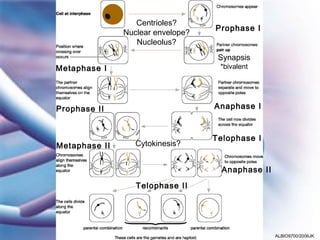
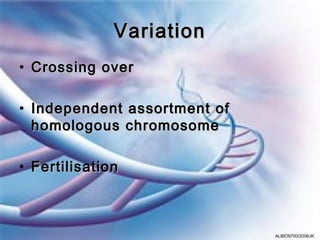
Meiosis involves two cell divisions that result in four haploid cells from one diploid cell. Meiosis I is the reduction division where homologous chromosomes separate and half the number of chromosomes are in each daughter cell. Meiosis II is similar to mitosis, where each daughter cell from Meiosis I divides to produce a total of four haploid cells that can fuse during fertilization. Crossing over and independent assortment of homologous chromosomes during Meiosis I introduces genetic variation.