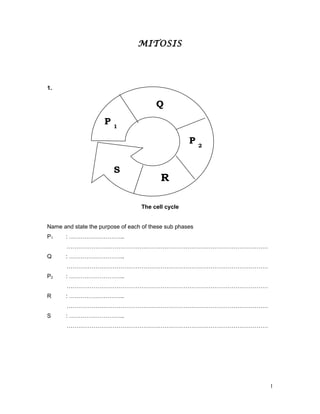
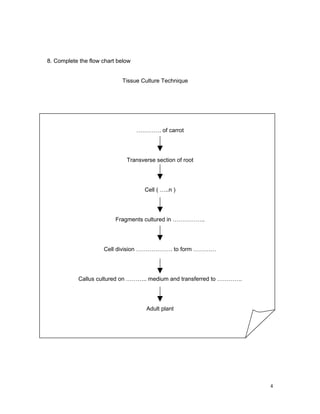
The document discusses mitosis and meiosis. It includes diagrams of the cell cycle and phases of mitosis and meiosis. It asks questions about the key differences between mitosis and meiosis such as their products and purpose. Questions assess understanding of concepts like crossing over, chromosome behavior in each phase, and how genetic variation arises in meiosis.