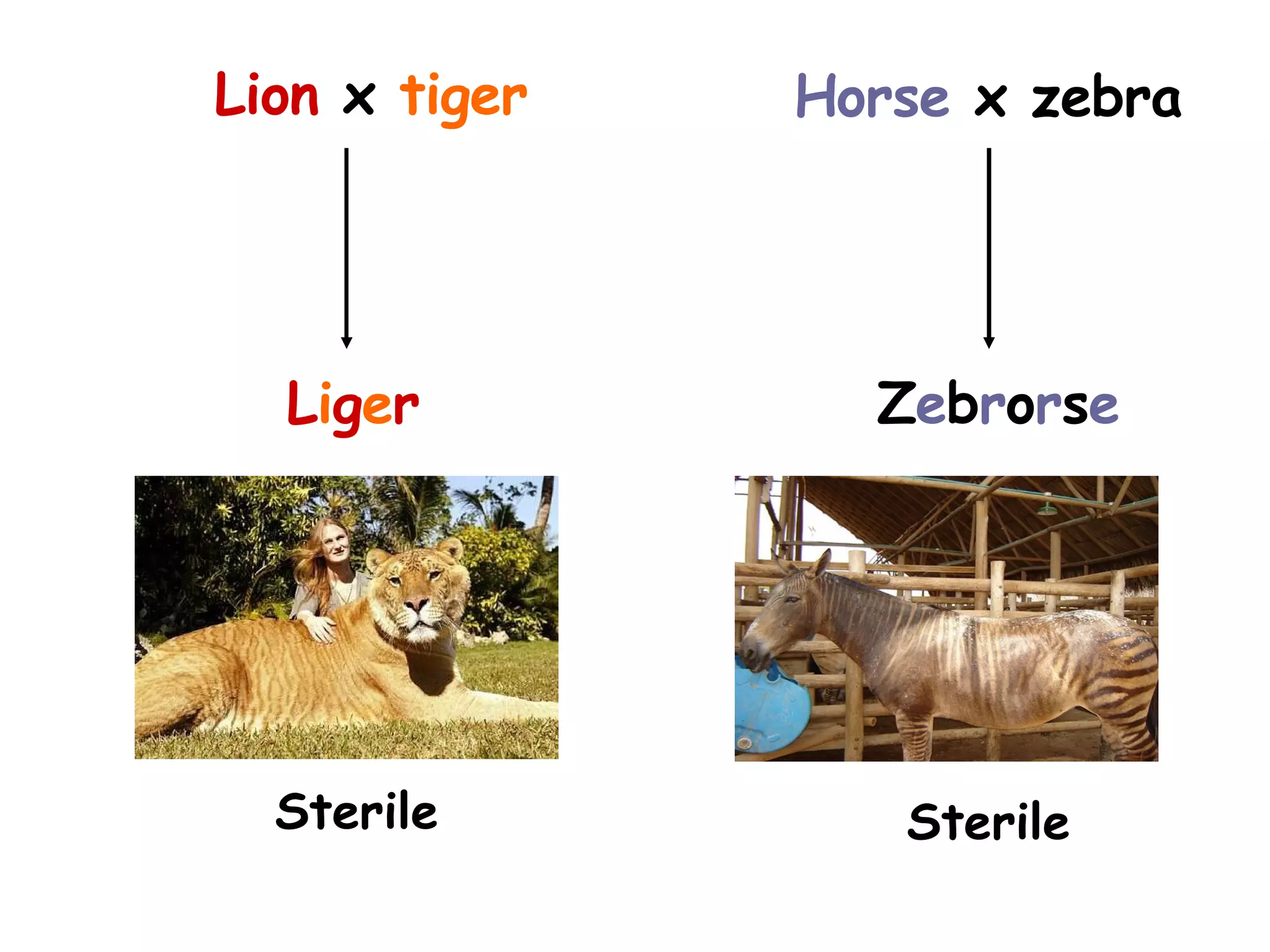
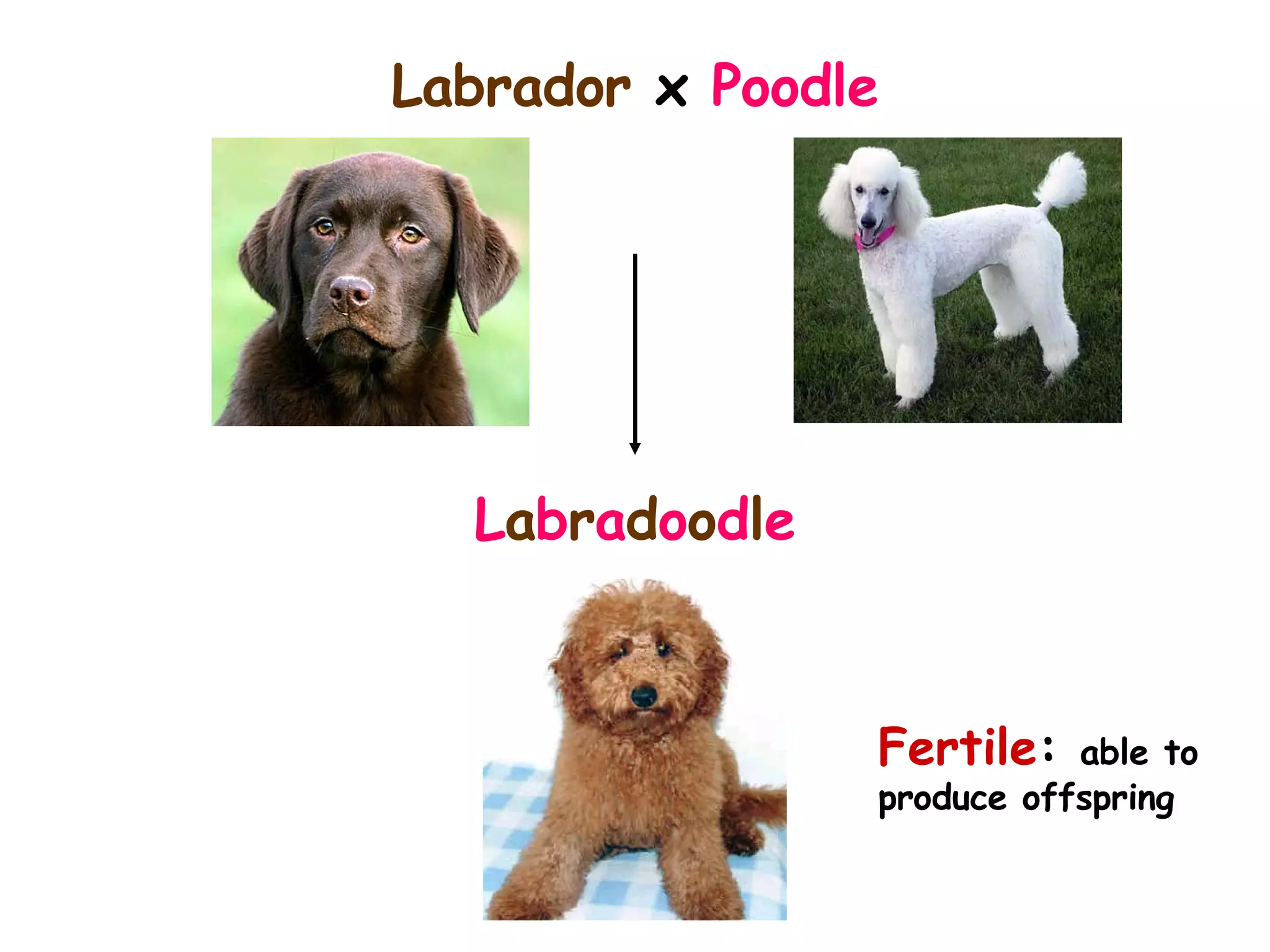
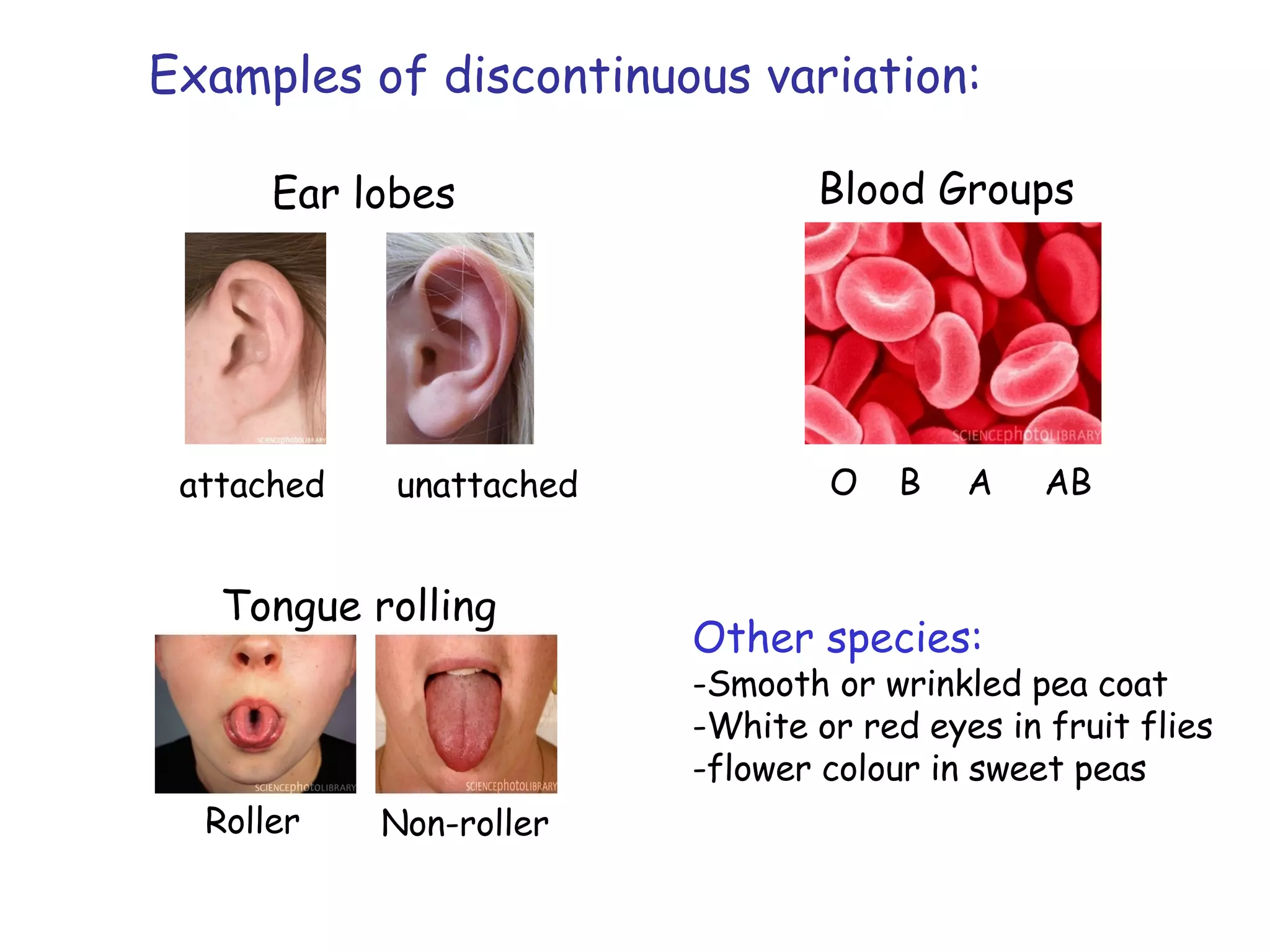
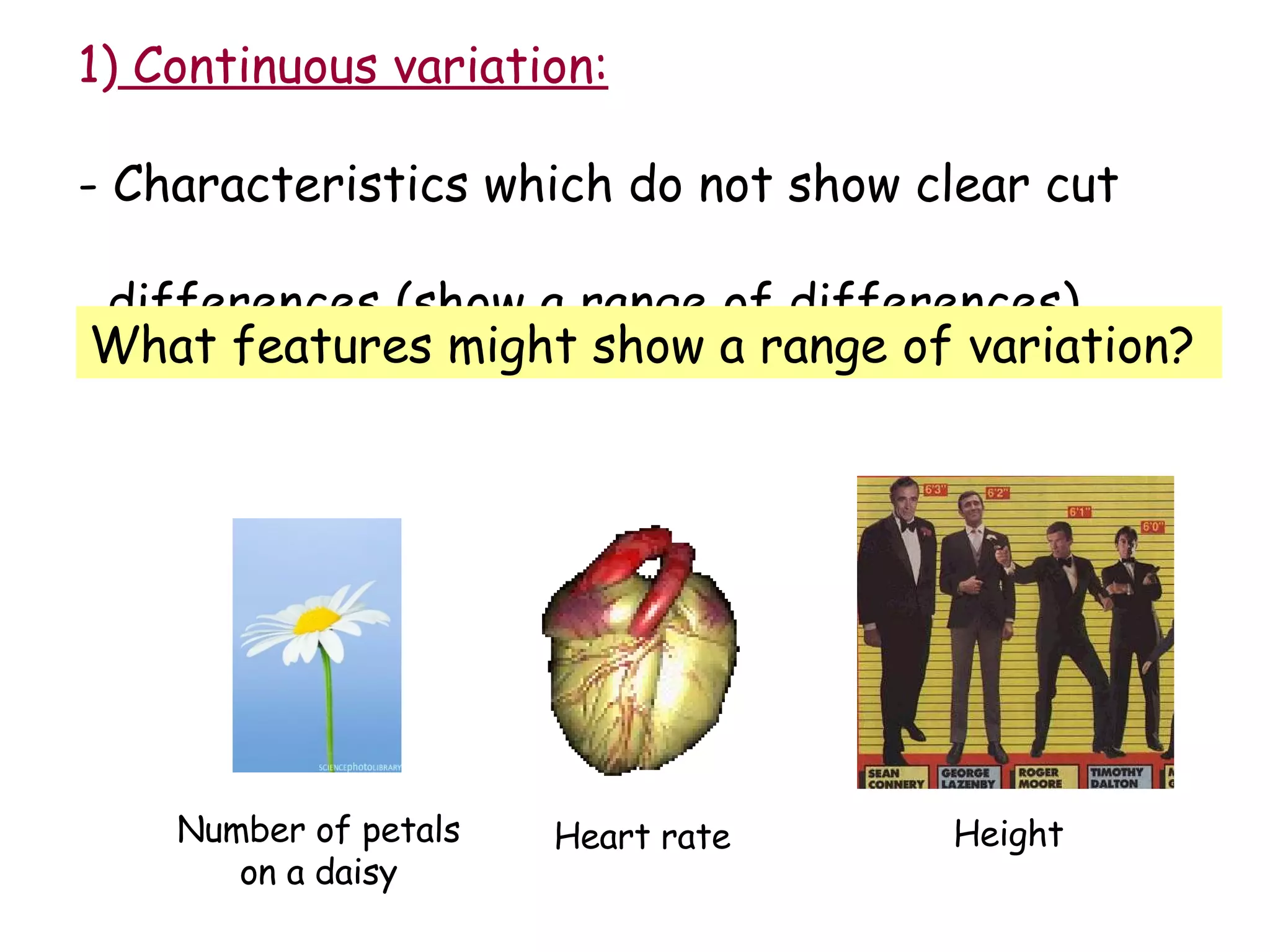
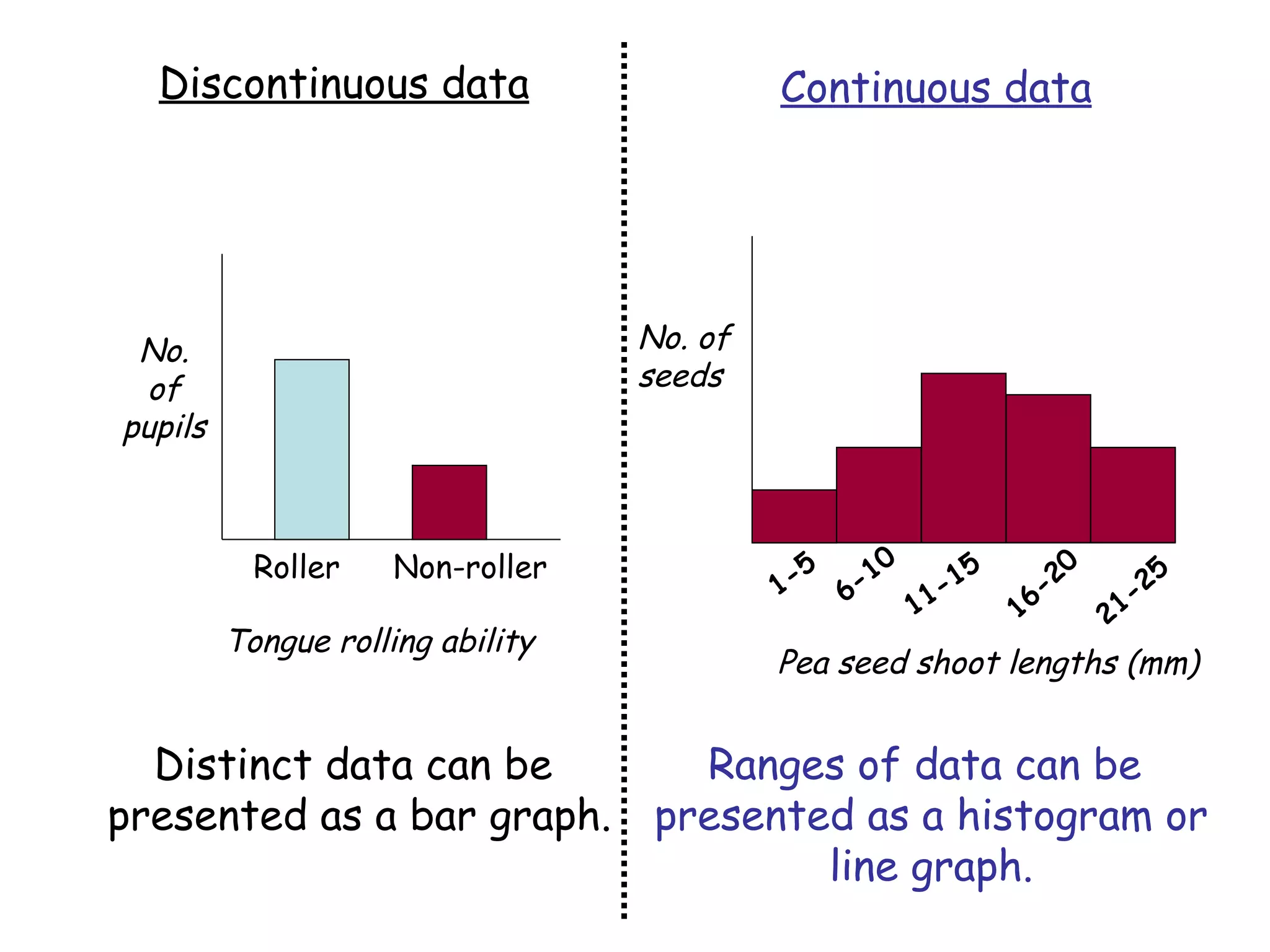
An alien visiting Earth for the first time would see many differences between humans. While all members of a species are similar, there is also variation between individuals in features like height, number of petals on a flower, or heart rate. Variation can be either discontinuous, where traits fall into distinct groups, or continuous, where traits show a range of differences. Examples of discontinuous human variations include blood type and ability to roll one's tongue, while continuous variations include height and heart rate.