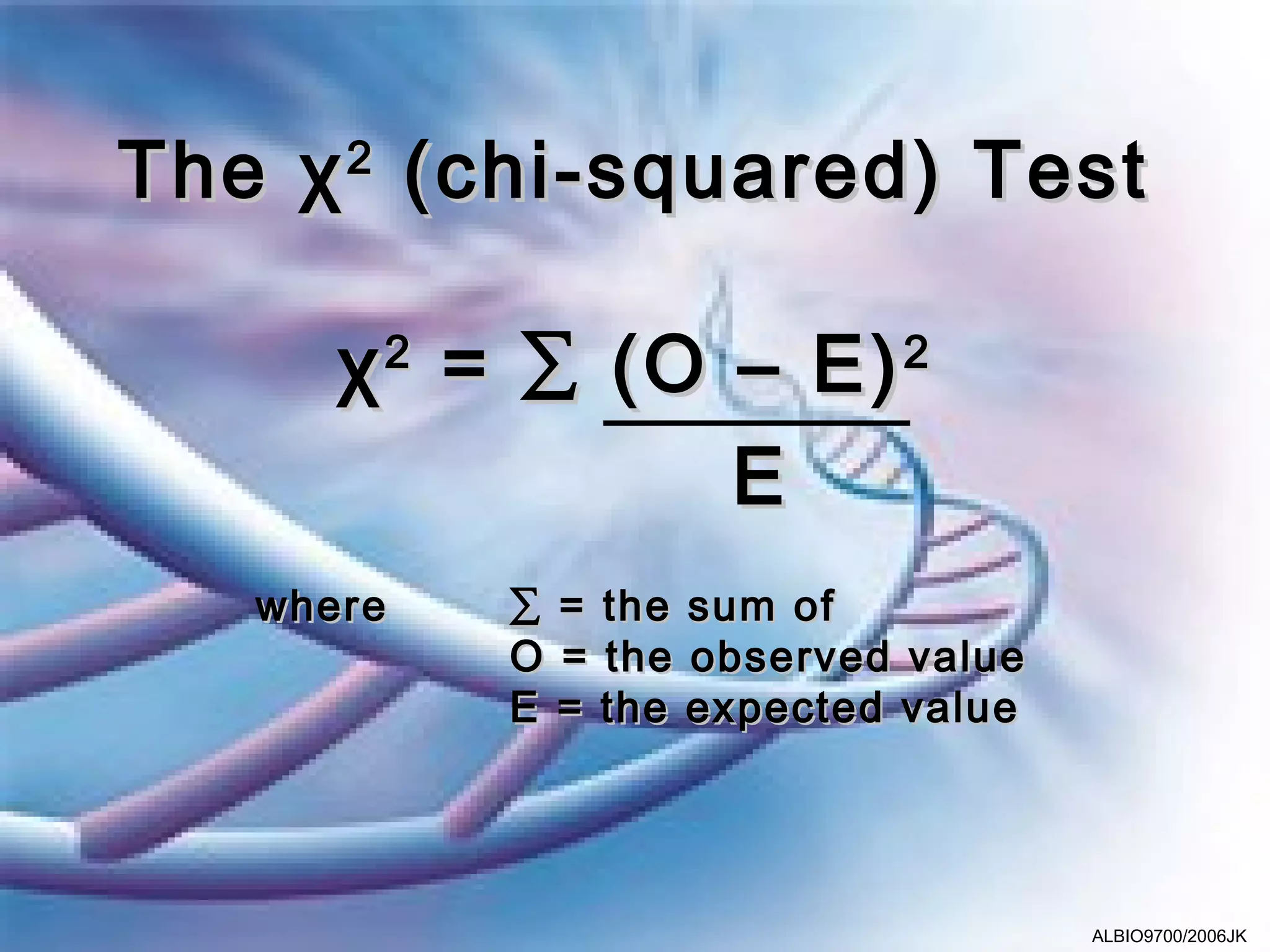
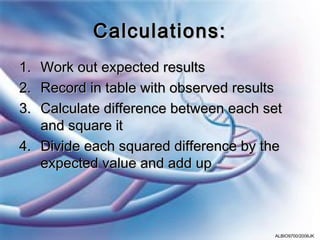
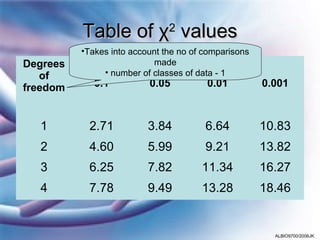
The chi-squared (χ2) test allows researchers to compare observed results to expected results and determine if any differences are statistically significant. The χ2 value is calculated by summing the squared differences between observed and expected values, divided by the expected value. Higher χ2 values indicate a lower probability that the differences are due to chance, as determined by comparing the χ2 value to a table of critical values. An example problem demonstrates using a χ2 test to analyze the results of a genetic cross.