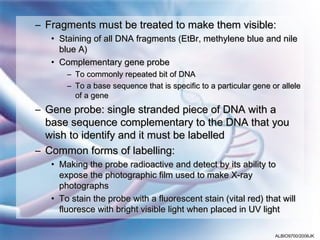
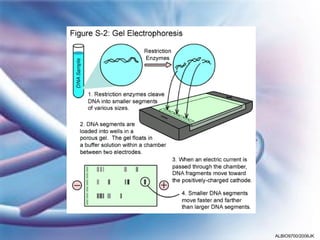
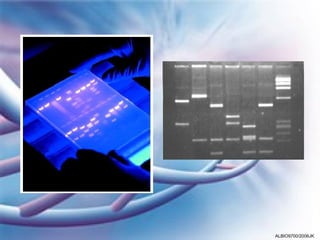
Electrophoresis is a method used in genetic fingerprinting and DNA sequencing. It separates DNA fragments based on their size and charge, allowing analysis of molecular structure. In genetic fingerprinting, DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis can be compared between samples to determine the source of DNA or if samples are related. DNA sequencing uses electrophoresis to separate DNA fragments by one base at a time, enabling determination of the order of bases within genes and chromosomes.