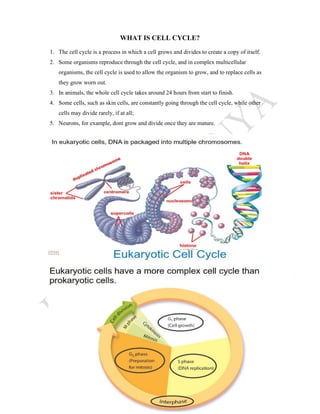
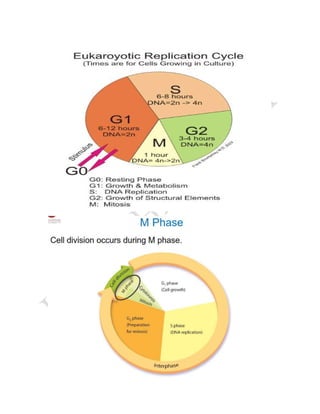
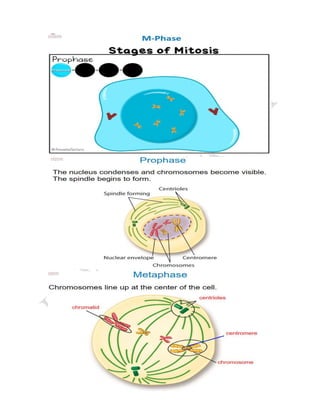
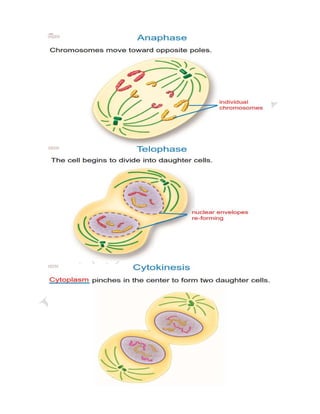
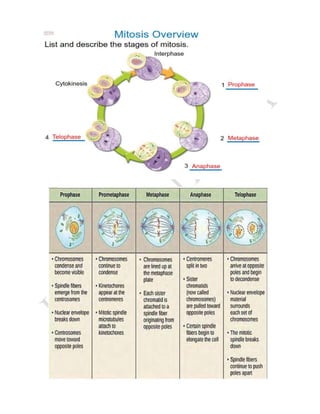
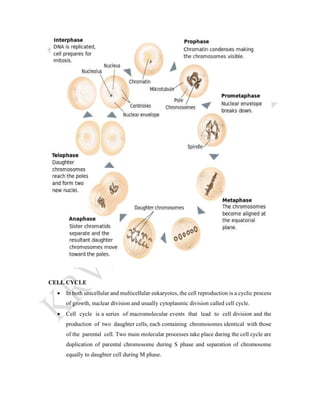
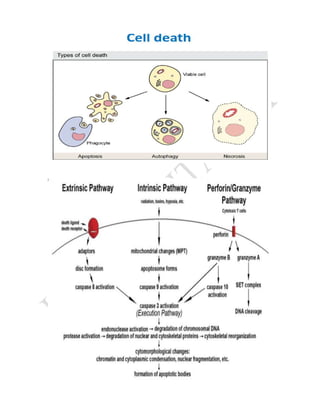
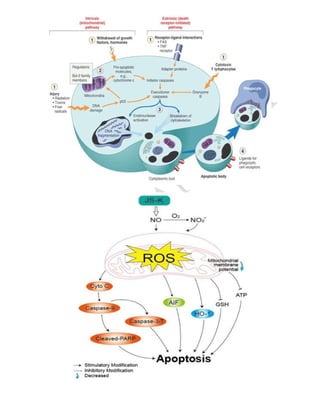
The cell cycle is the process by which a cell grows and divides into two daughter cells. It consists of four main phases - G1 phase (cell growth), S phase (DNA replication), G2 phase (more cell growth), and M phase (mitosis and cytokinesis). In M phase, the cell divides into two identical daughter cells each with the same number and type of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The cell cycle allows for cell growth, replication, and replacement of old or damaged cells.