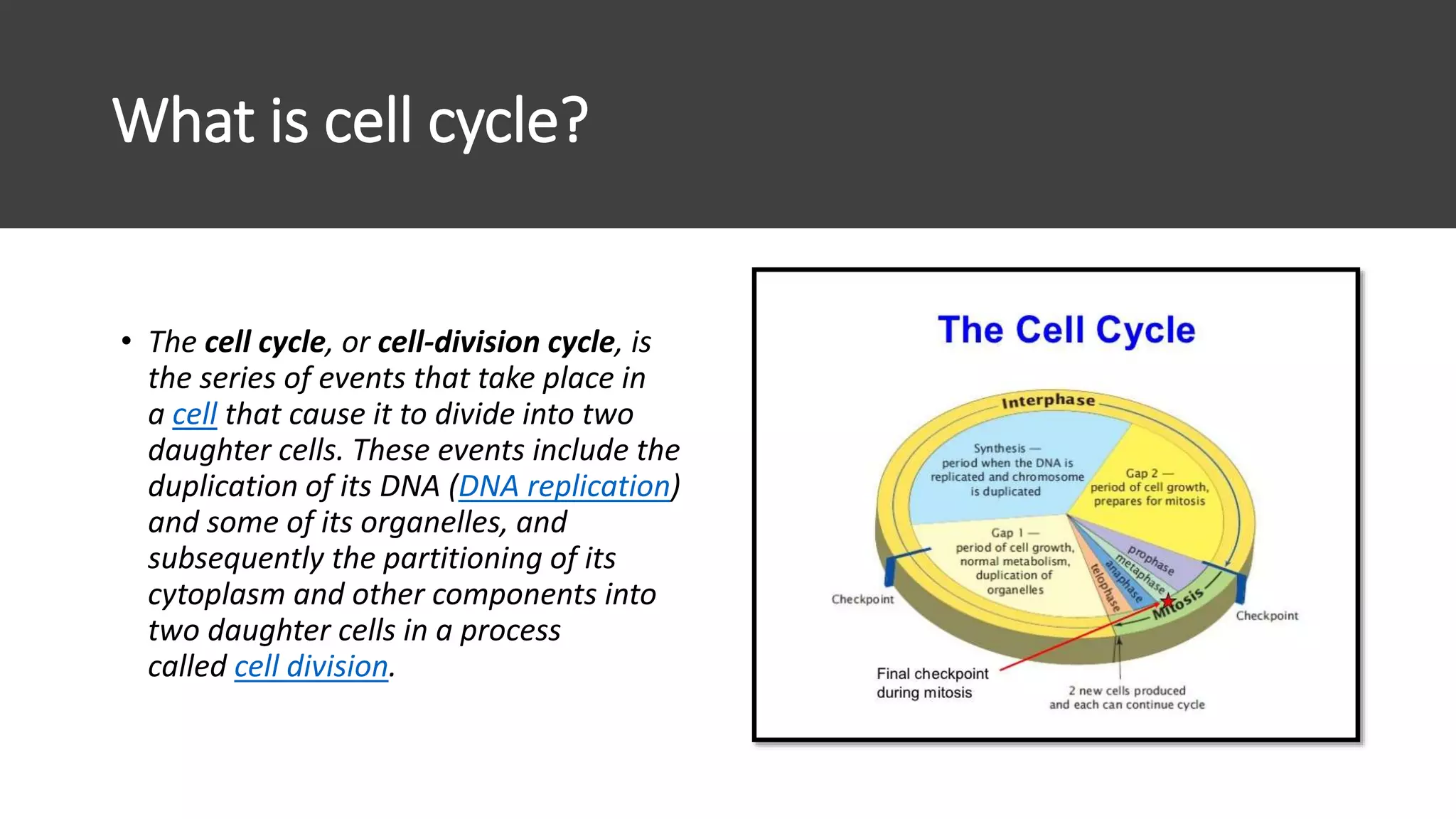
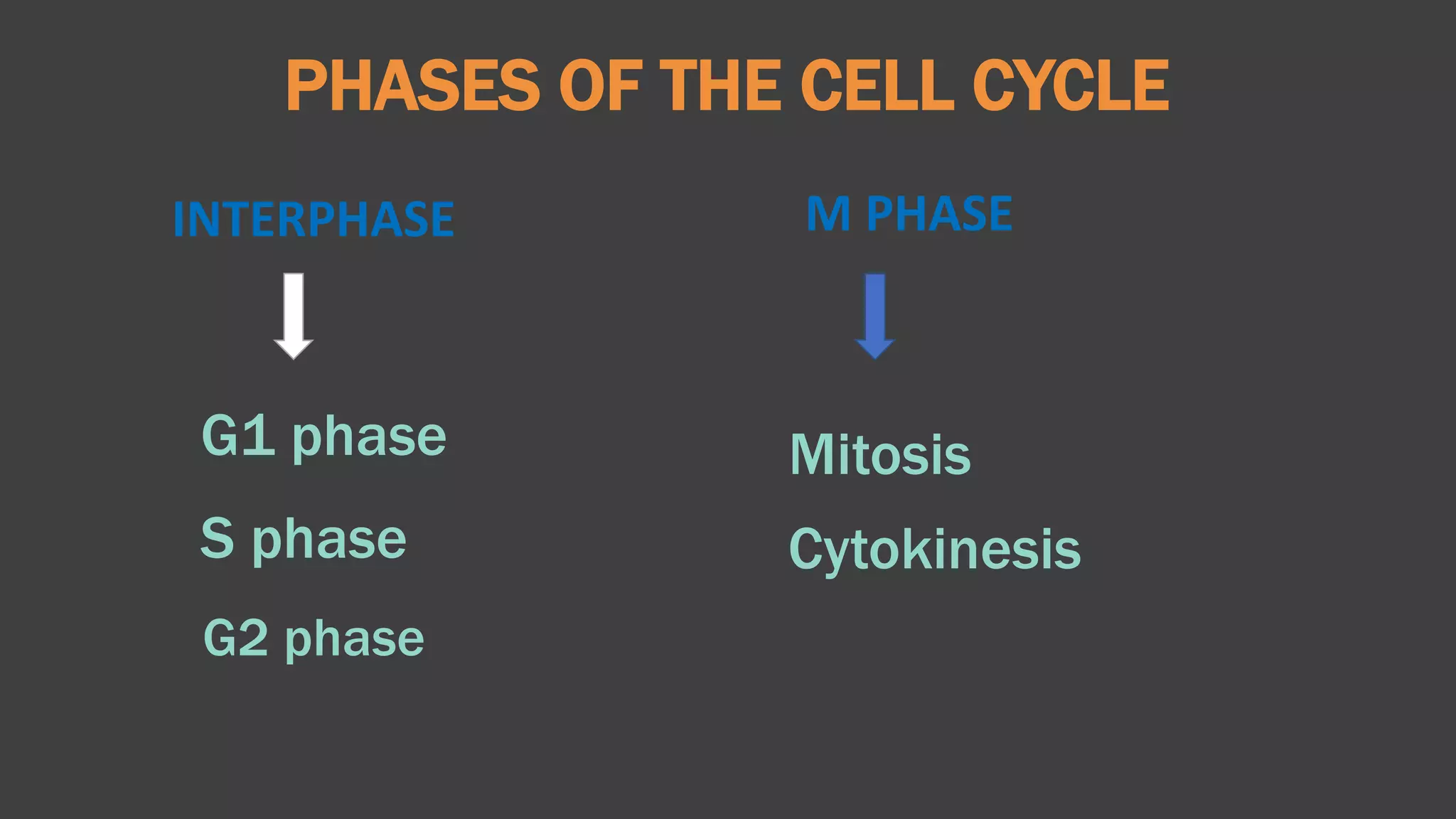
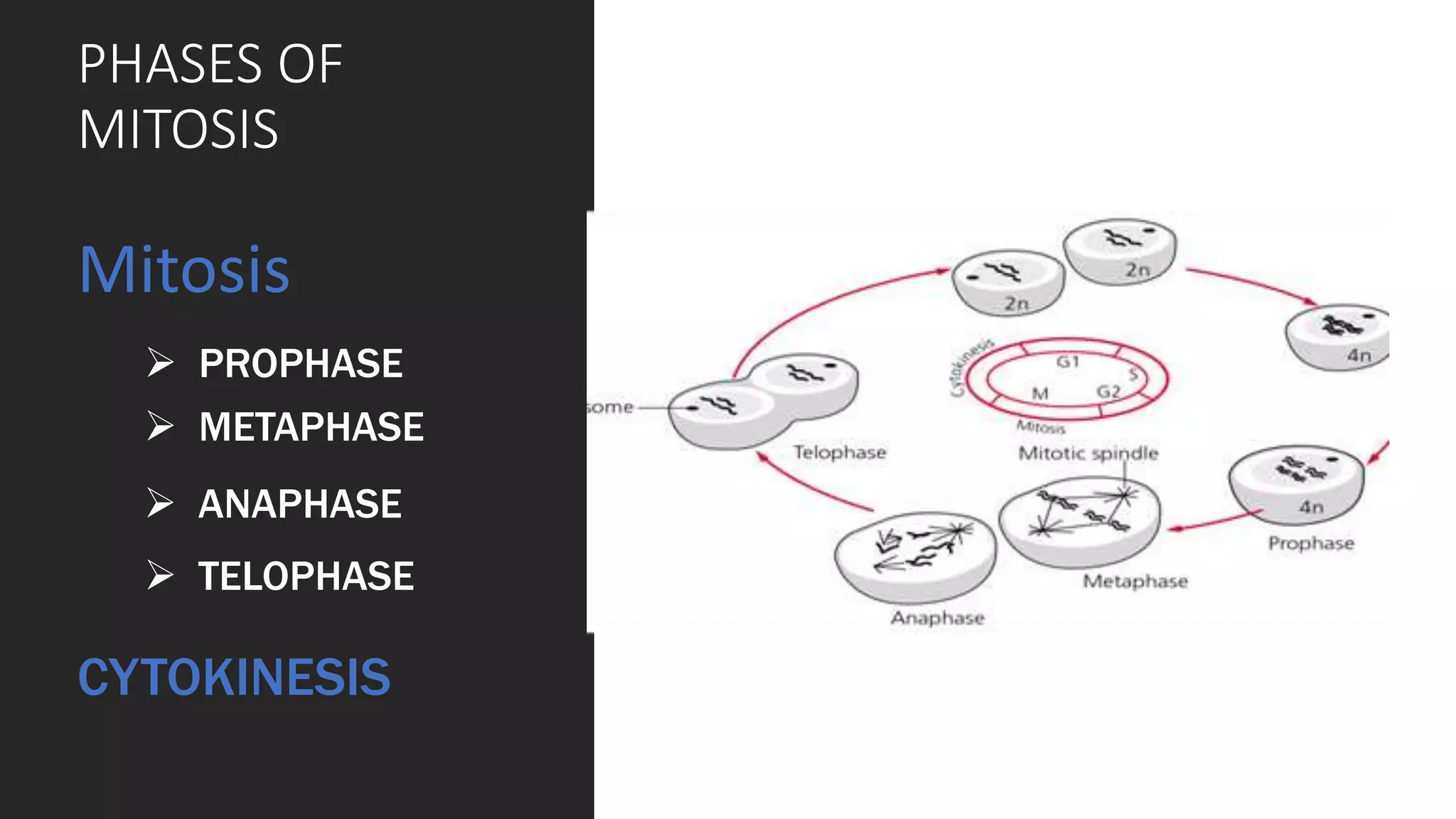
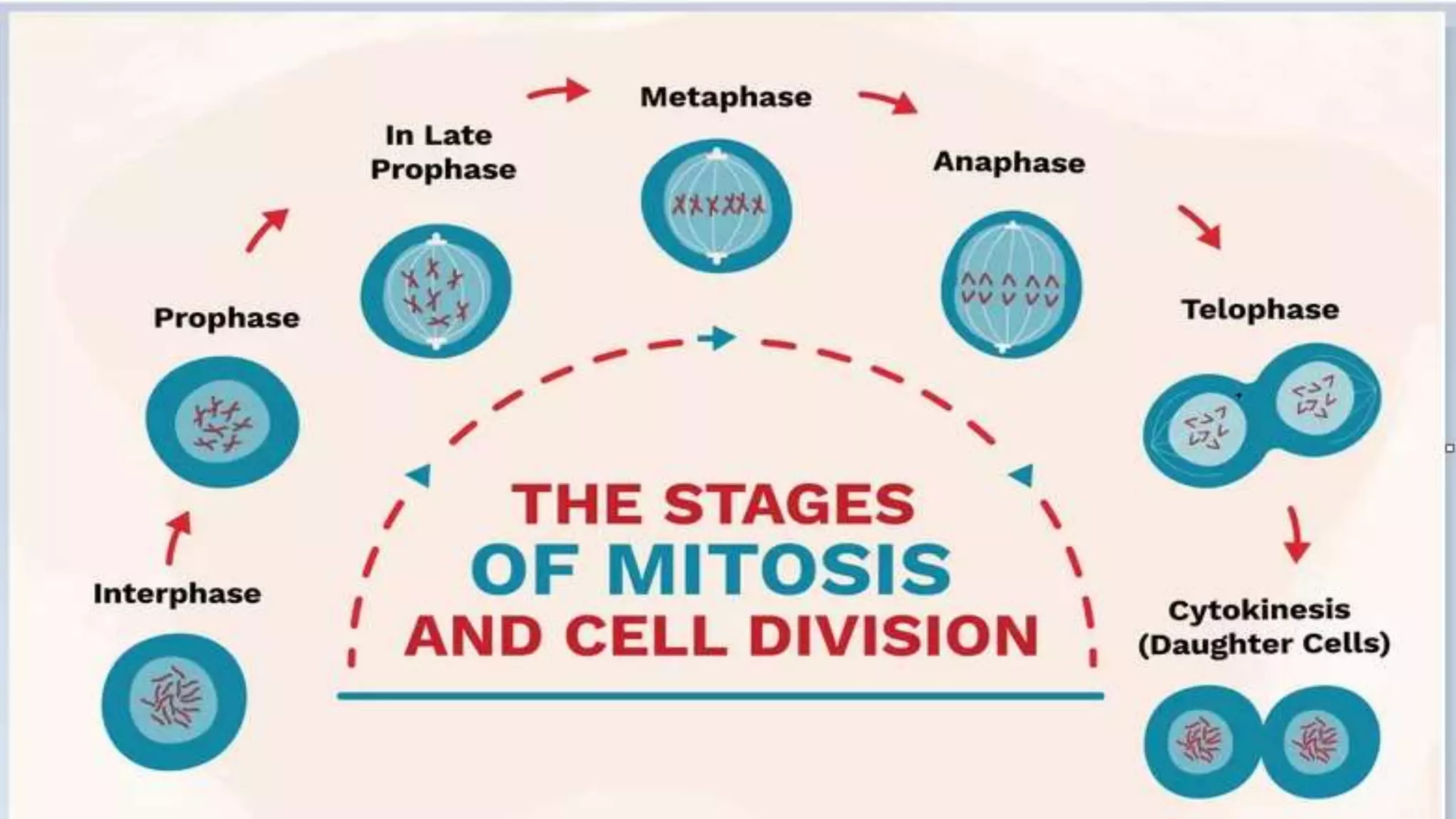
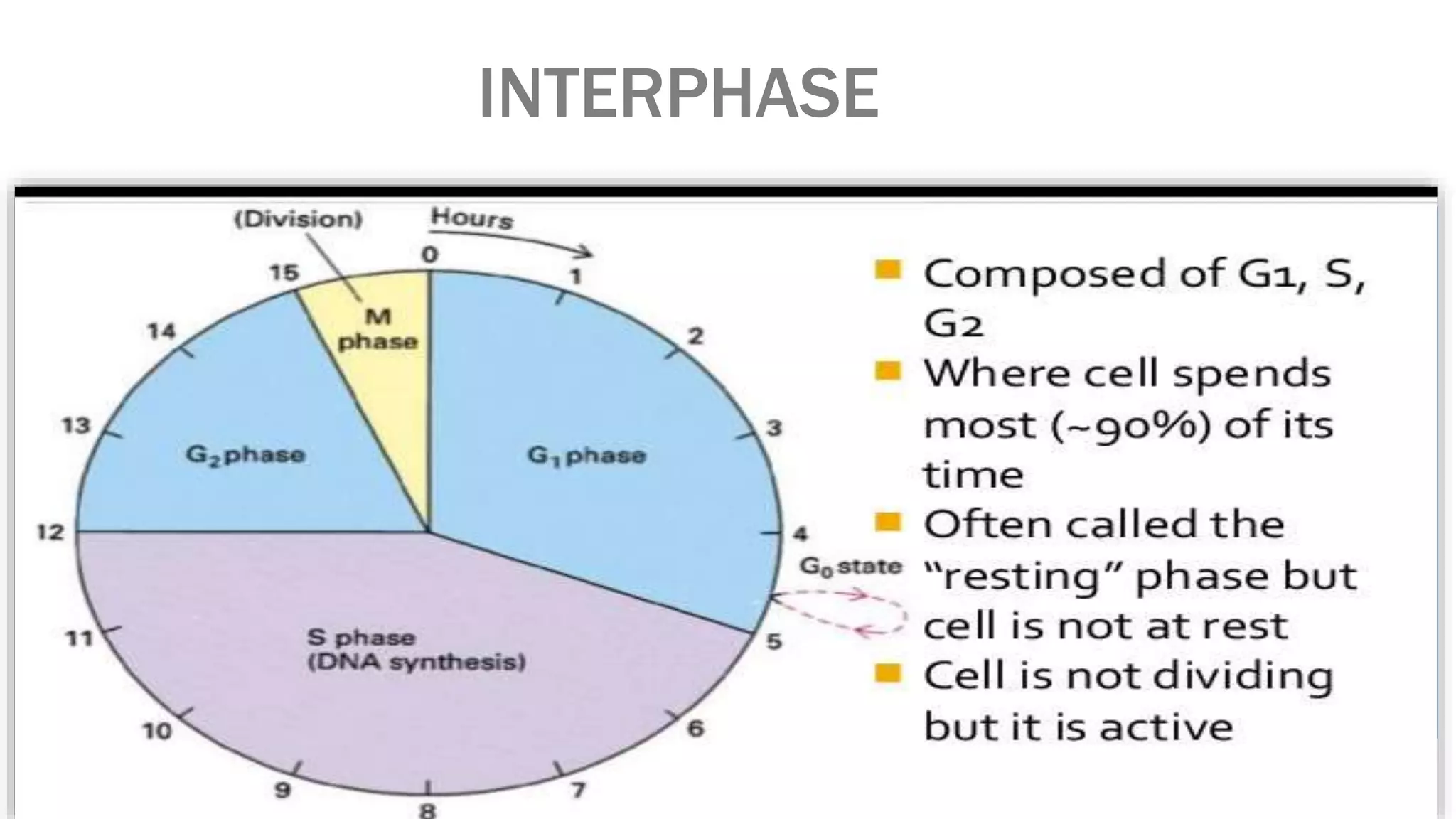
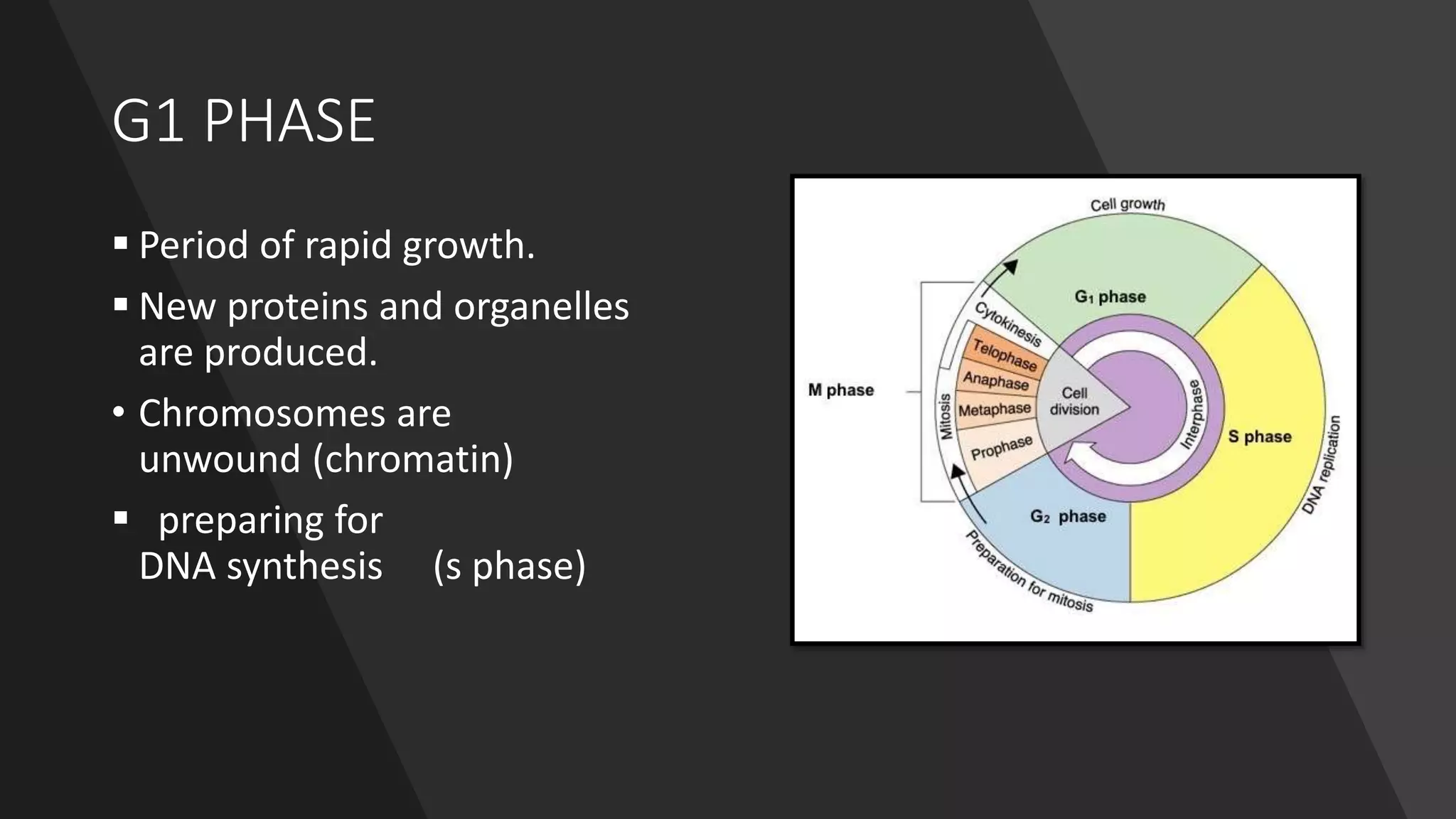
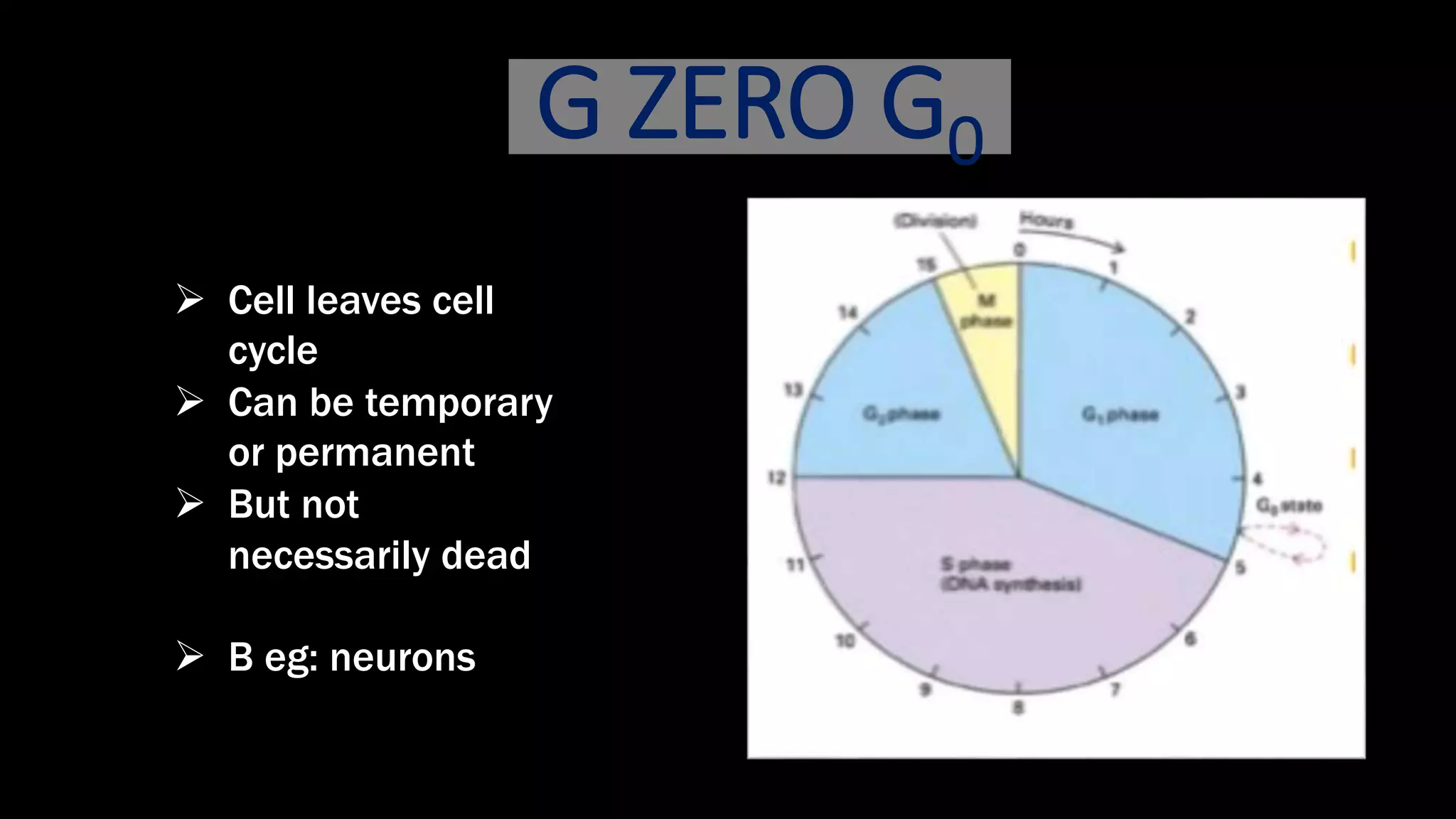
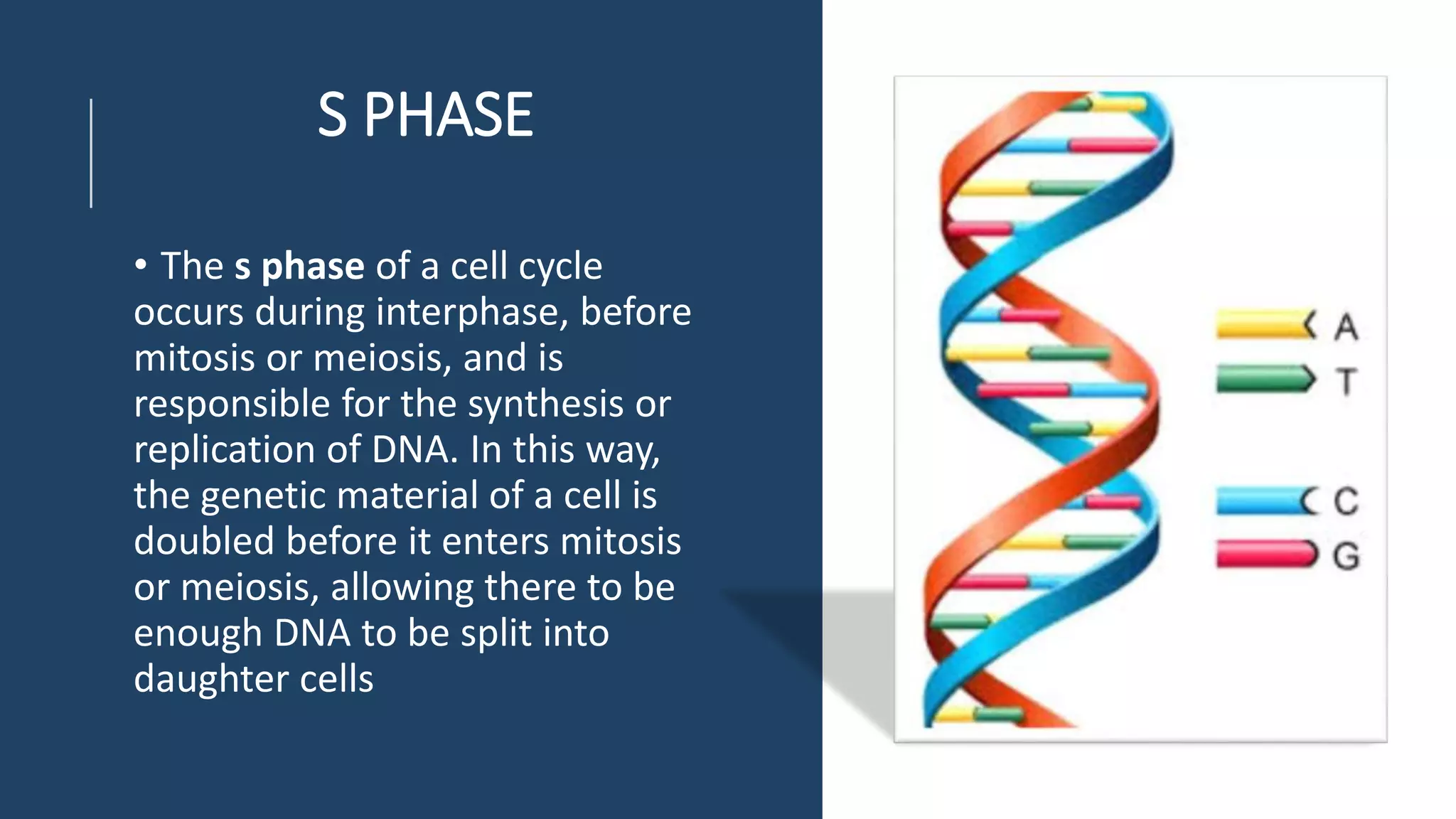
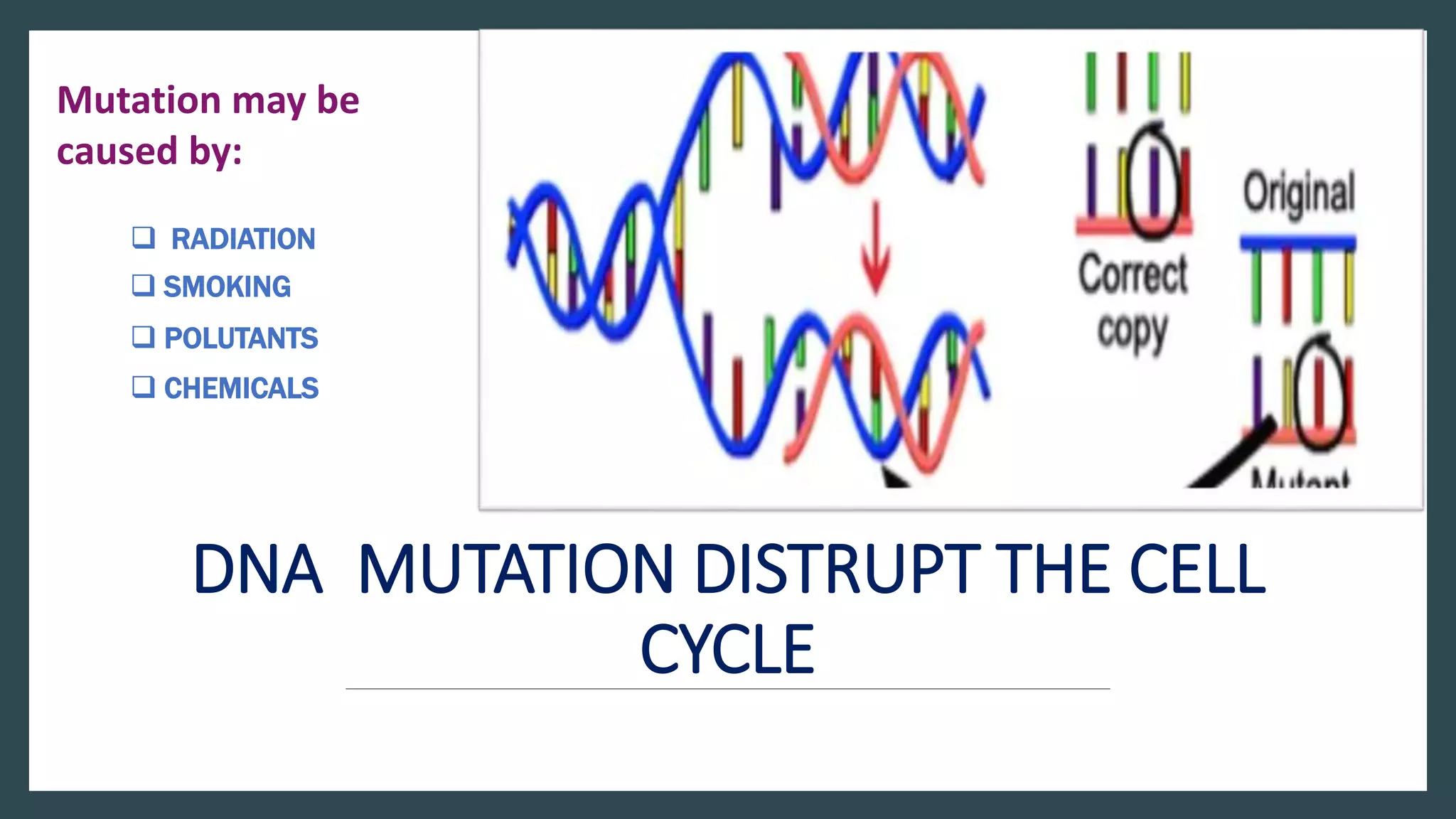
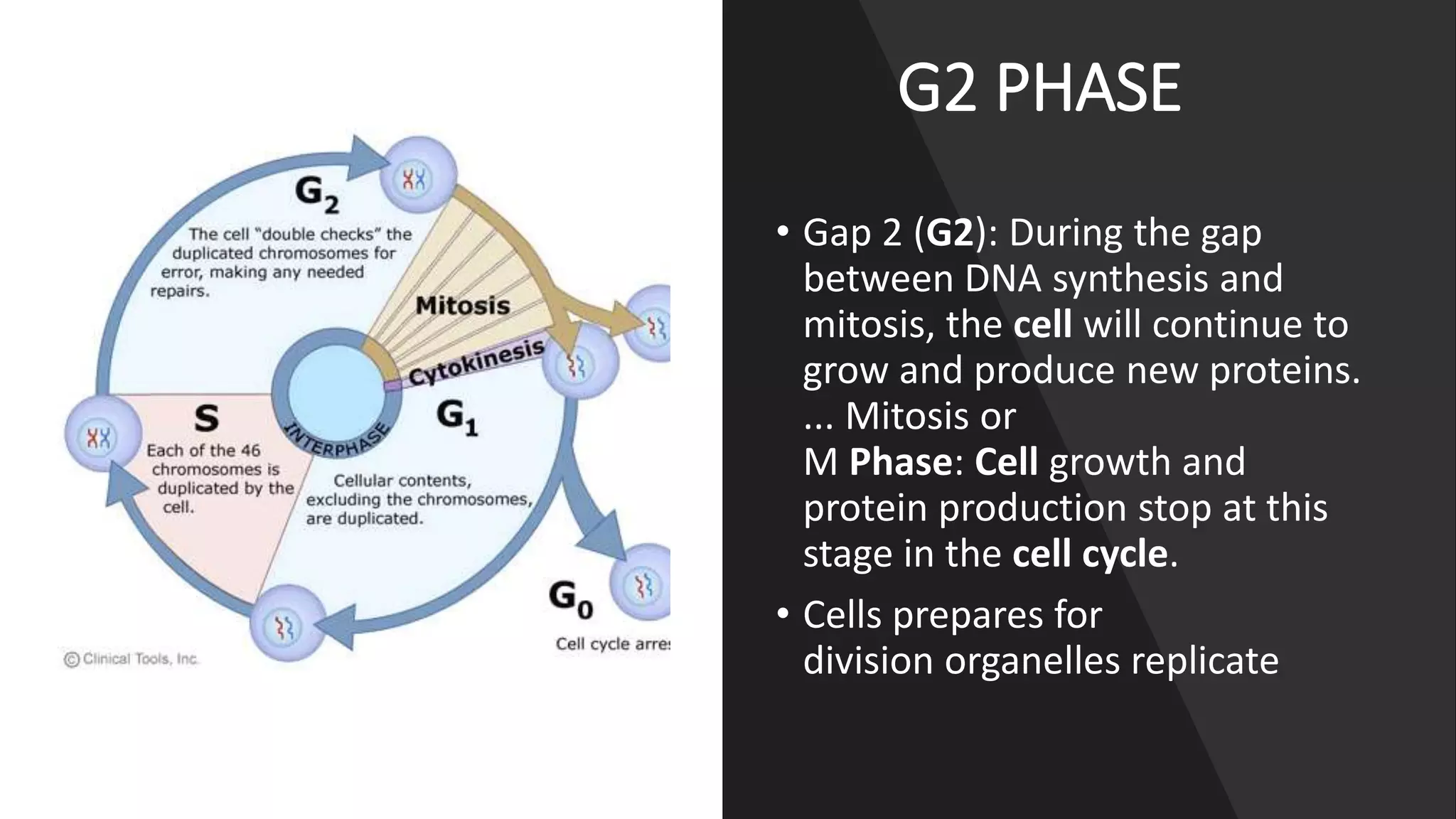
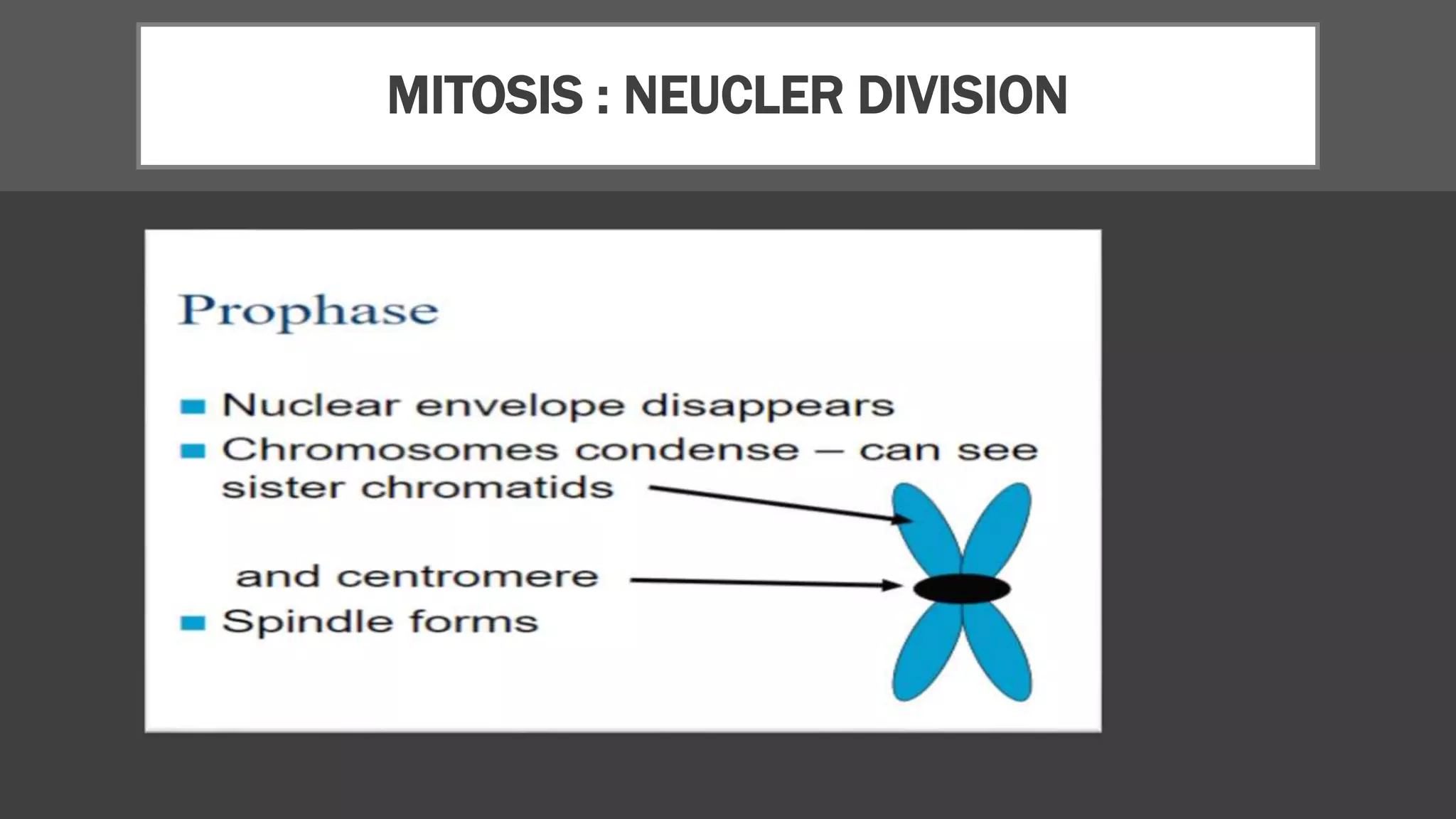
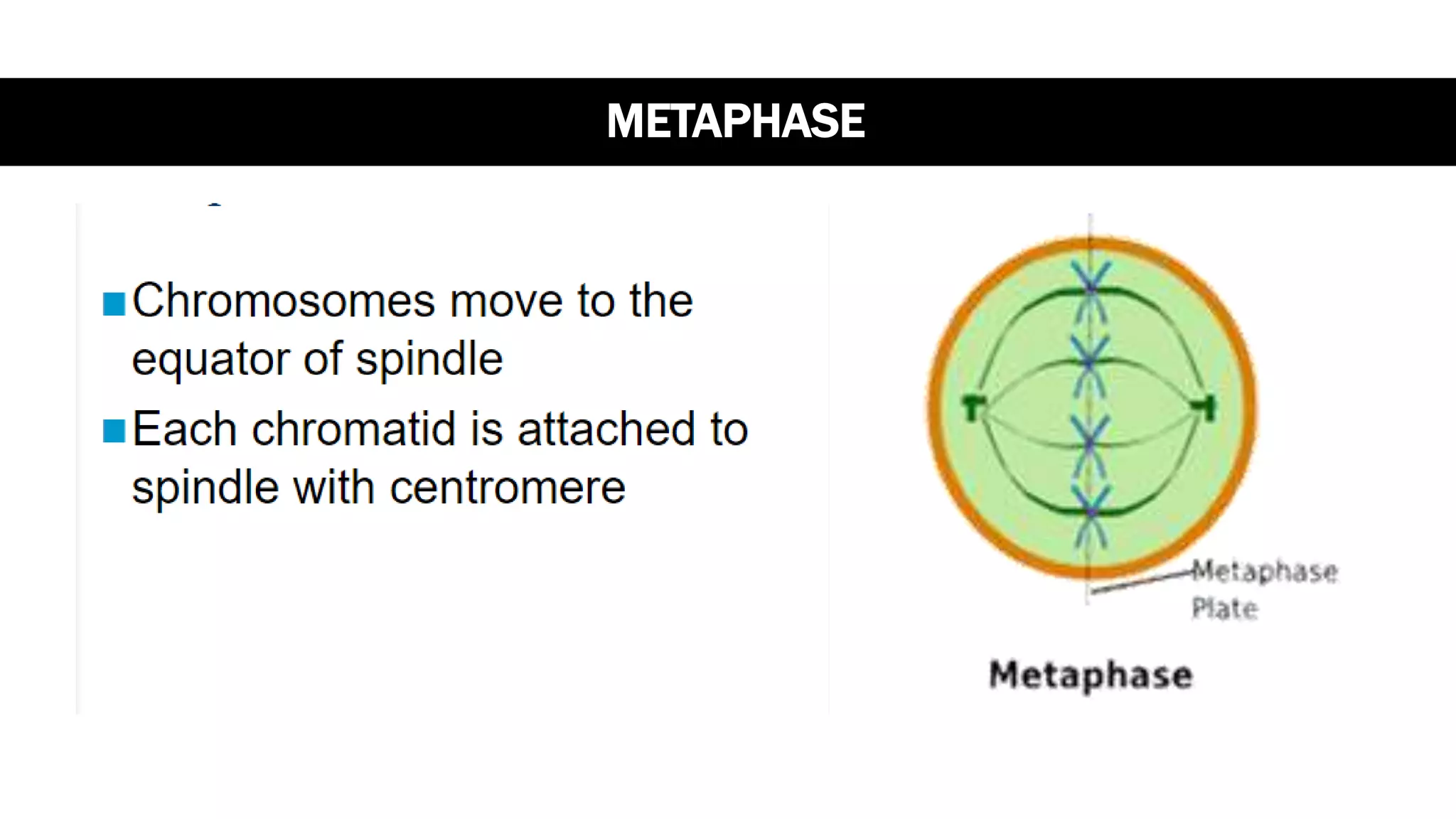
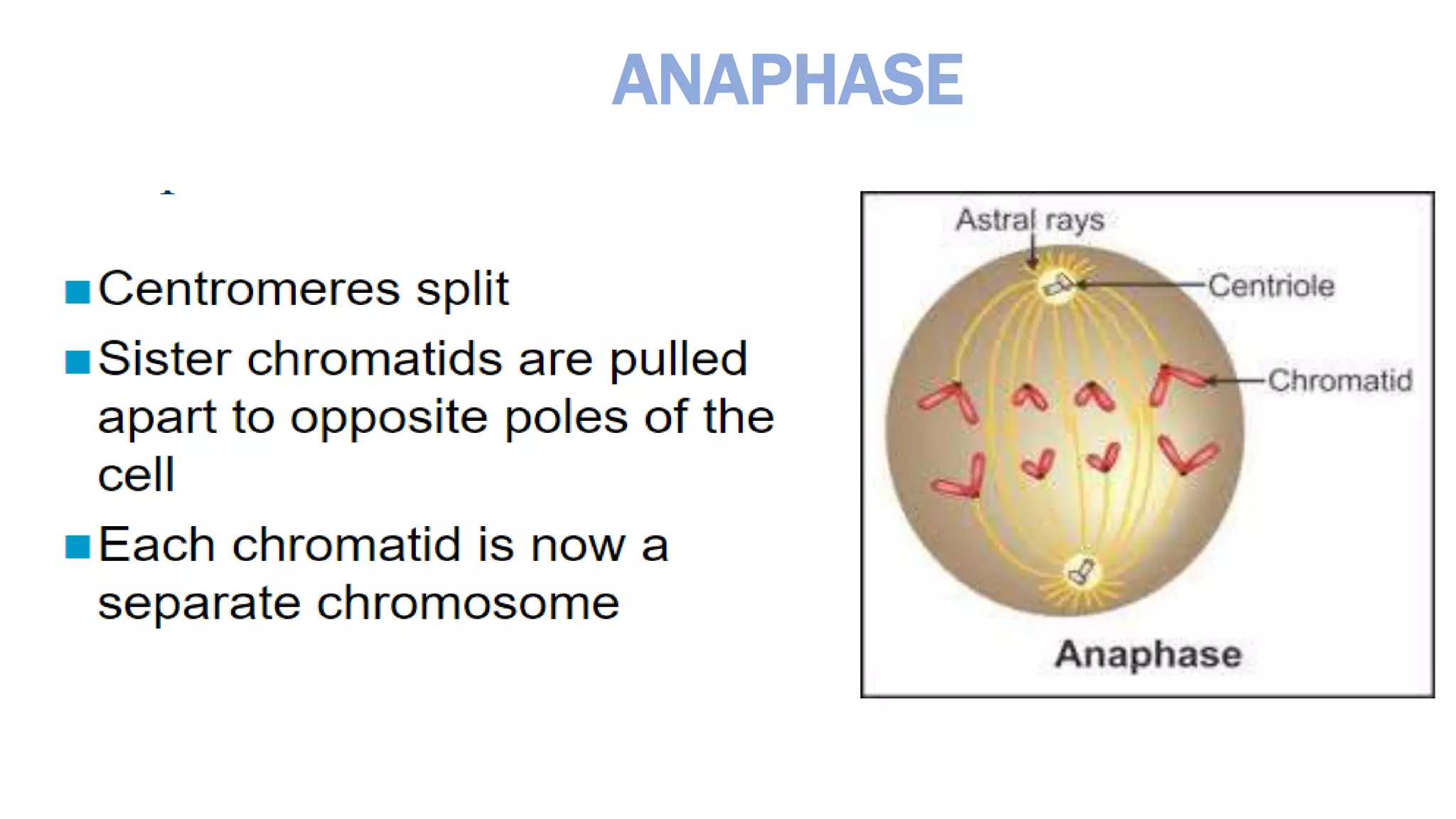
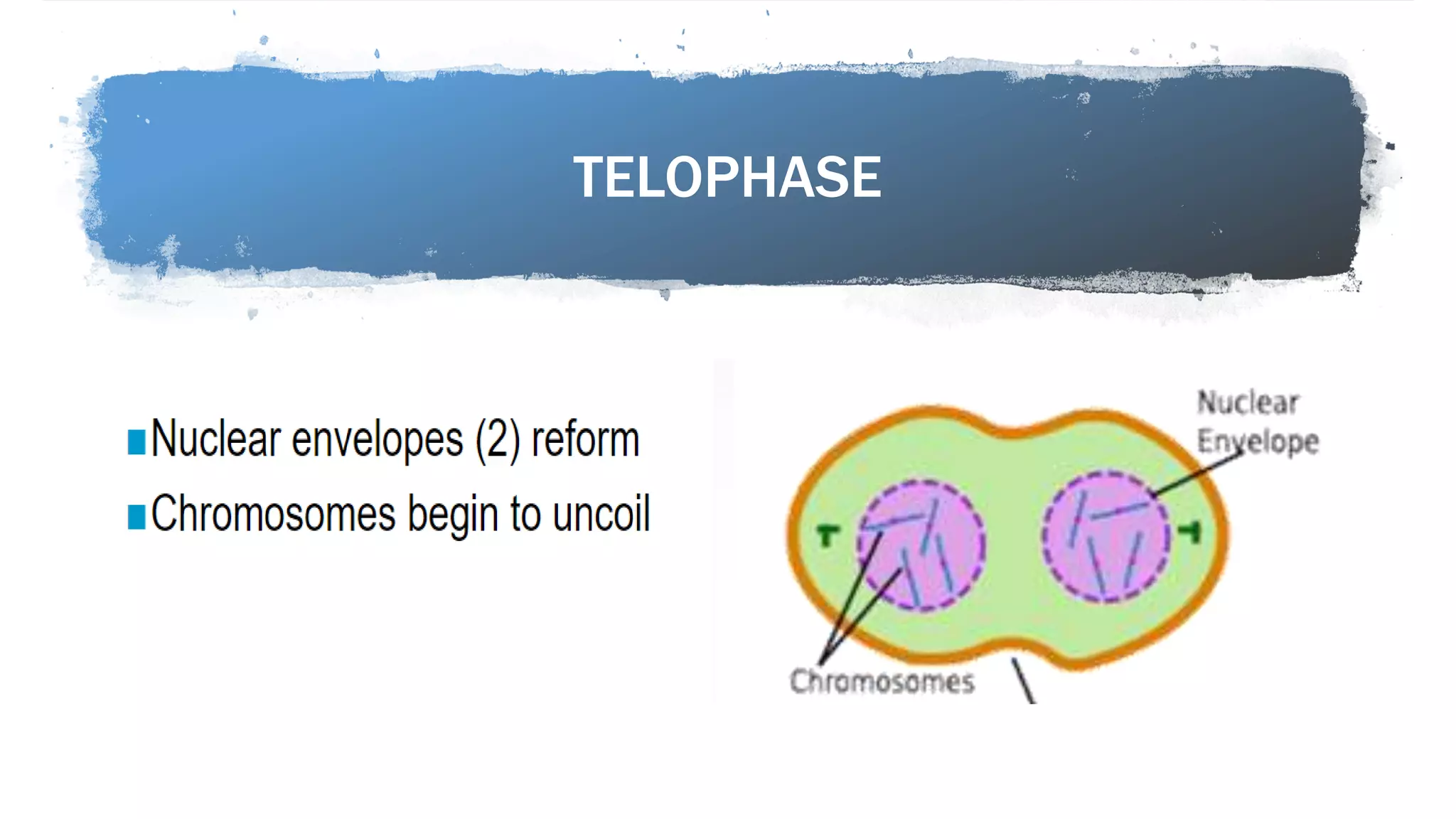
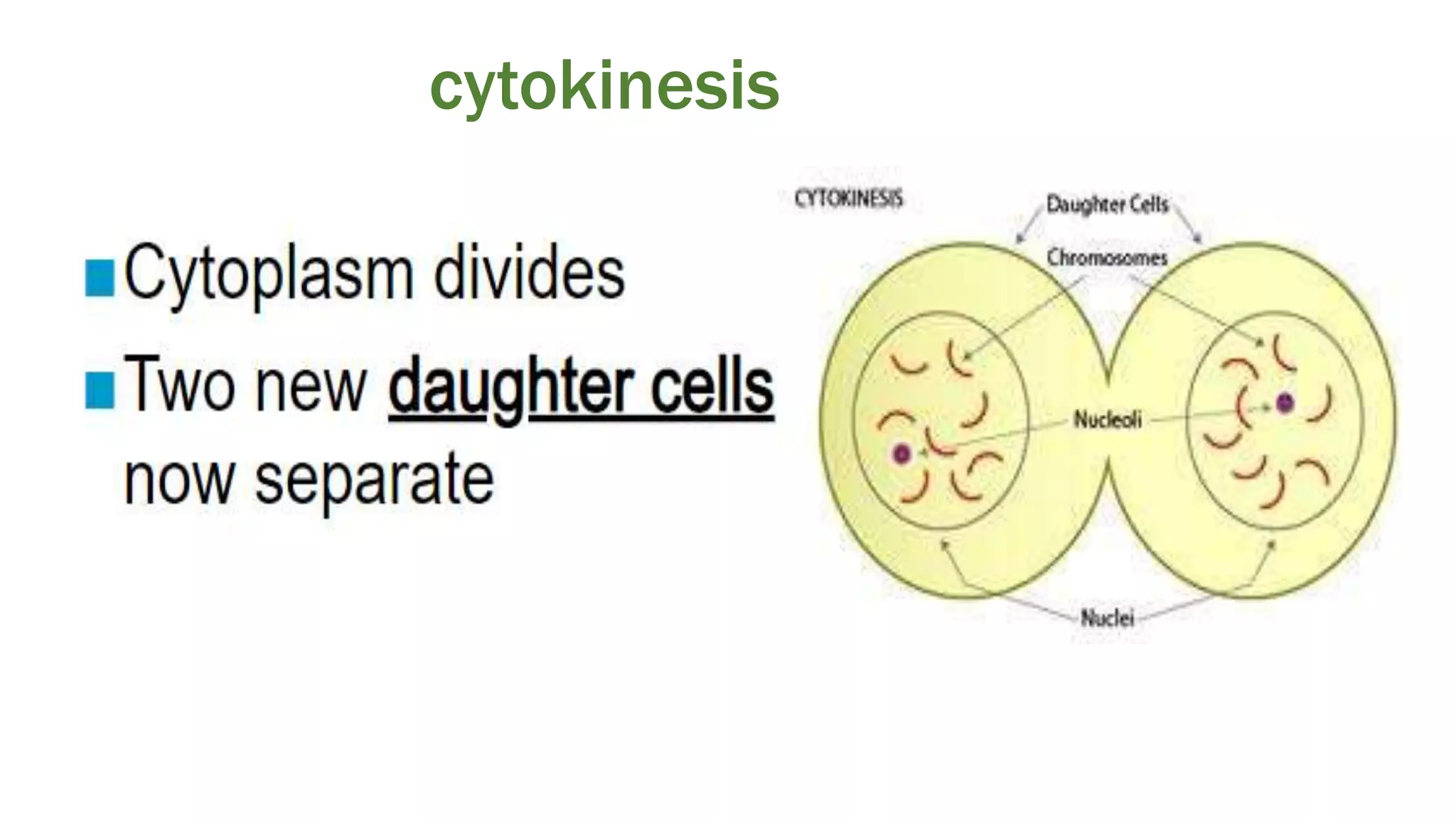
The cell cycle is the series of events that cause a cell to divide into two daughter cells. It includes DNA replication, organelle duplication, and cell division. The cell cycle consists of interphase and the M phase. Interphase includes the G1, S, and G2 phases where the cell grows and duplicates its DNA. The M phase is mitosis where the cell divides into two identical daughter cells followed by cytokinesis where the cell cytoplasm is partitioned. Mitosis consists of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase where the chromosomes align and separate. The document provides details on each phase of the cell cycle.