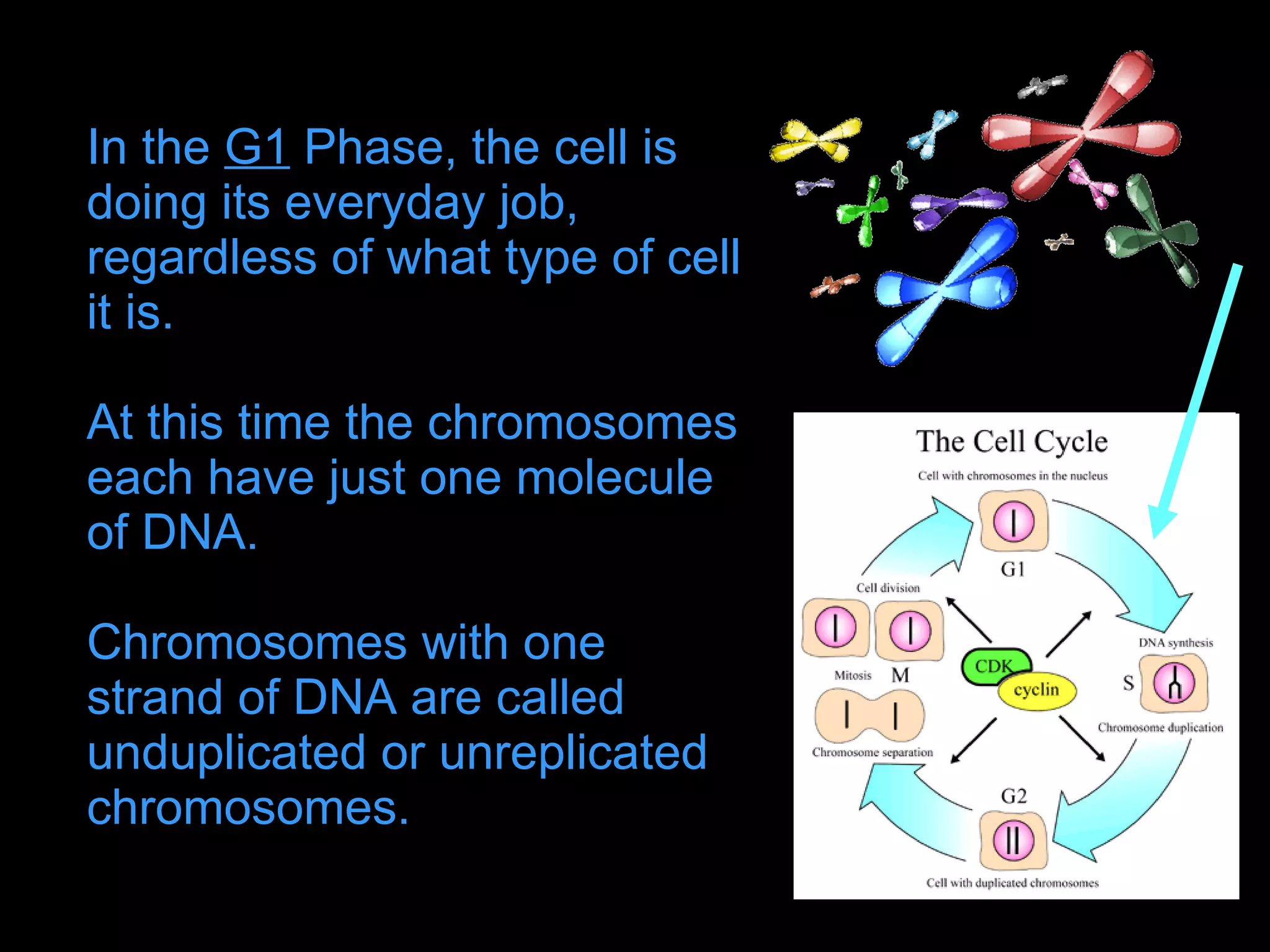
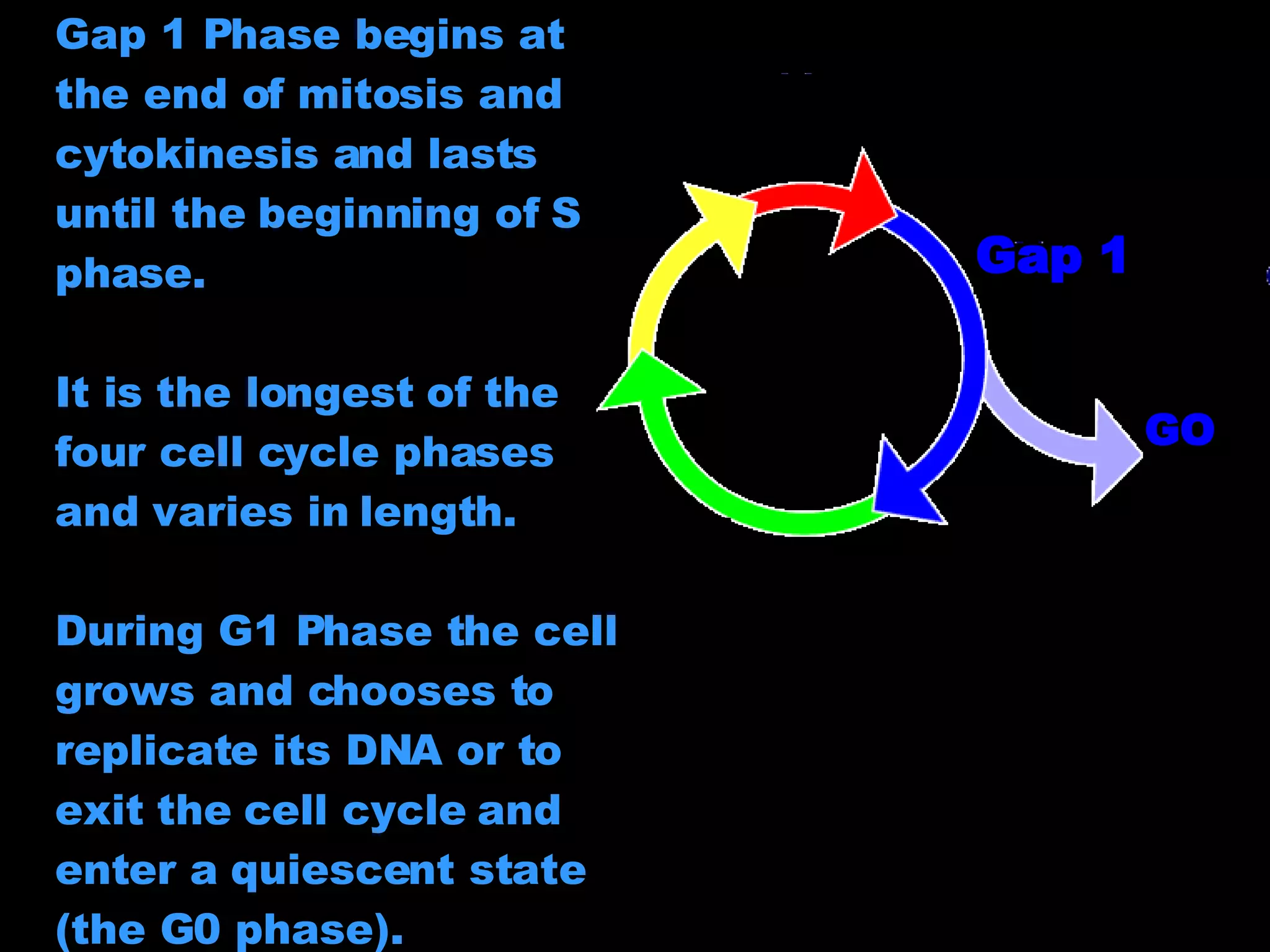
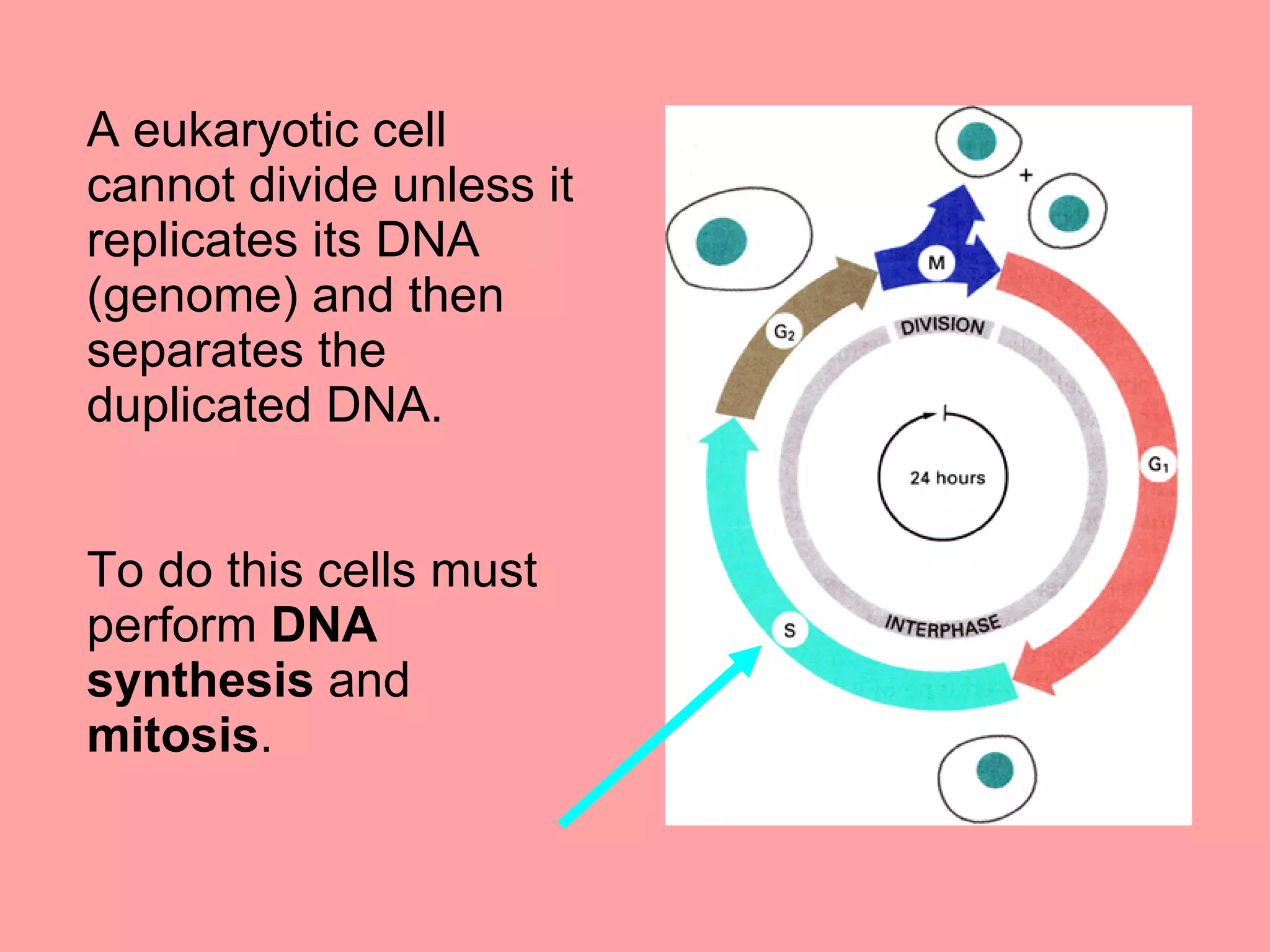
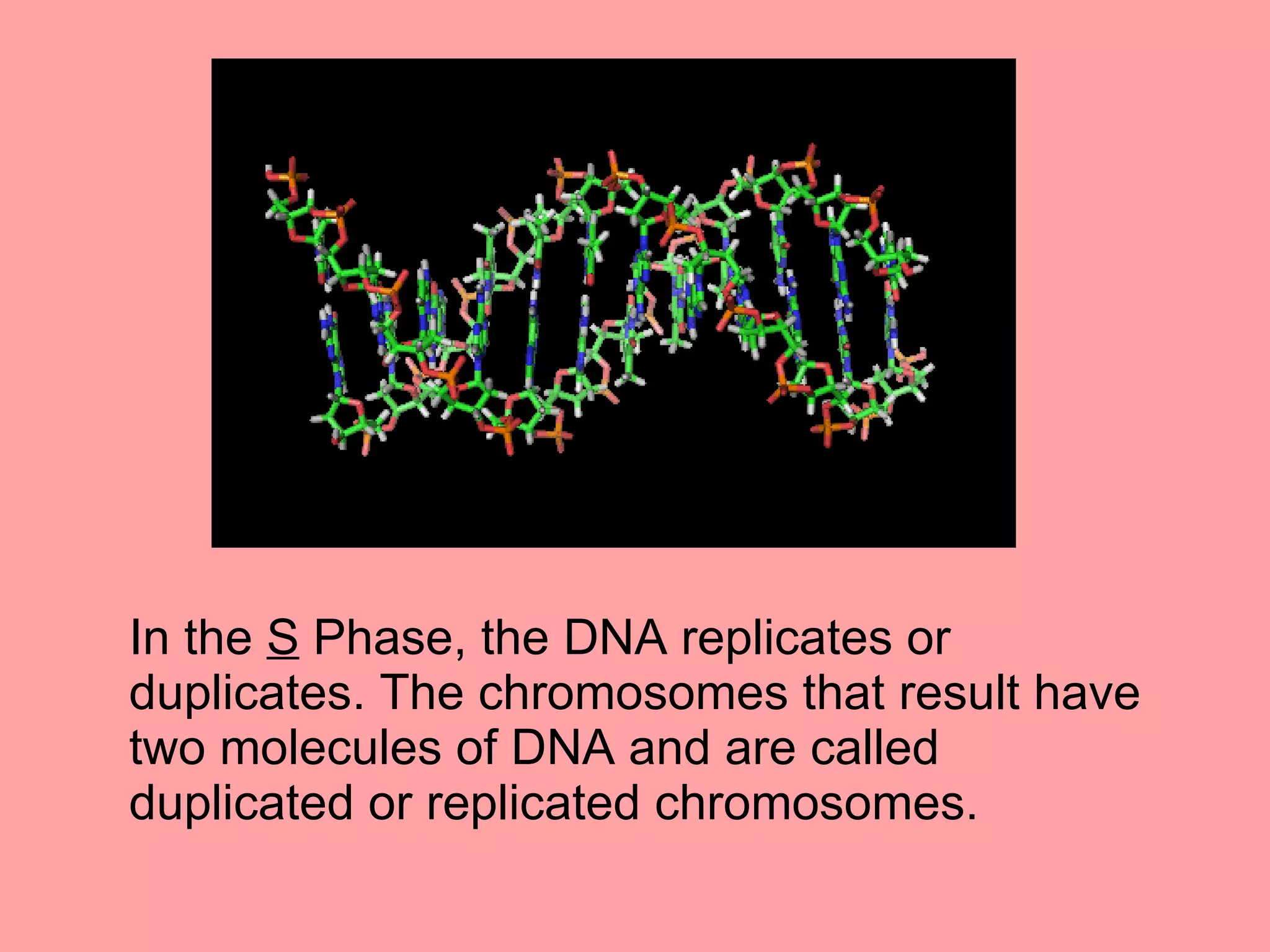
The cell cycle is required for cell growth and division into two daughter cells. It consists of four main phases: G1 phase for growth and DNA replication preparation; S phase for DNA replication; G2 phase for more growth and mitosis preparation; and M phase for mitosis and cell division. Cells monitor conditions and determine if they will continue through the cycle or exit into quiescence during the G1 and G2 checkpoints. DNA replication occurs in S phase, and chromosomes are separated in mitosis during M phase, resulting in two identical daughter cells that reenter G1 to repeat the cycle.