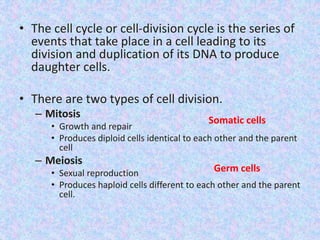
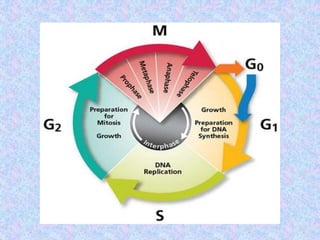
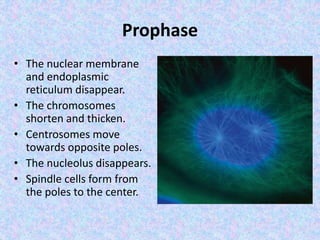
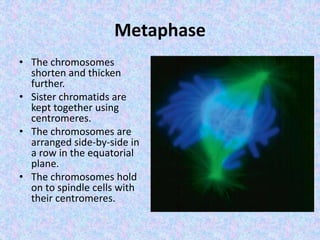
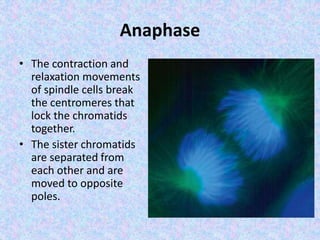
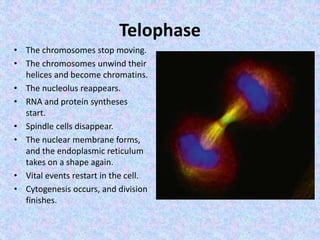
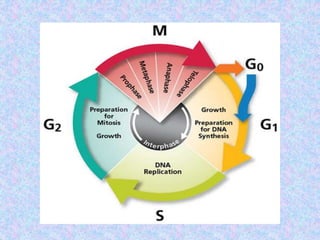
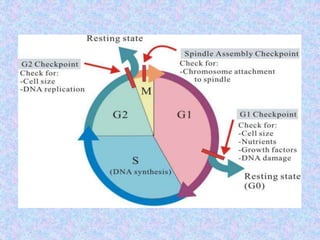
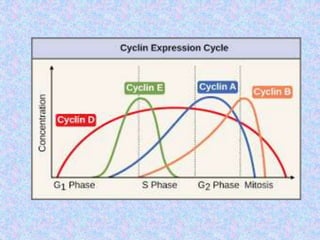
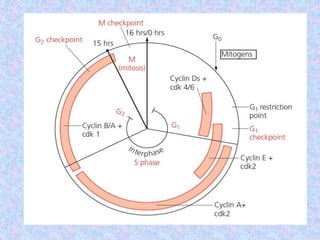
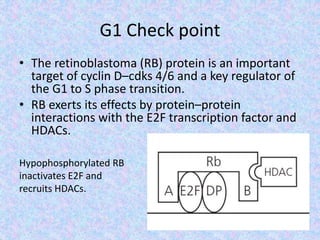
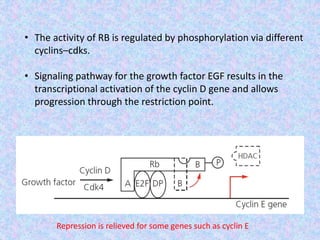
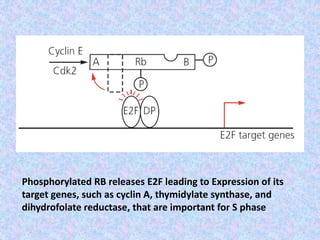
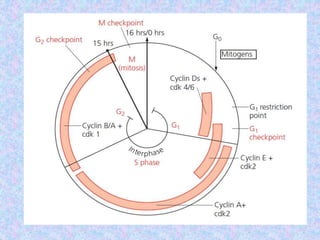
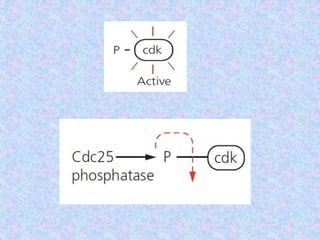
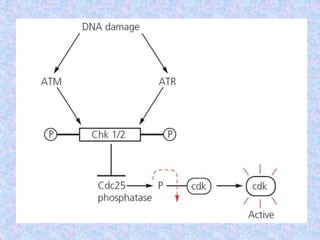
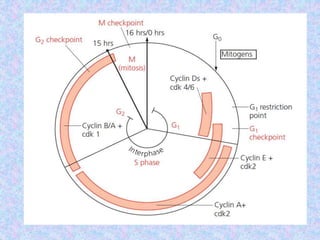
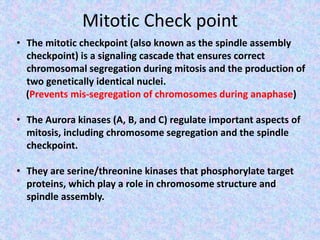
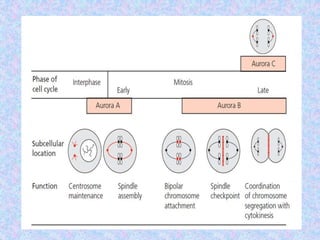
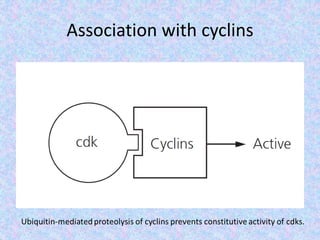
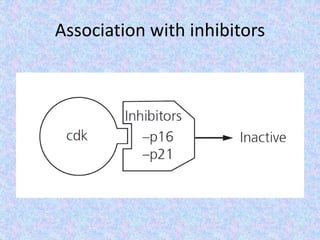
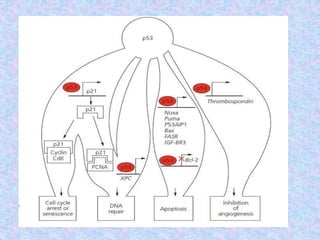
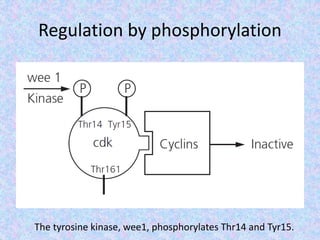
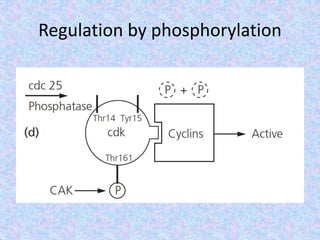
The document summarizes the cell cycle and its regulation. It describes the main stages of the cell cycle - interphase consisting of G1, S, and G2 phases and the M phase. Key regulators of the cell cycle include cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, and checkpoints like G1, G2, and M that ensure fidelity of DNA replication and chromosome segregation. Dysregulation of these processes can lead to genomic instability and cancer.