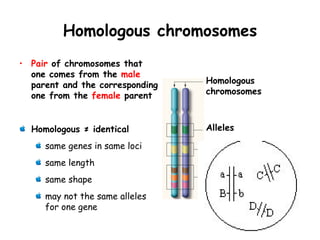
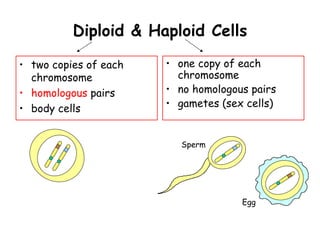
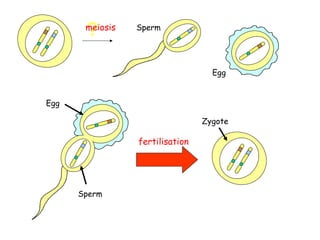
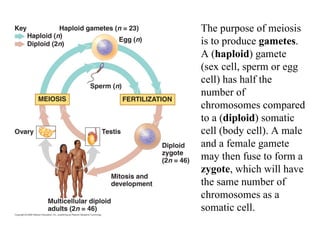
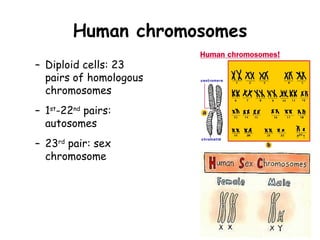
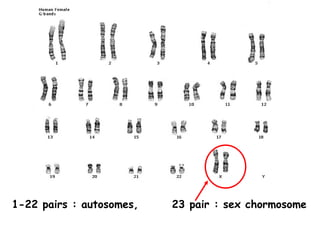
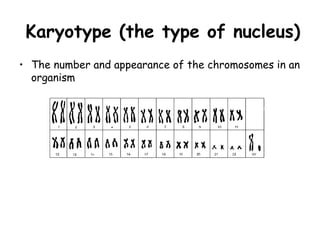
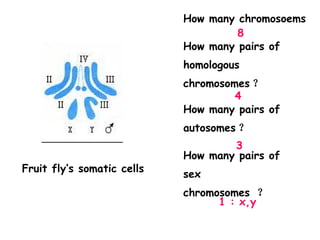
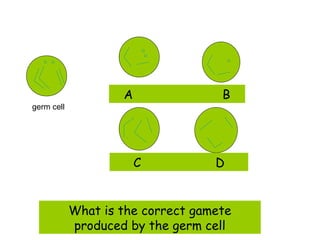
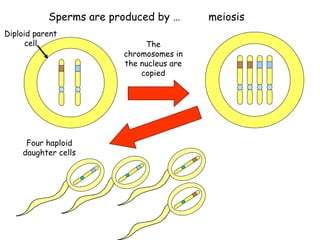
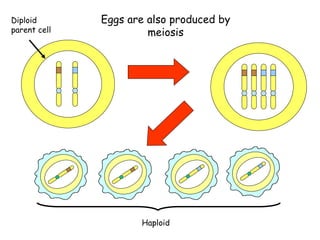
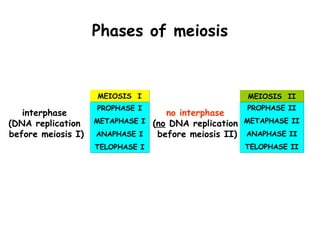
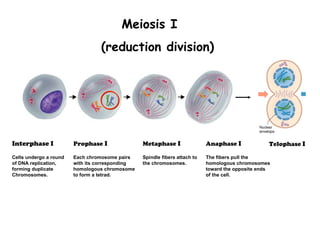
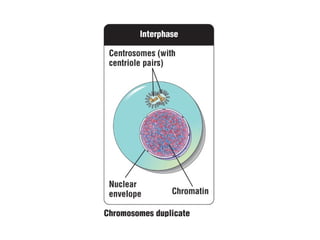
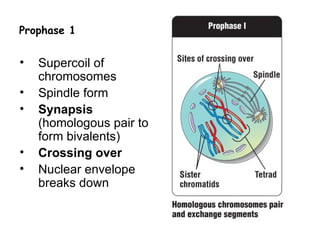
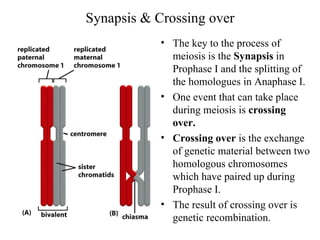
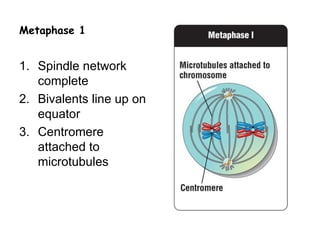
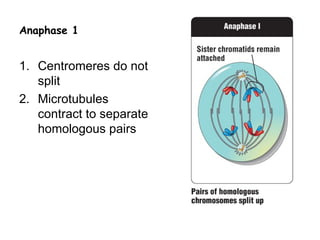
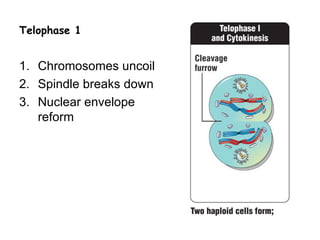
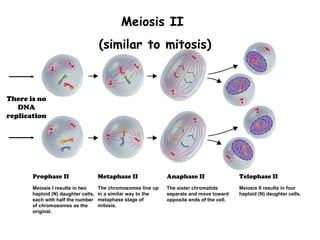
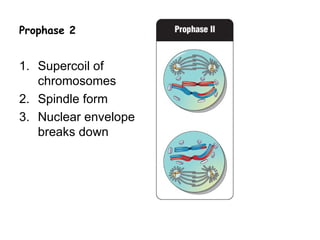
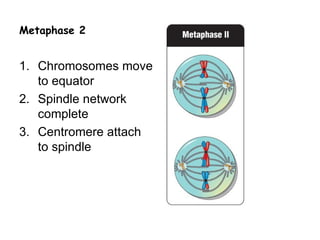
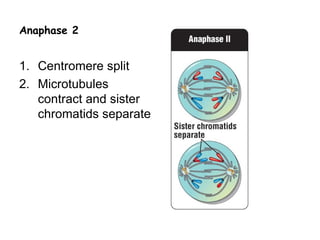
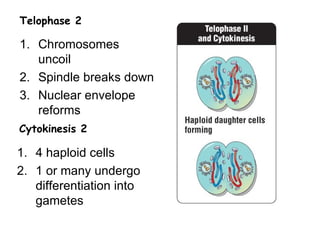
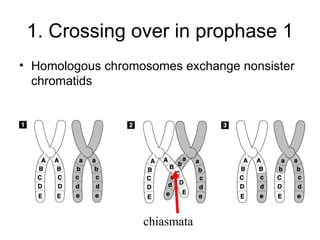
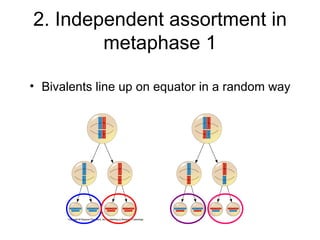
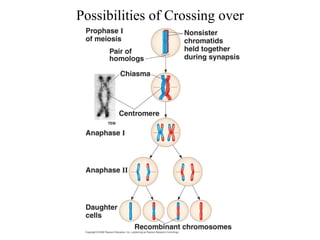
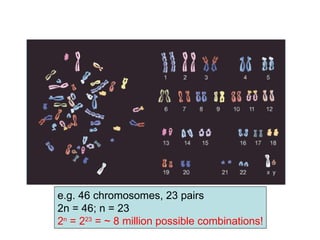
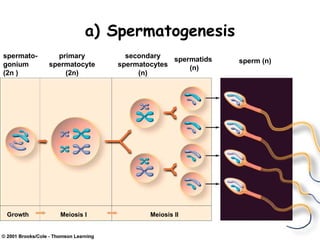
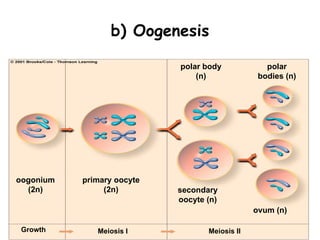
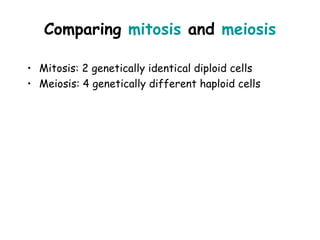
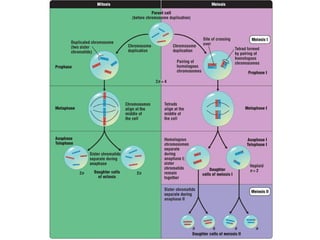
Meiosis produces gametes through two rounds of cell division beginning with one diploid cell and ending with four haploid cells. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair and separate, reducing the chromosome number by half. Meiosis II separates sister chromatids, further dividing the cell and its genetic material. The steps of crossing over and independent assortment in meiosis I contribute to genetic variation among gametes and offspring.