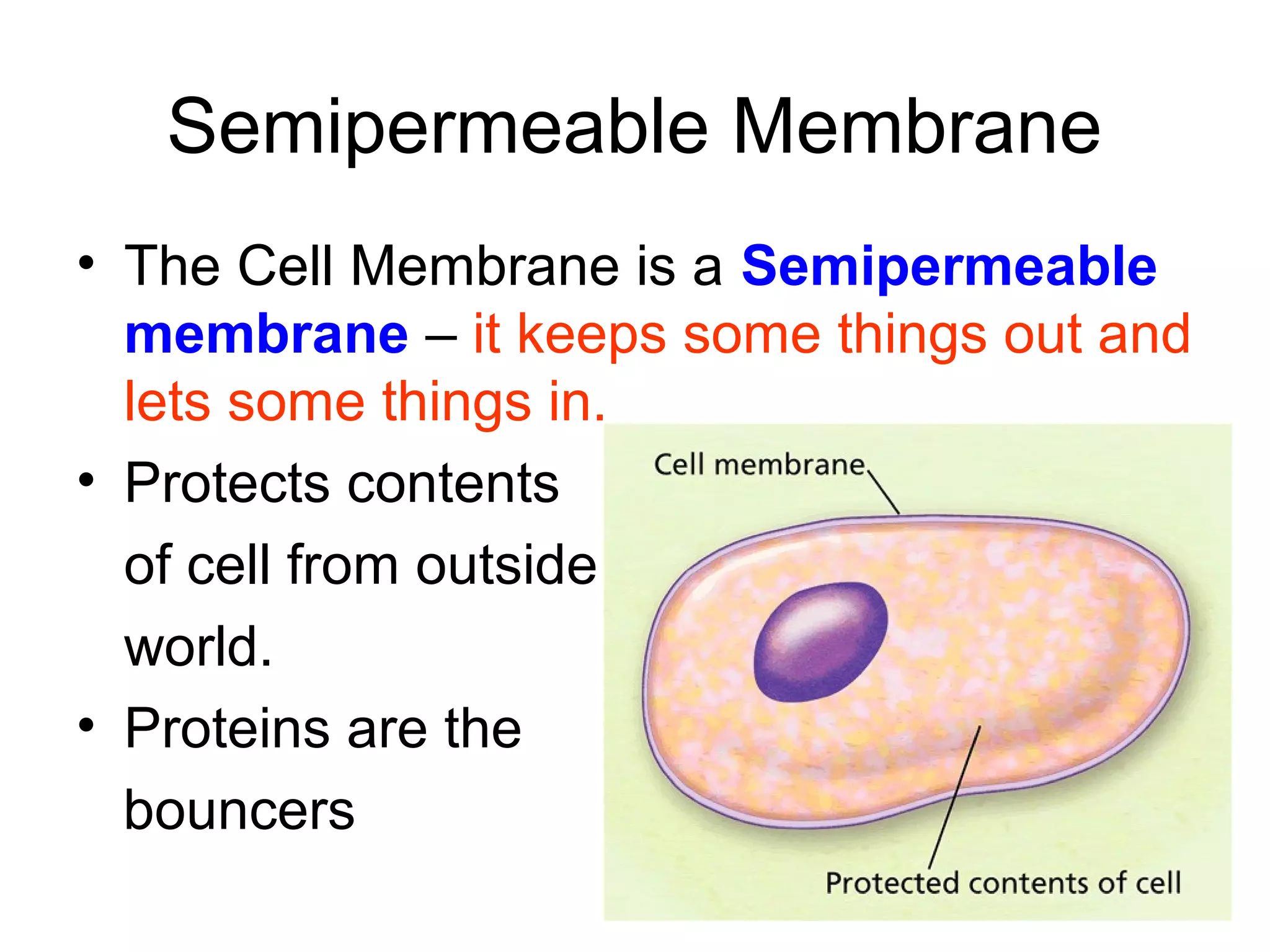
1) The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing some materials to pass through via passive transport while blocking others.
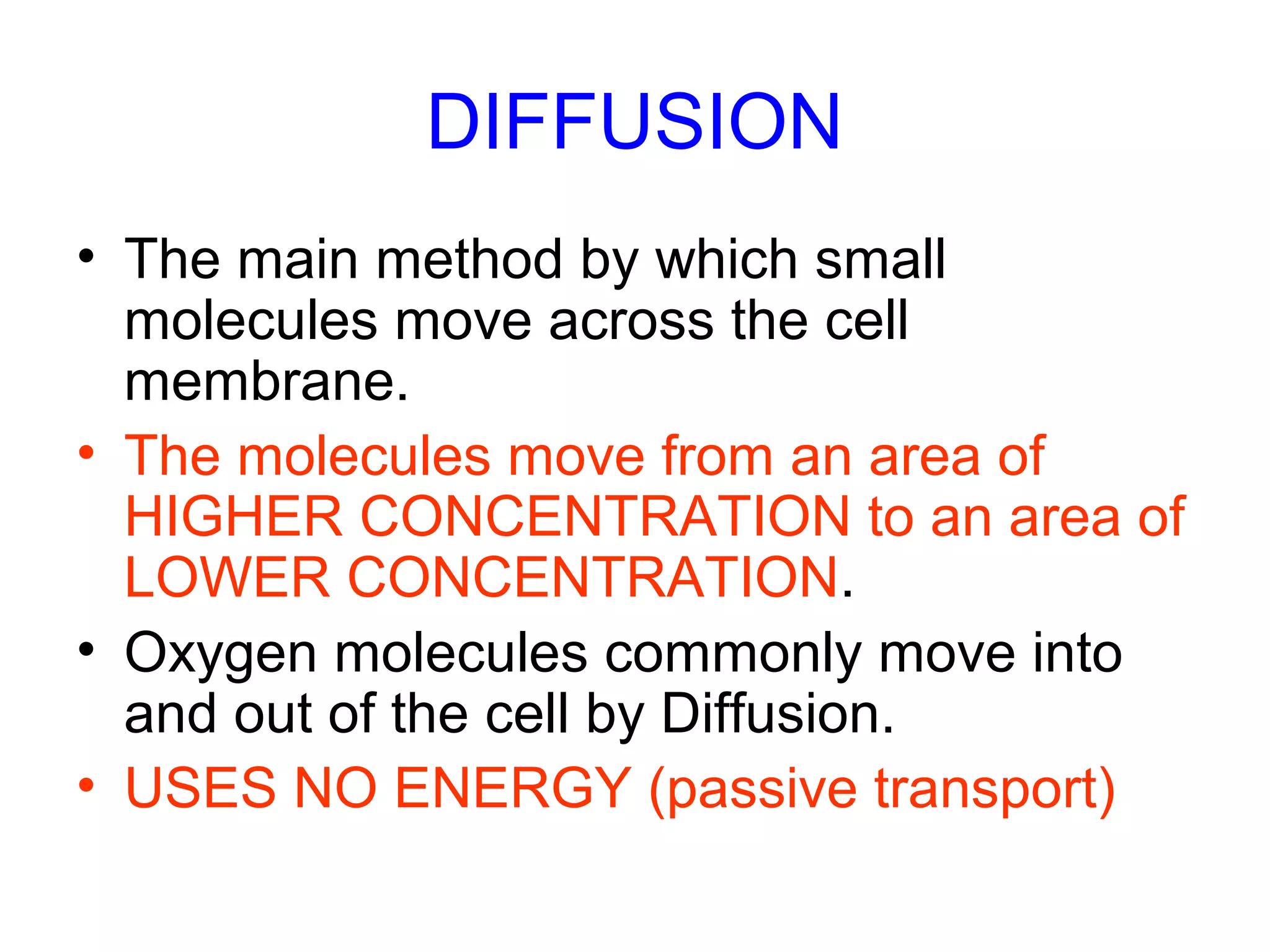
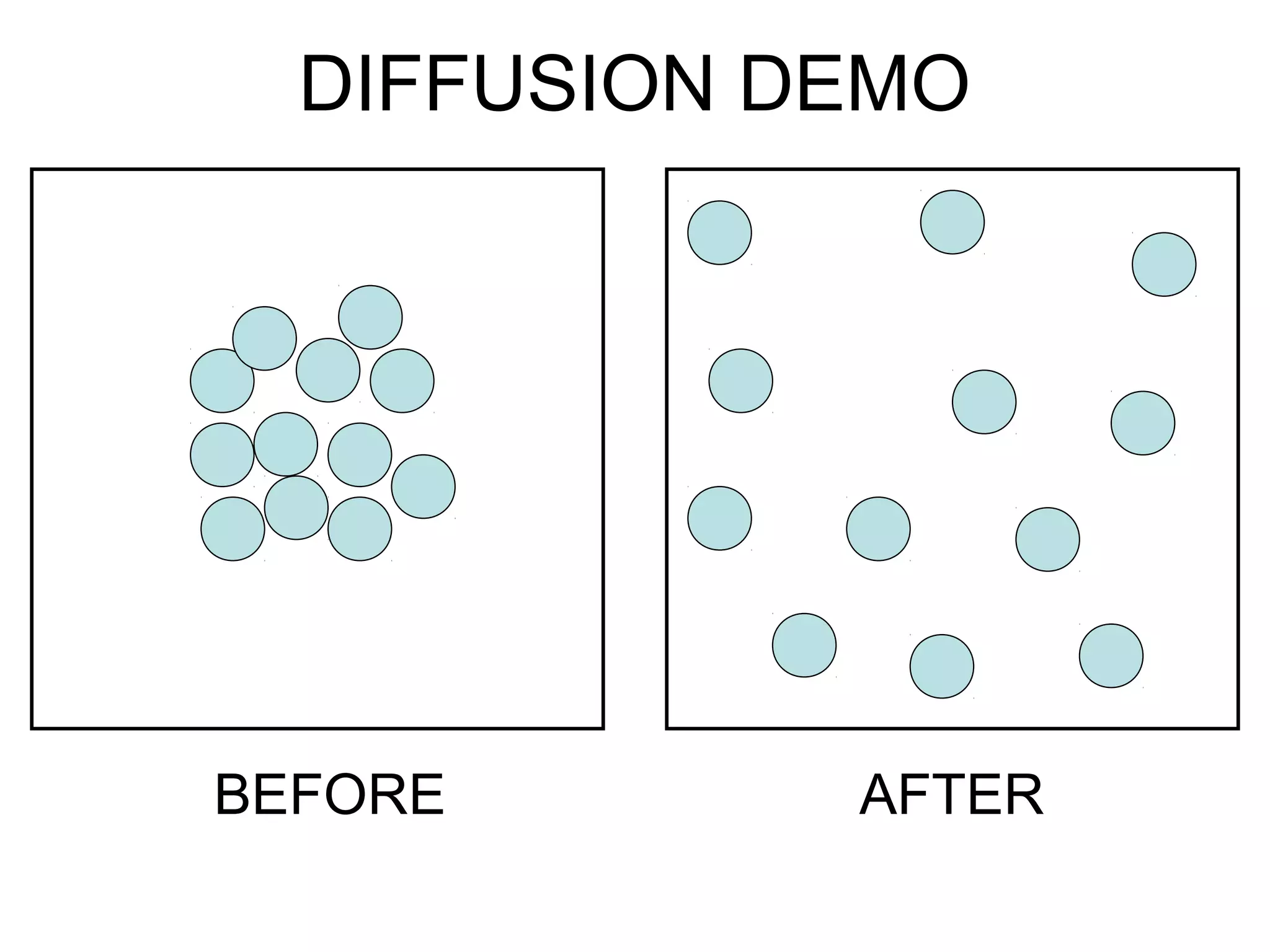
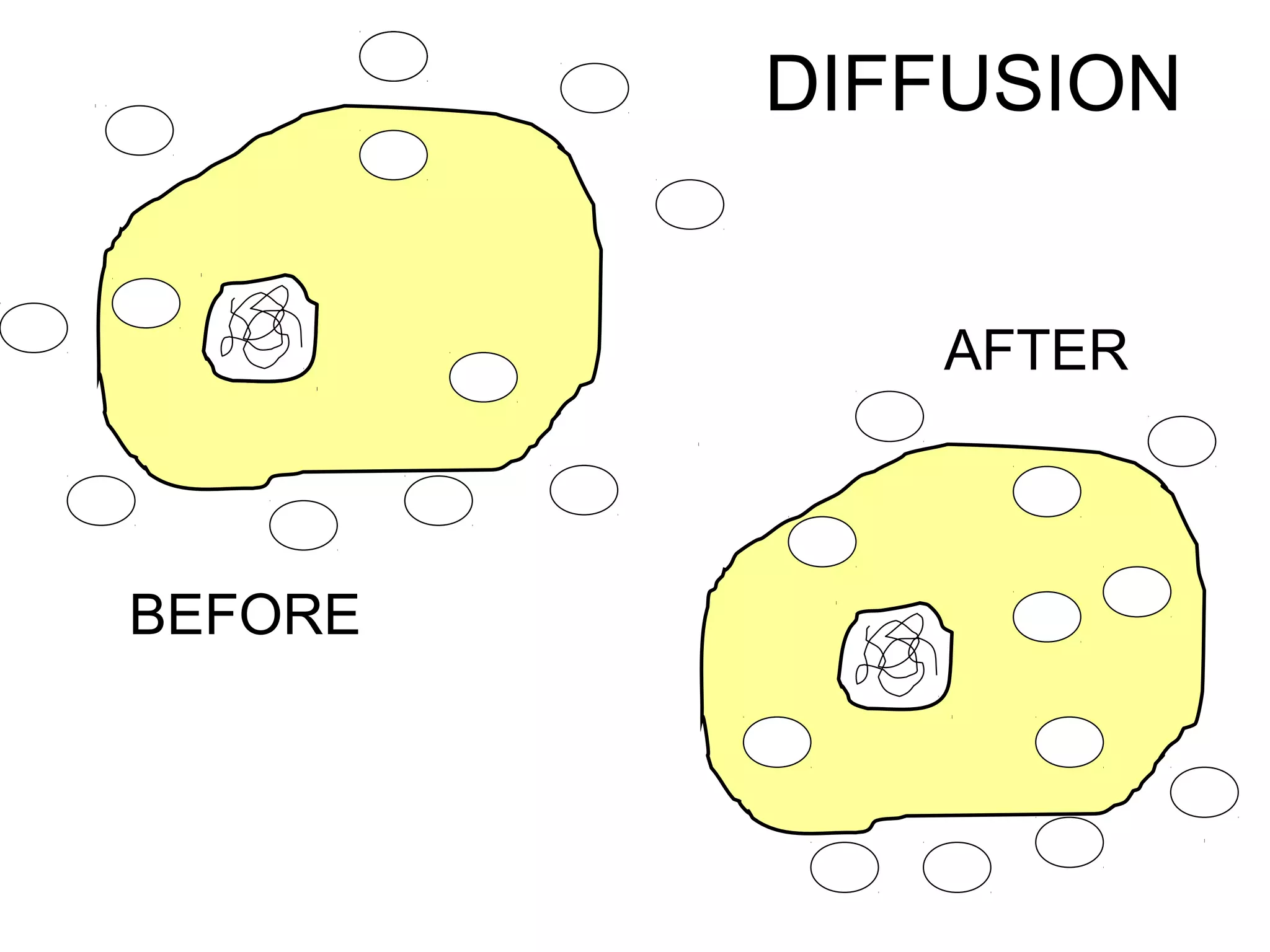
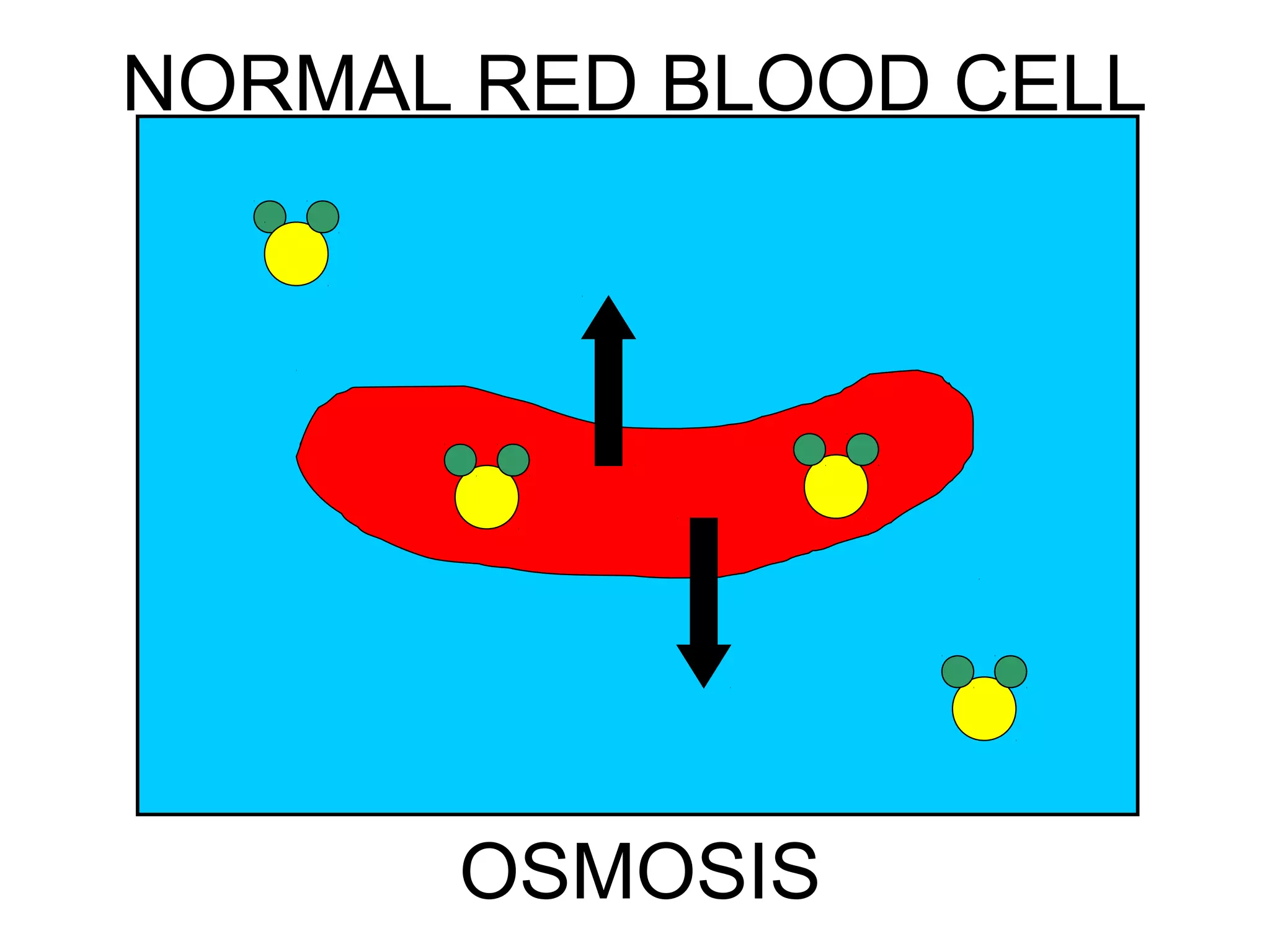
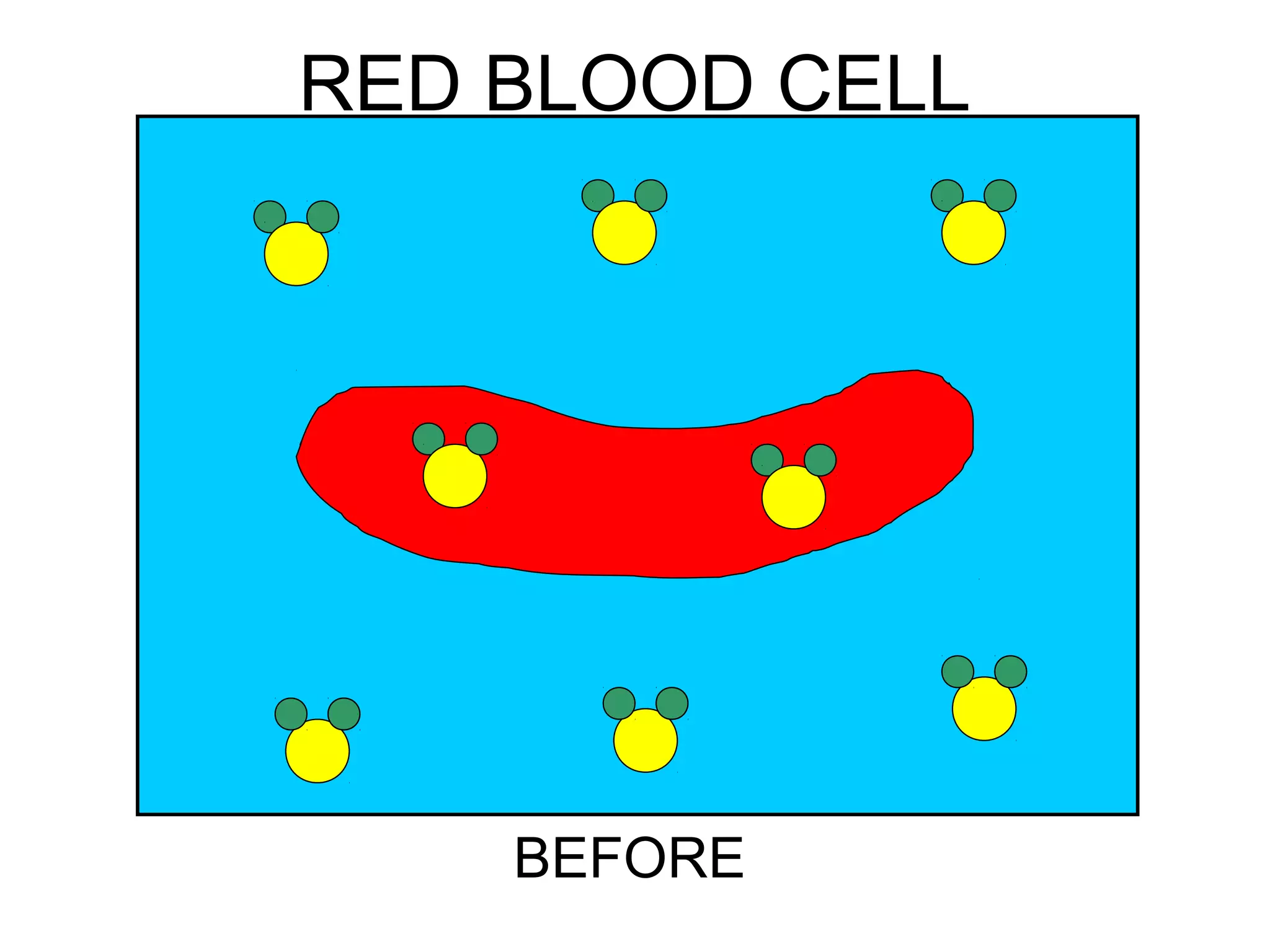
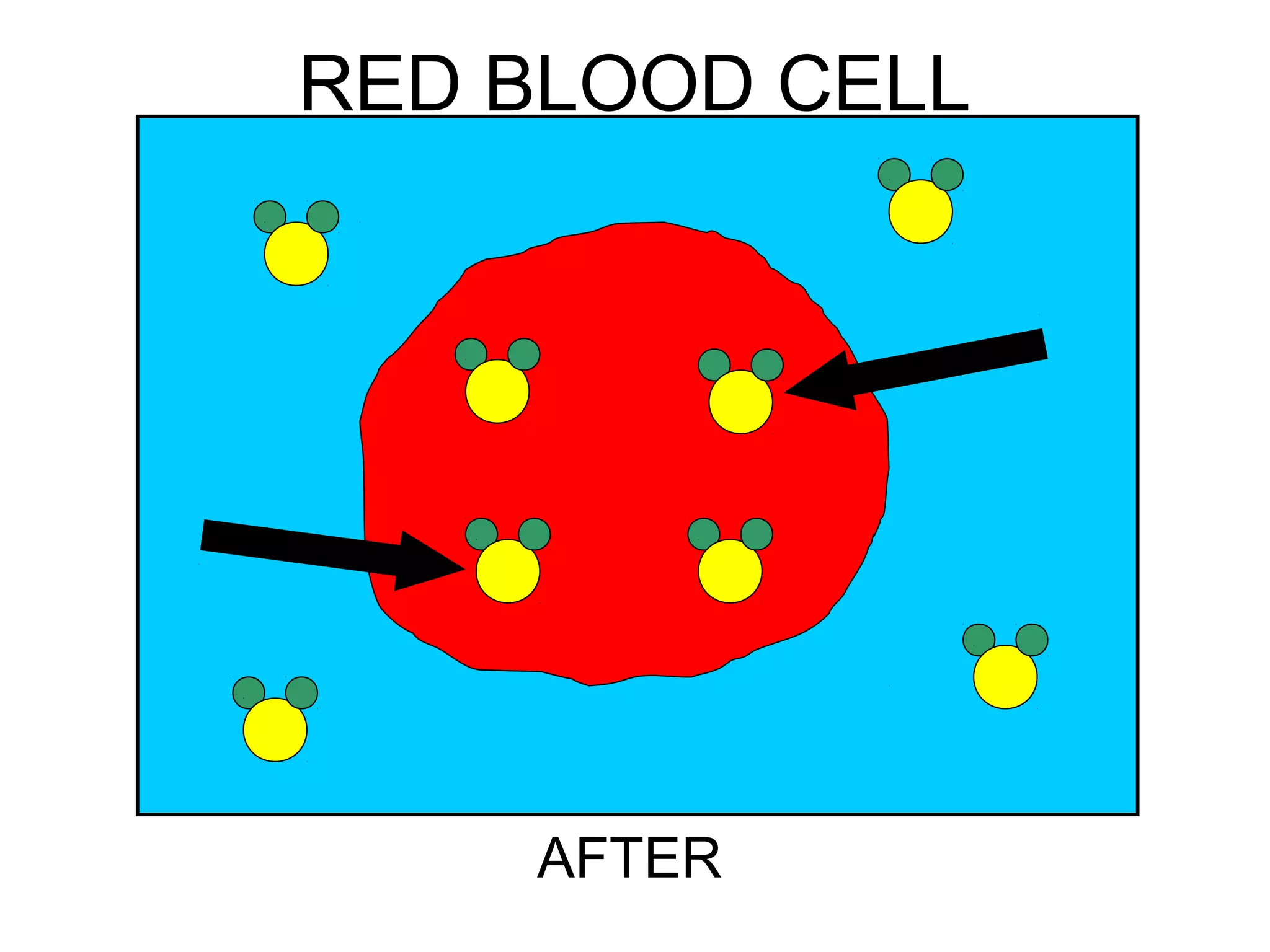
2) Passive transport includes diffusion and osmosis, which move materials across the membrane from high to low concentration without energy.
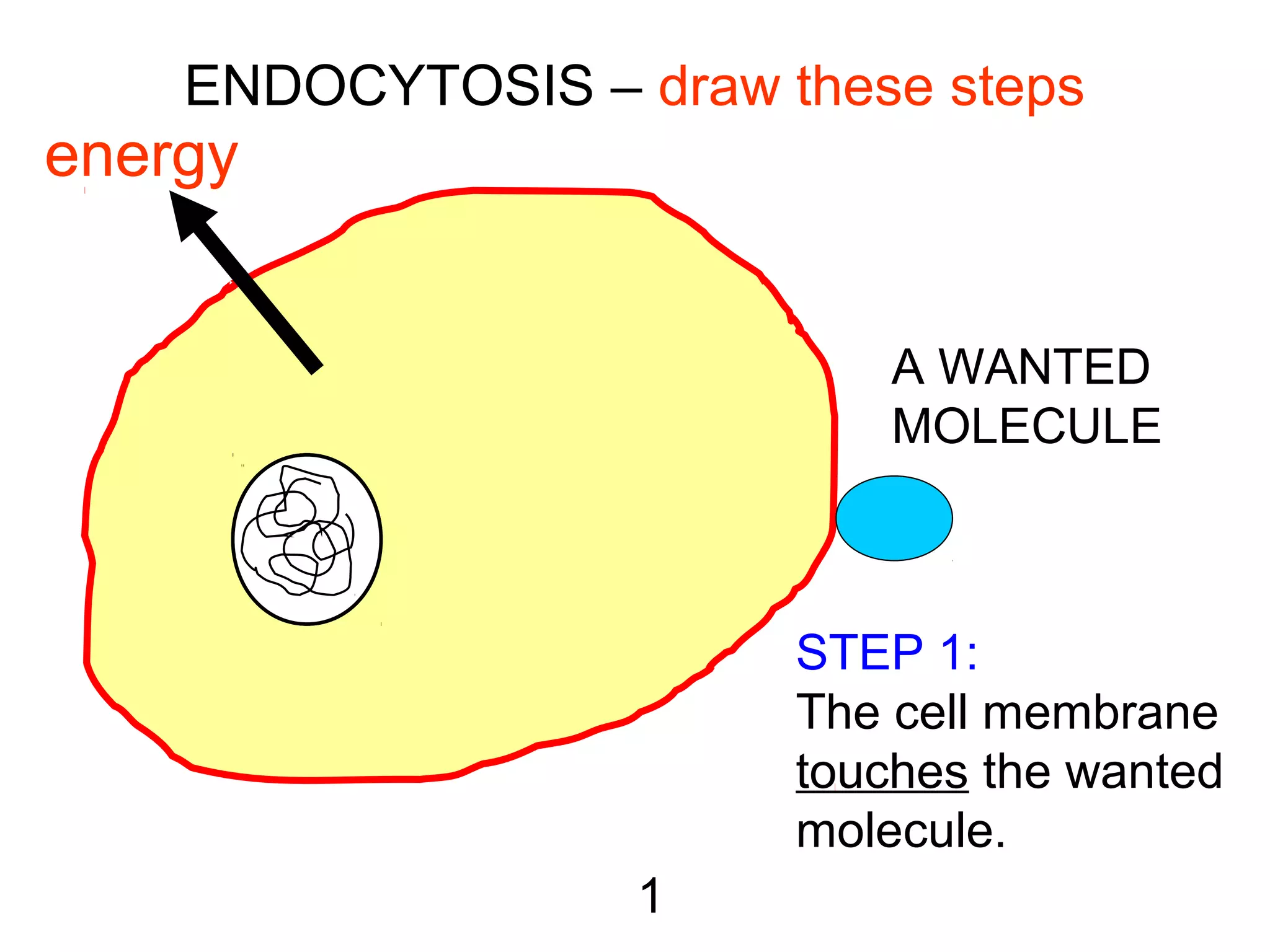
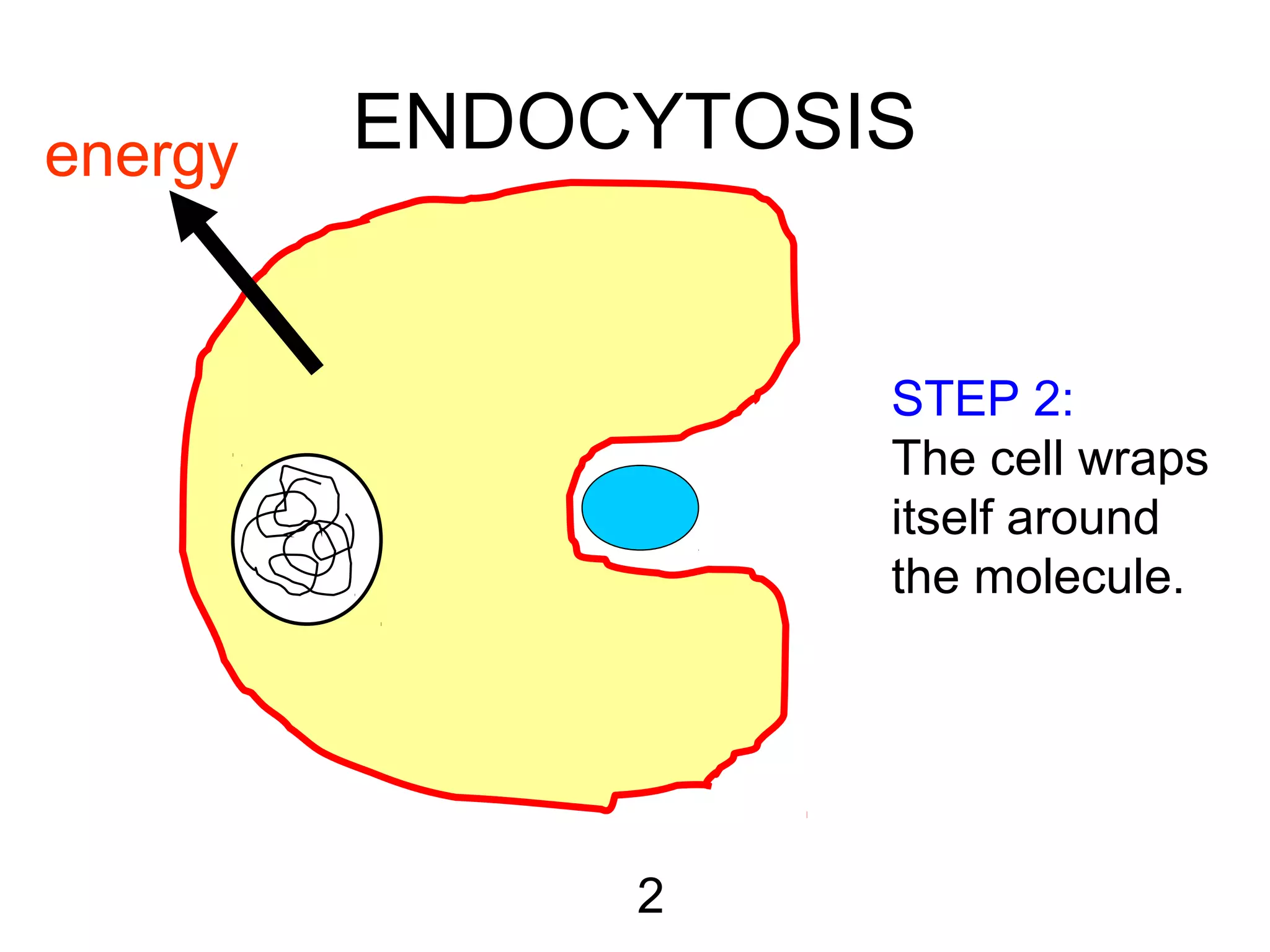
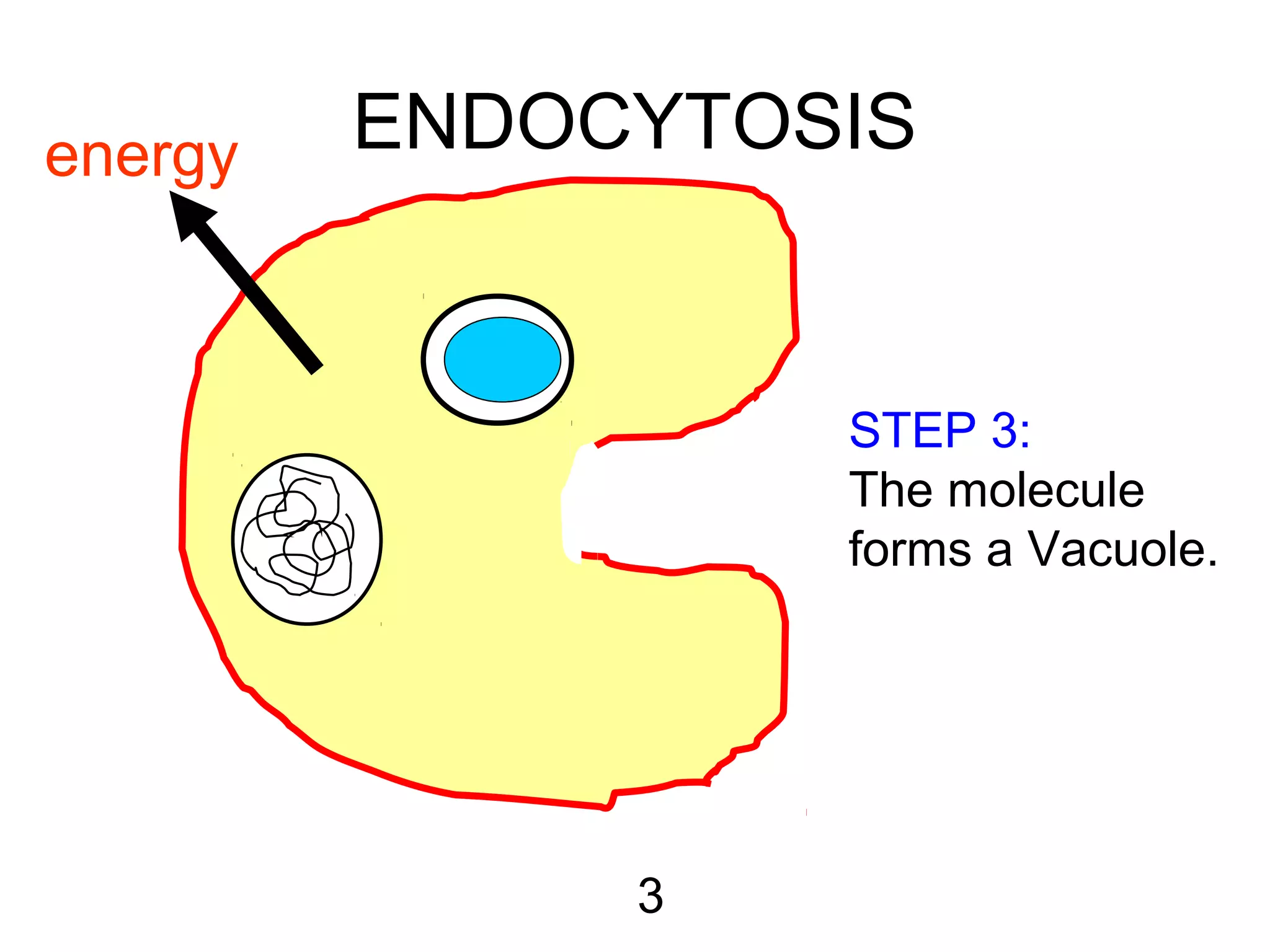
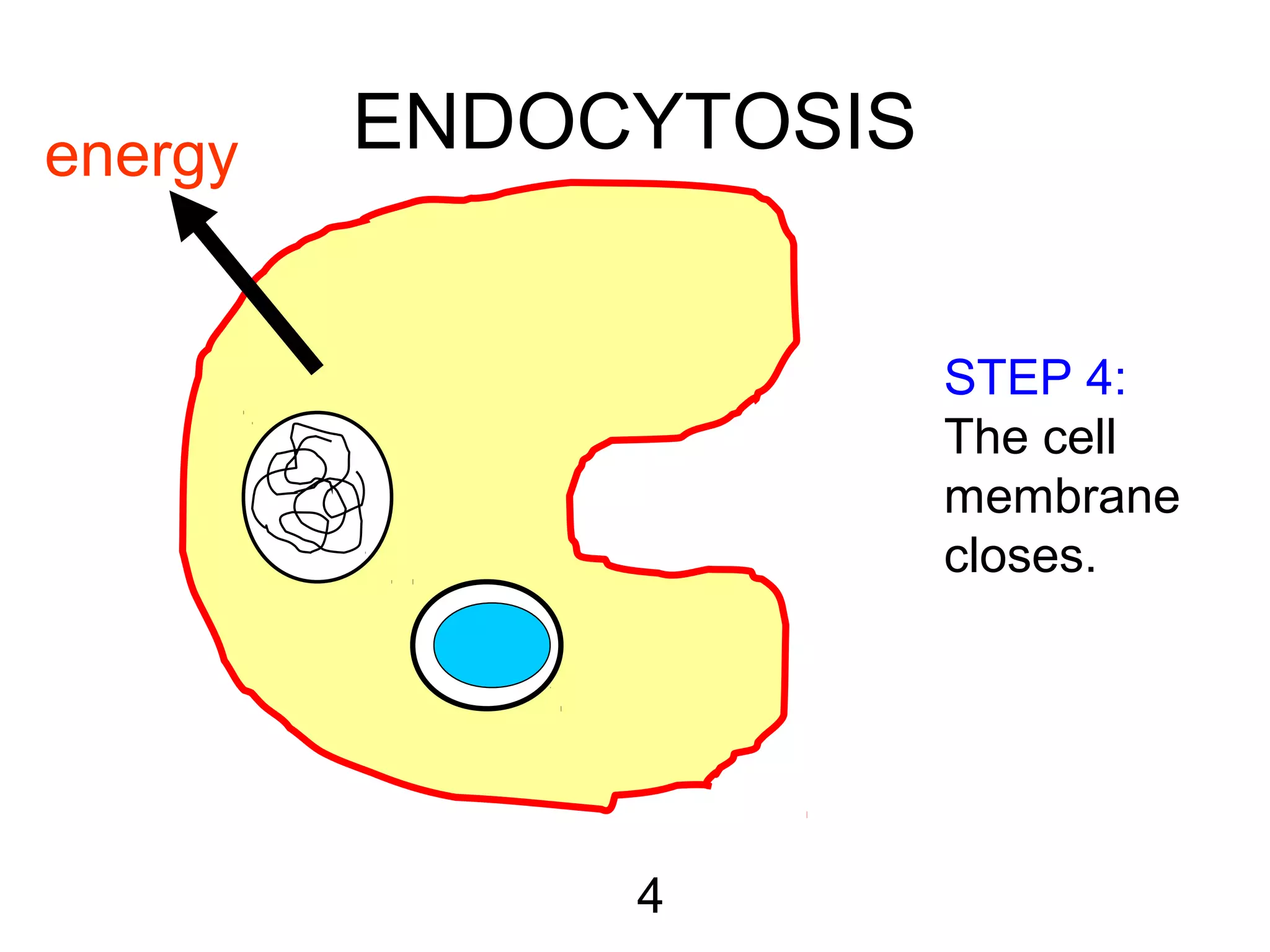
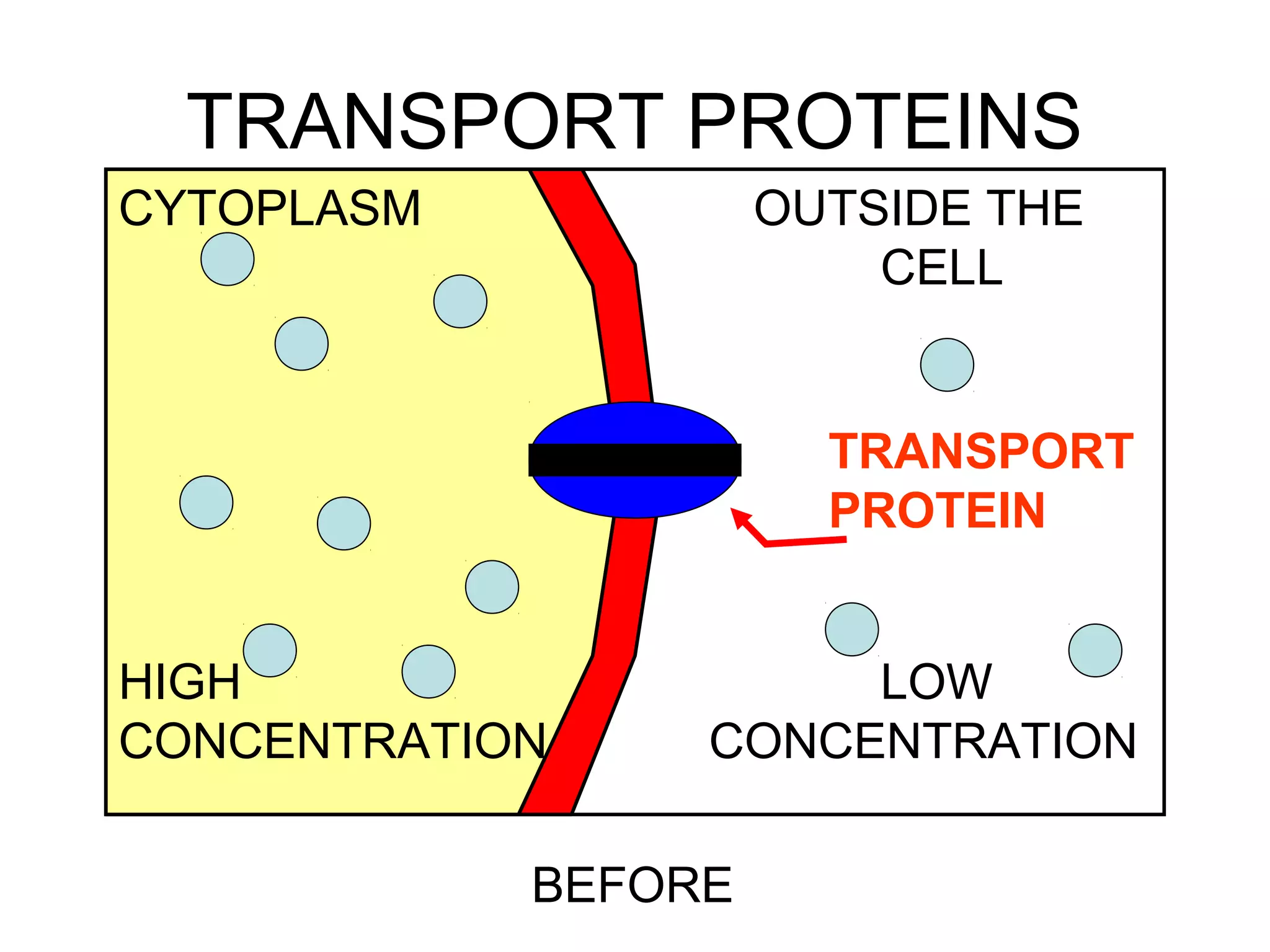
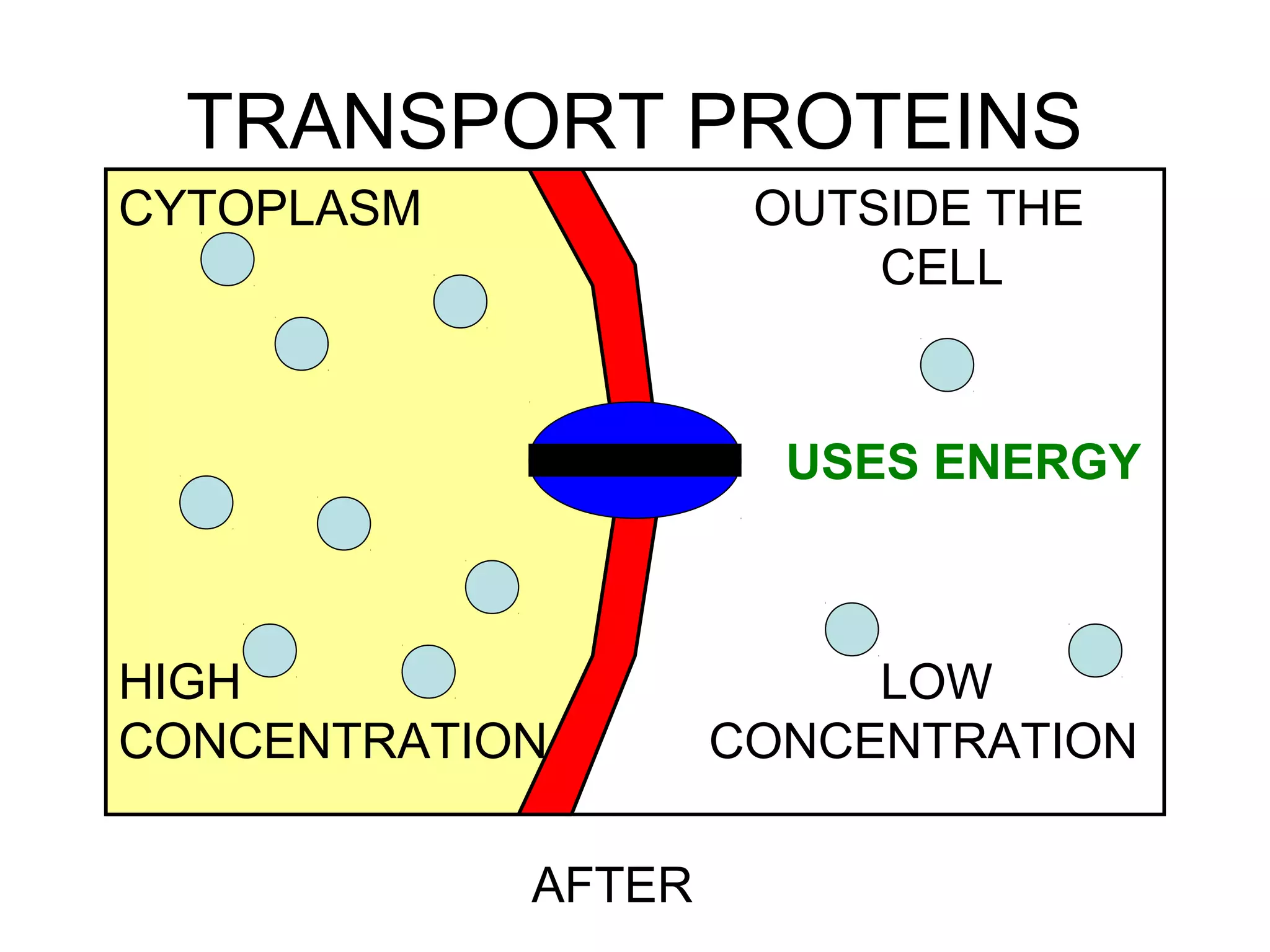
3) Active transport uses energy to move materials against their concentration gradient or bring larger particles into the cell through endocytosis. Transport proteins assist with this process.