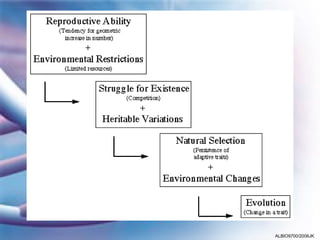
This document discusses key concepts of natural selection and evolution, including that organisms overproduce offspring but population sizes remain stable, indicating competition for survival. There is genetic variation within species on which natural selection acts, favoring traits that increase reproductive success. Examples are provided of natural selection in finches and moths. Selection changes allele frequencies over generations, driving evolutionary change.