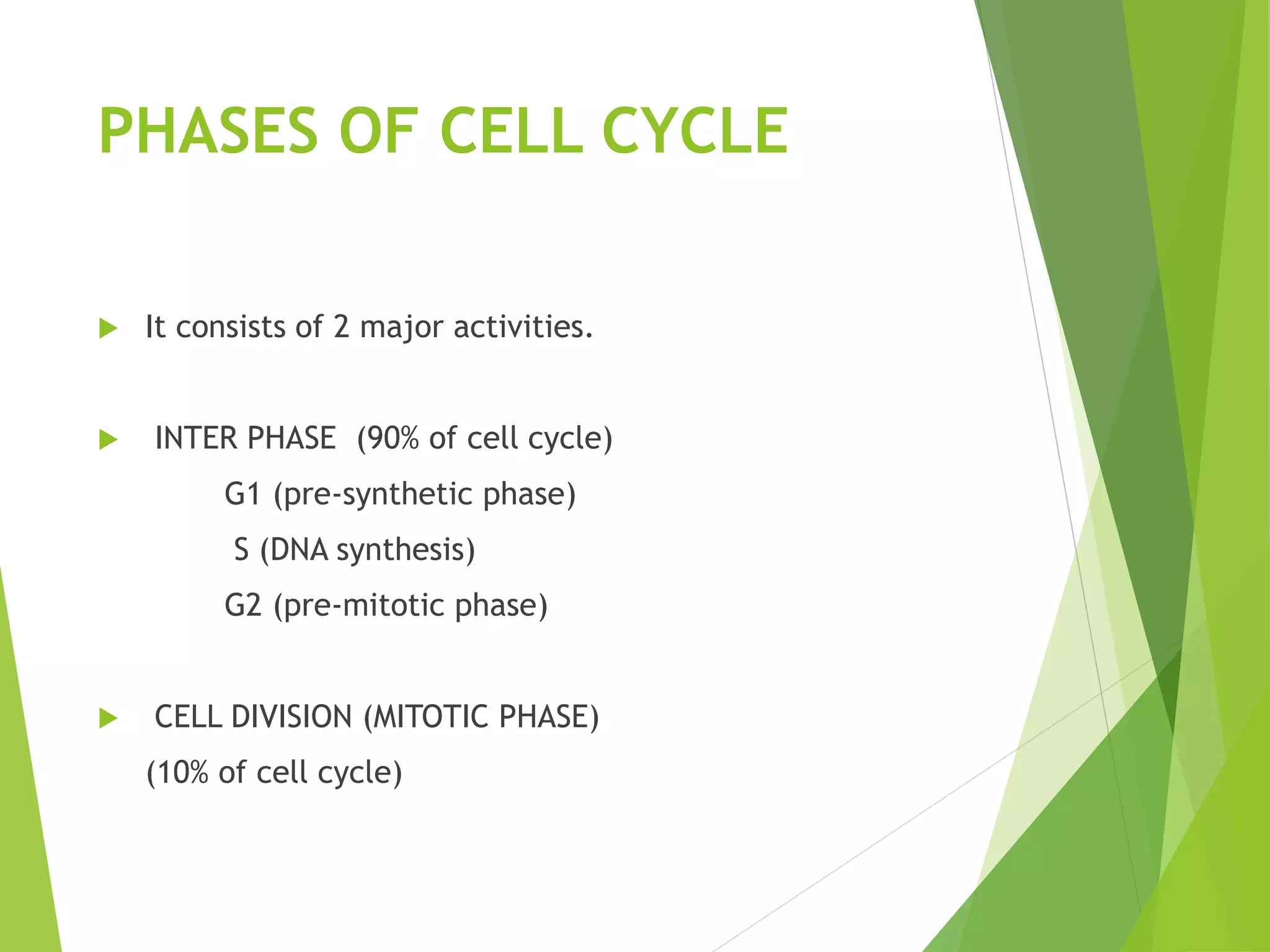
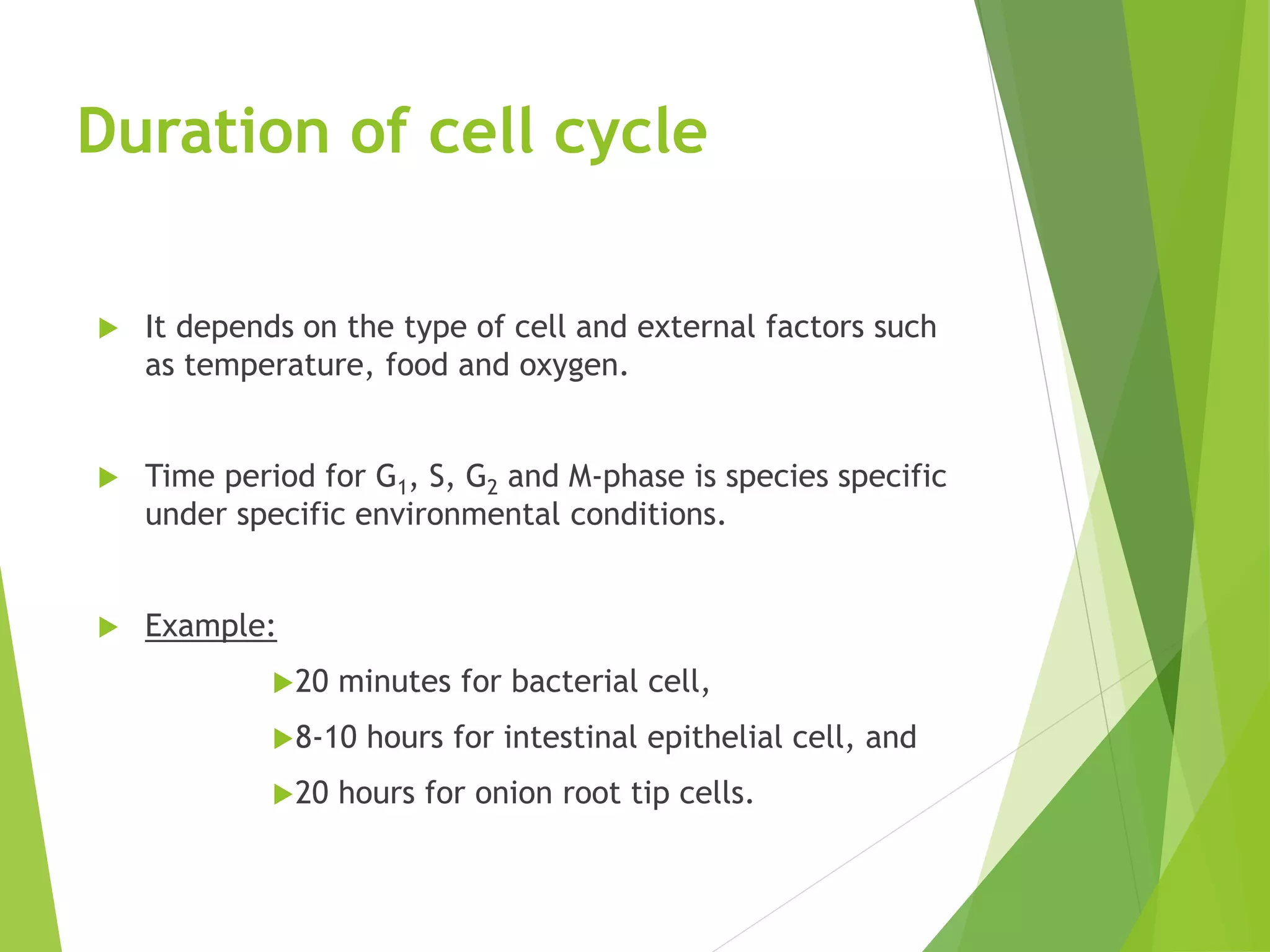
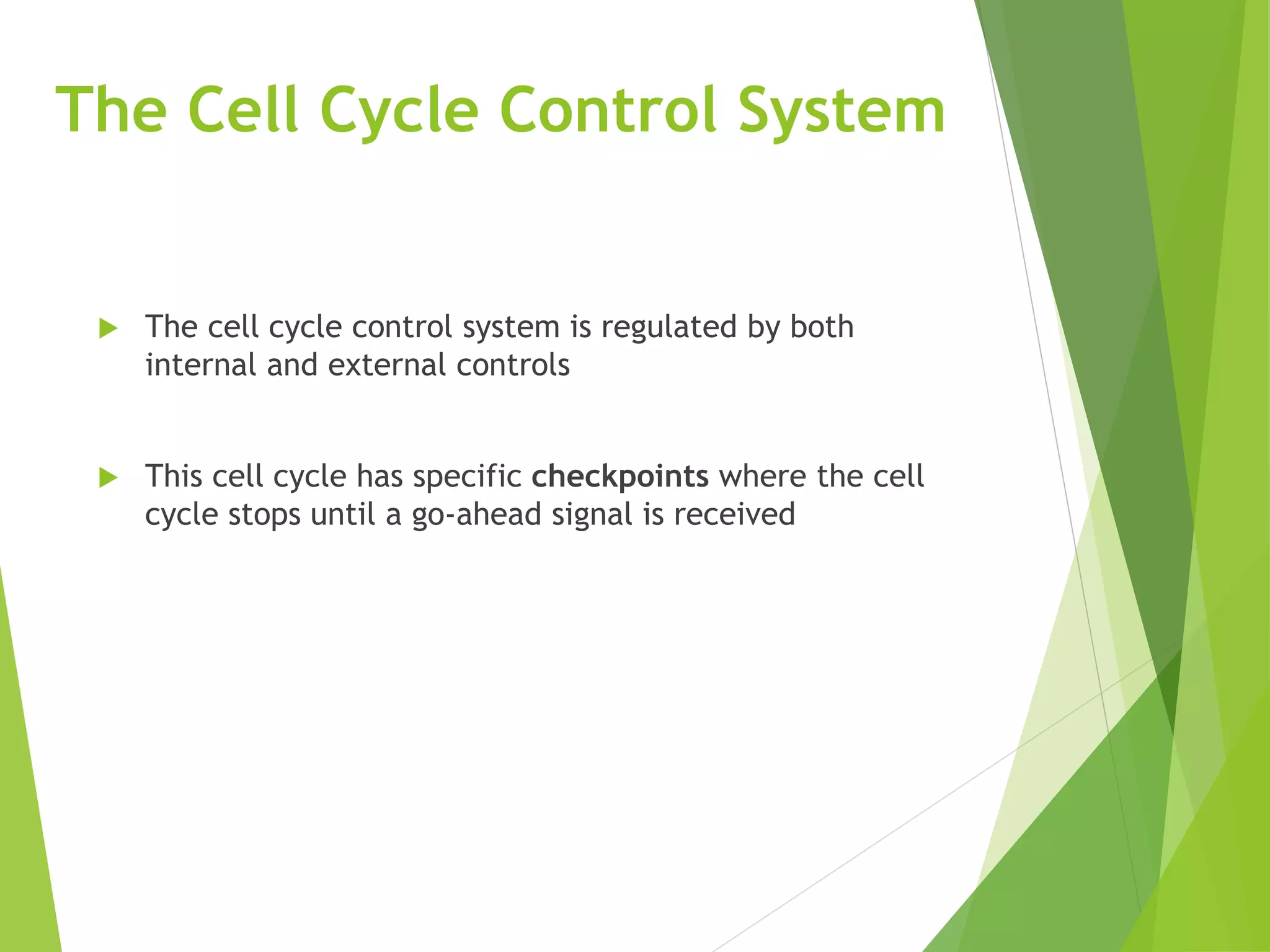
El ciclo celular es una serie de eventos que una célula atraviesa desde su formación hasta su división, que incluye las fases de interfase y mitosis. La regulación del ciclo celular se realiza a través de puntos de control que utilizan señales químicas, garantizando que las células se dividan solo cuando sea apropiado. Este proceso es fundamental para el crecimiento celular y se aplica en áreas como el tratamiento del cáncer.